This version of the form is not currently in use and is provided for reference only. Download this version of
IRS Form 8889
for the current year.
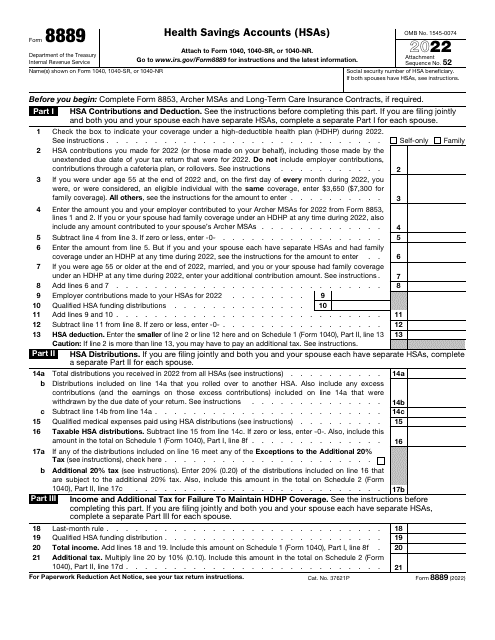
IRS Form 8889 Health Savings Accounts (Hsas)
What Is IRS Form 8889?
This is a tax form that was released by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) - a subdivision of the U.S. Department of the Treasury. Check the official IRS-issued instructions before completing and submitting the form.
FAQ
Q: What is IRS Form 8889?
A: IRS Form 8889 is a tax form used to report contributions, distributions, and other activity related to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs).
Q: What is a Health Savings Account (HSA)?
A: A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged savings account that is used in conjunction with a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) to pay for qualified medical expenses.
Q: Who can contribute to an HSA?
A: Individuals who are covered by a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) and are not covered by any other non-HDHP health plan can contribute to an HSA.
Q: How much can I contribute to an HSA?
A: For 2021, the maximum contribution limit for an individual with self-only HDHP coverage is $3,600, and for an individual with family HDHP coverage, it is $7,200. These limits are subject to annual adjustment by the IRS.
Q: What are the tax benefits of an HSA?
A: Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and any interest or investment earnings grow tax-free. Withdrawals used for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free.
Q: What are qualified medical expenses?
A: Qualified medical expenses include most medical, dental, and vision expenses, as well as prescription medications and certain other healthcare expenses.
Q: Do I need to file IRS Form 8889 even if I did not contribute to my HSA?
A: Yes, you still need to file IRS Form 8889 to report any distributions or other activity related to your HSA, even if you did not make any contributions.
Form Details:
- A 1-page form available for download in PDF;
- Actual and valid for filing 2023 taxes;
- Editable, printable, and free;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a fillable version of IRS Form 8889 through the link below or browse more documents in our library of IRS Forms.