Universal Design for Learning Guidelines
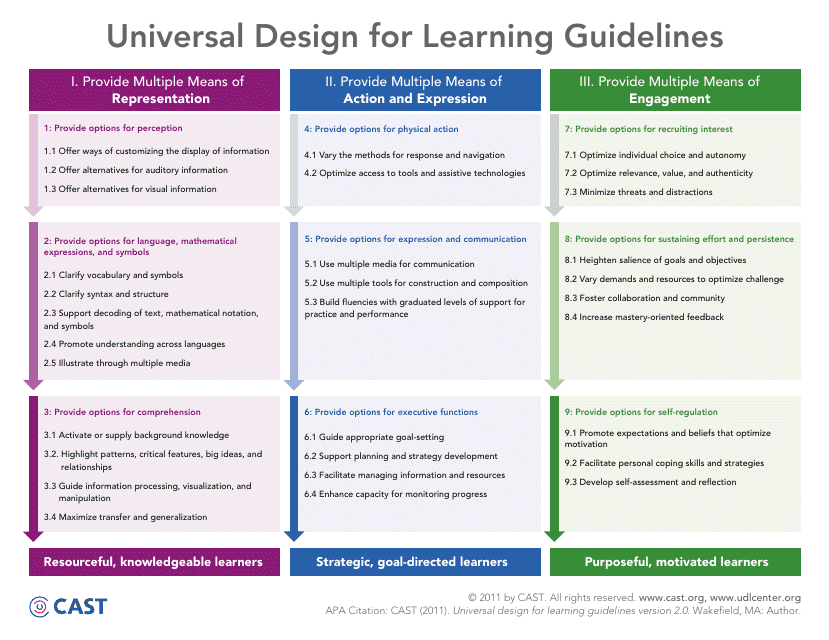
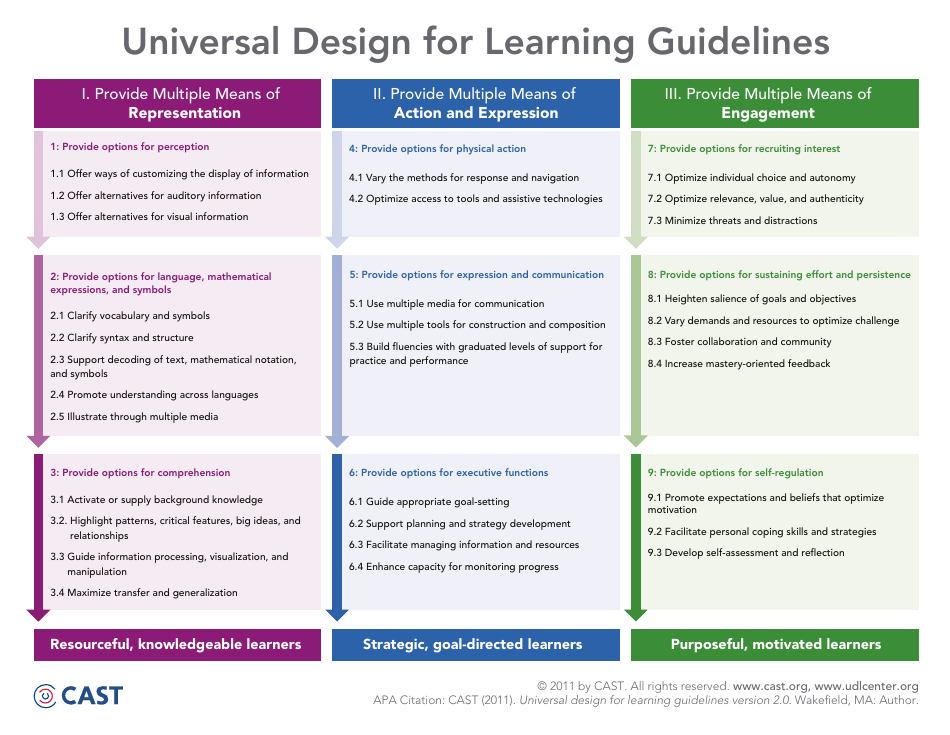
The Universal Design for Learning (UDL) Guidelines are for designing inclusive and accessible educational materials and methods that can be used by all students, including those with different learning styles, abilities, and disabilities.
The Universal Design for Learning Guidelines are not filed by any specific entity. They were developed and published by the Center for Applied Special Technology (CAST), an organization that promotes inclusive education practices.
FAQ
Q: What are the Universal Design for Learning (UDL) Guidelines?
A: The Universal Design for Learning (UDL) Guidelines are a set of principles that provide educators with strategies and techniques to design accessible and inclusive learning experiences for all students, including those with diverse learning needs.
Q: What is the purpose of the UDL Guidelines?
A: The purpose of the UDL Guidelines is to help educators create flexible learning environments that can be customized to meet the needs of individual learners.
Q: How many UDL Guidelines are there?
A: There are three UDL Guidelines: Engagement, Representation, and Action and Expression.
Q: What does the Engagement guideline focus on?
A: The Engagement guideline focuses on providing multiple ways for students to become engaged and motivated in their learning.
Q: What does the Representation guideline focus on?
A: The Representation guideline focuses on providing multiple ways for students to access and understand information.
Q: What does the Action and Expression guideline focus on?
A: The Action and Expression guideline focuses on providing multiple ways for students to demonstrate their knowledge and skills.
Q: Who can benefit from using the UDL Guidelines?
A: All students can benefit from the use of the UDL Guidelines, including students with disabilities and English language learners.
Q: Are the UDL Guidelines legally required?
A: The UDL Guidelines are not legally required, but they provide a framework for creating inclusive educational environments that align with legal requirements, such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act.