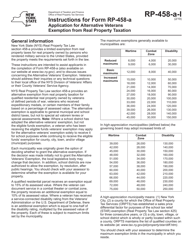
Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism: Comparing Critical Features From an Instructional Design Perspective, Peggy a. Ertmer and Timothy J. Newby - International Society for Performance Improvement
This document compares and discusses the critical features of Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and Constructivism from an instructional design perspective. It is published by the International Society for Performance Improvement (ISPI).
FAQ
Q: What are Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and Constructivism?
A: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and Constructivism are three different theories of learning.
Q: What is Behaviorism?
A: Behaviorism is a theory that focuses on observable behavior and the stimulus-response relationship.
Q: What is Cognitivism?
A: Cognitivism is a theory that emphasizes mental processes, such as thinking, memory, and problem-solving, in learning.
Q: What is Constructivism?
A: Constructivism is a theory that emphasizes the active construction of knowledge by the learner.
Q: How do Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and Constructivism differ?
A: Behaviorism focuses on observable behavior, Cognitivism focuses on mental processes, and Constructivism emphasizes active learning and knowledge construction.
Q: How do these theories relate to instructional design?
A: These theories inform instructional design by guiding the selection of appropriate instructional strategies and methods.
Q: What are some critical features of Behaviorism?
A: Critical features of Behaviorism include the use of reinforcement, conditioning, and external stimuli to shape behavior.
Q: What are some critical features of Cognitivism?
A: Critical features of Cognitivism include attention, memory, and problem-solving strategies.
Q: What are some critical features of Constructivism?
A: Critical features of Constructivism include active learning, collaboration, and the construction of meaning by the learner.