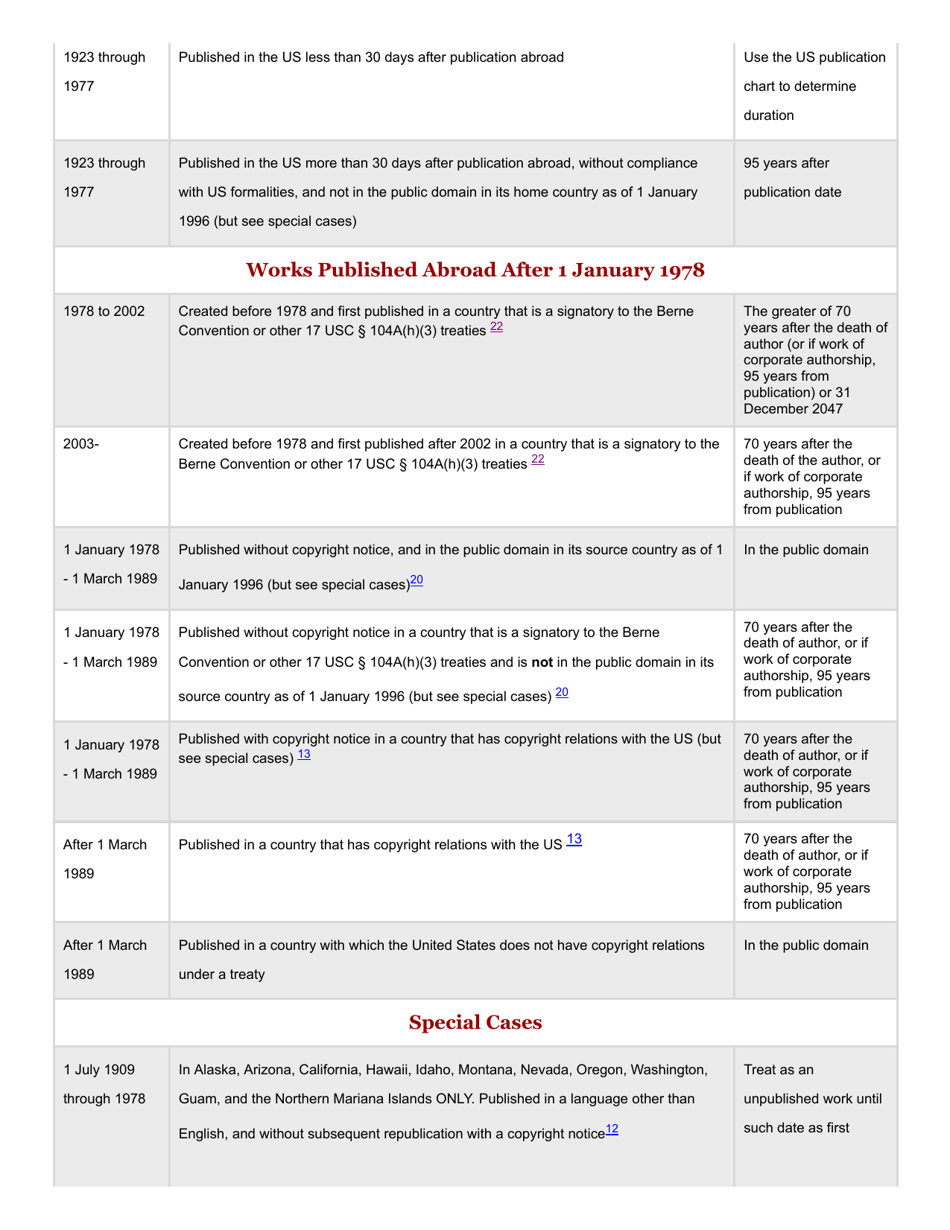
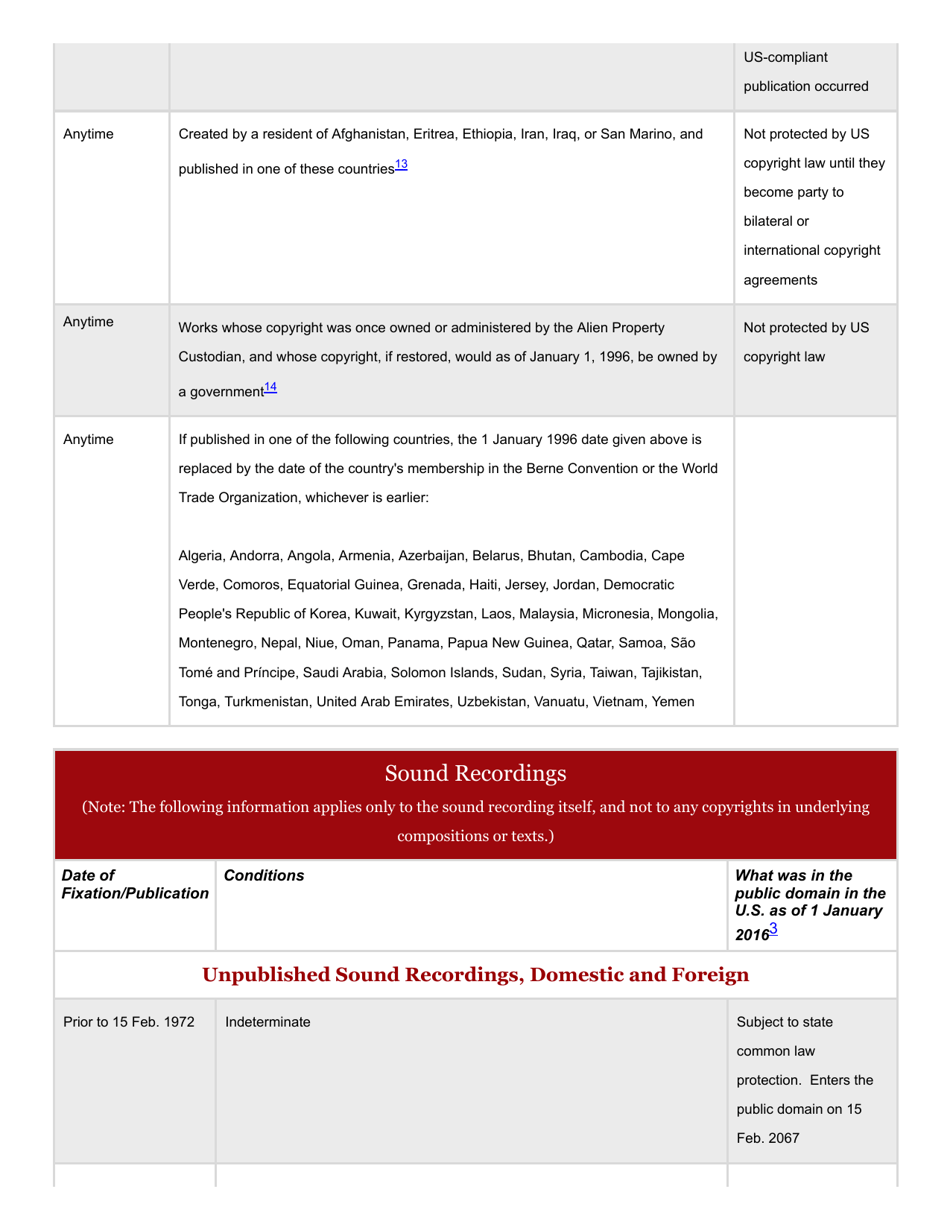
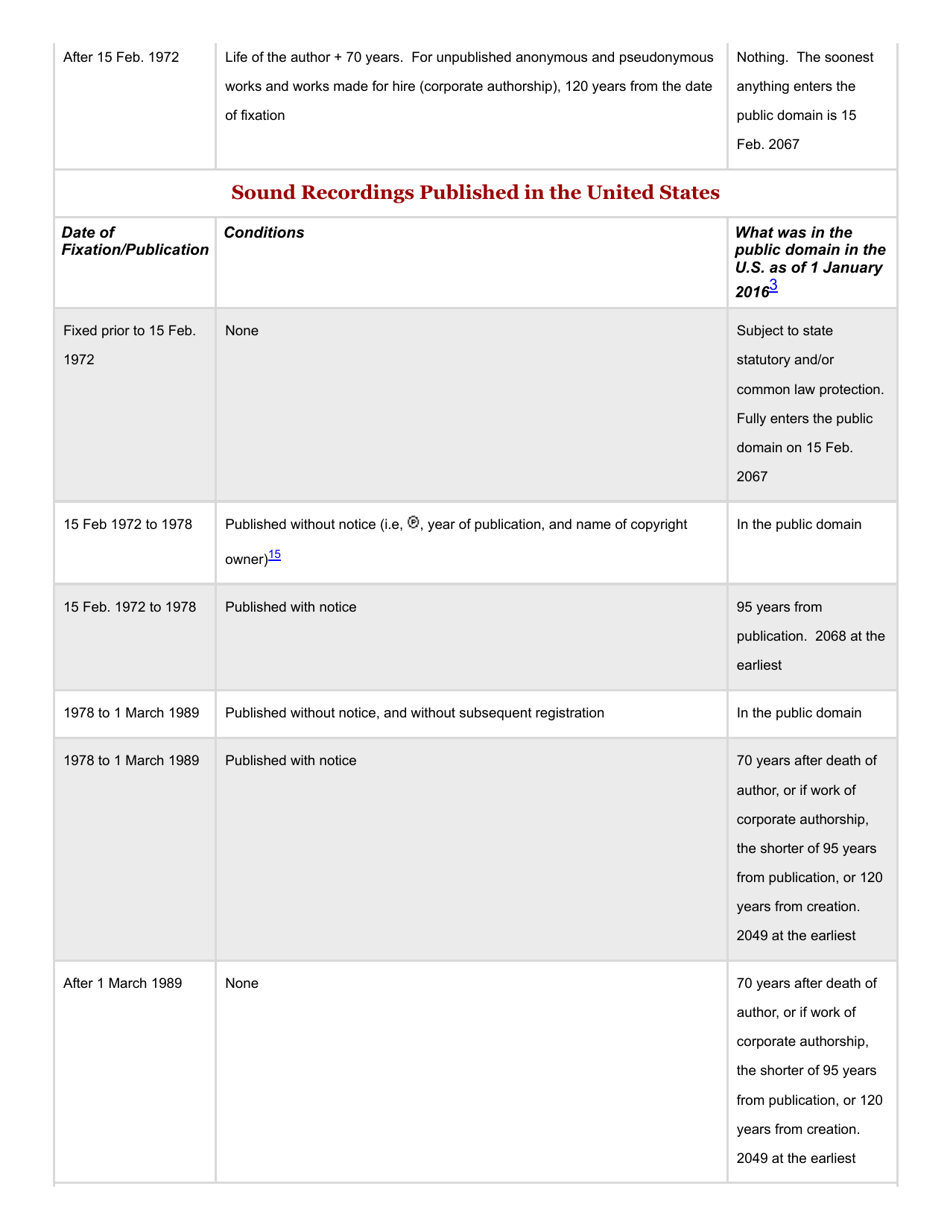
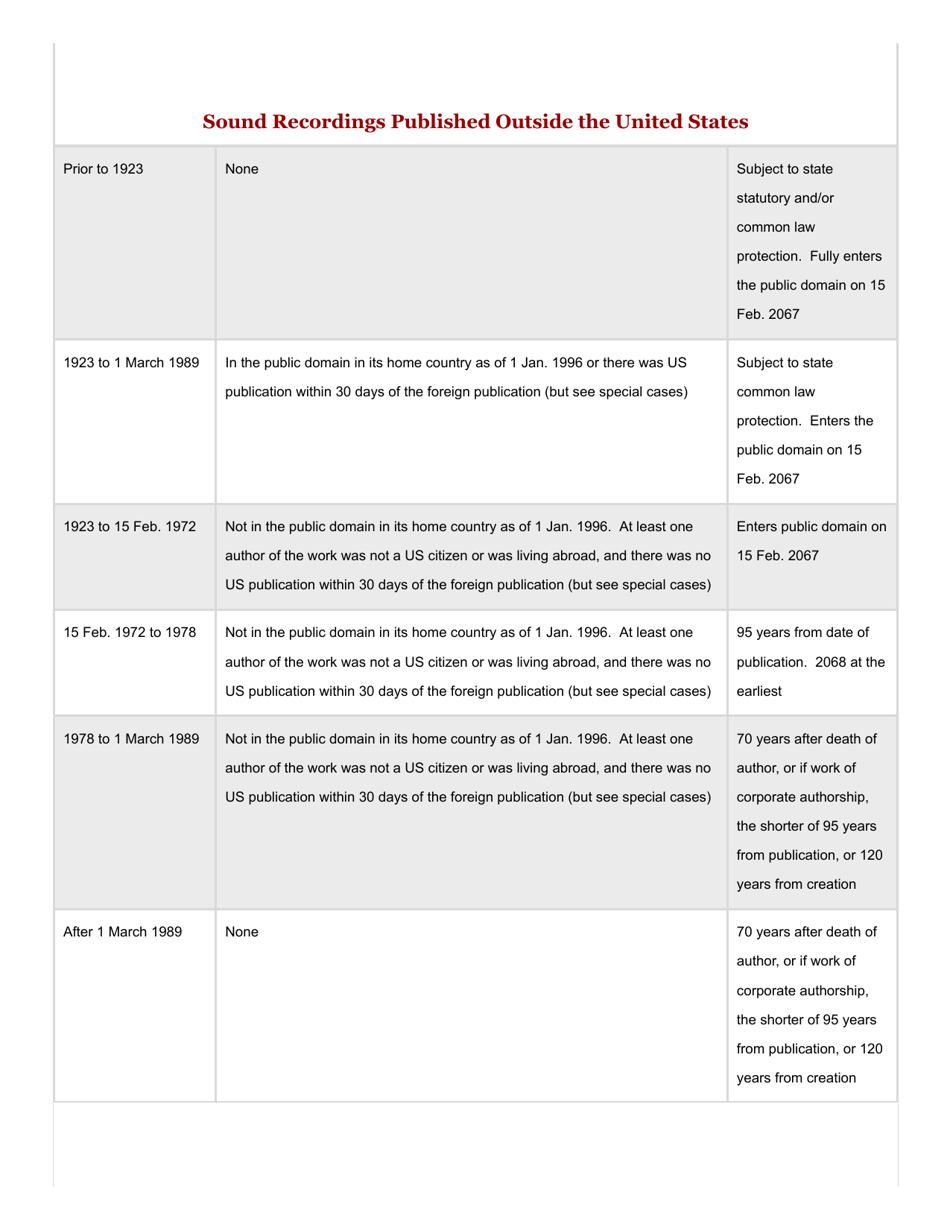
This version of the form is not currently in use and is provided for reference only. Download this version of
the document
for the current year.
Copyright Term and the Public Domain in the United States - Cornell Copyright Information Center
The Cornell Copyright Information Center provides information on copyright terms and the public domain in the United States. It helps people understand how long copyright protection lasts for different types of works and when works enter the public domain, where they can be freely accessed and used by the public.
The Cornell Copyright Information Center does not file the copyright term or determine the public domain status in the United States. They provide information and resources related to copyright law, but the regulation of copyright term and public domain is administered by the United States Copyright Office.
FAQ
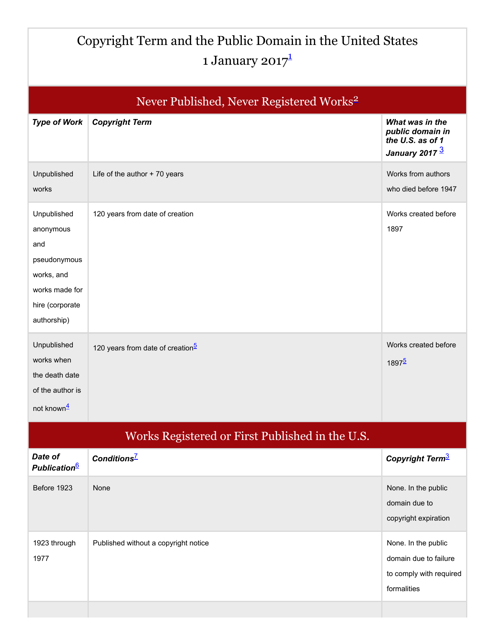
Q: What is the Copyright Term in the United States?
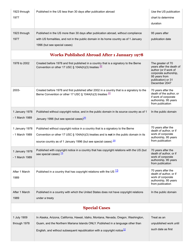
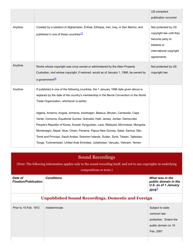
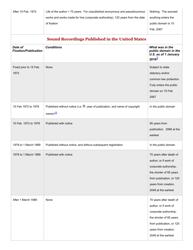
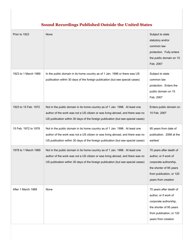
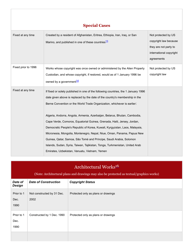
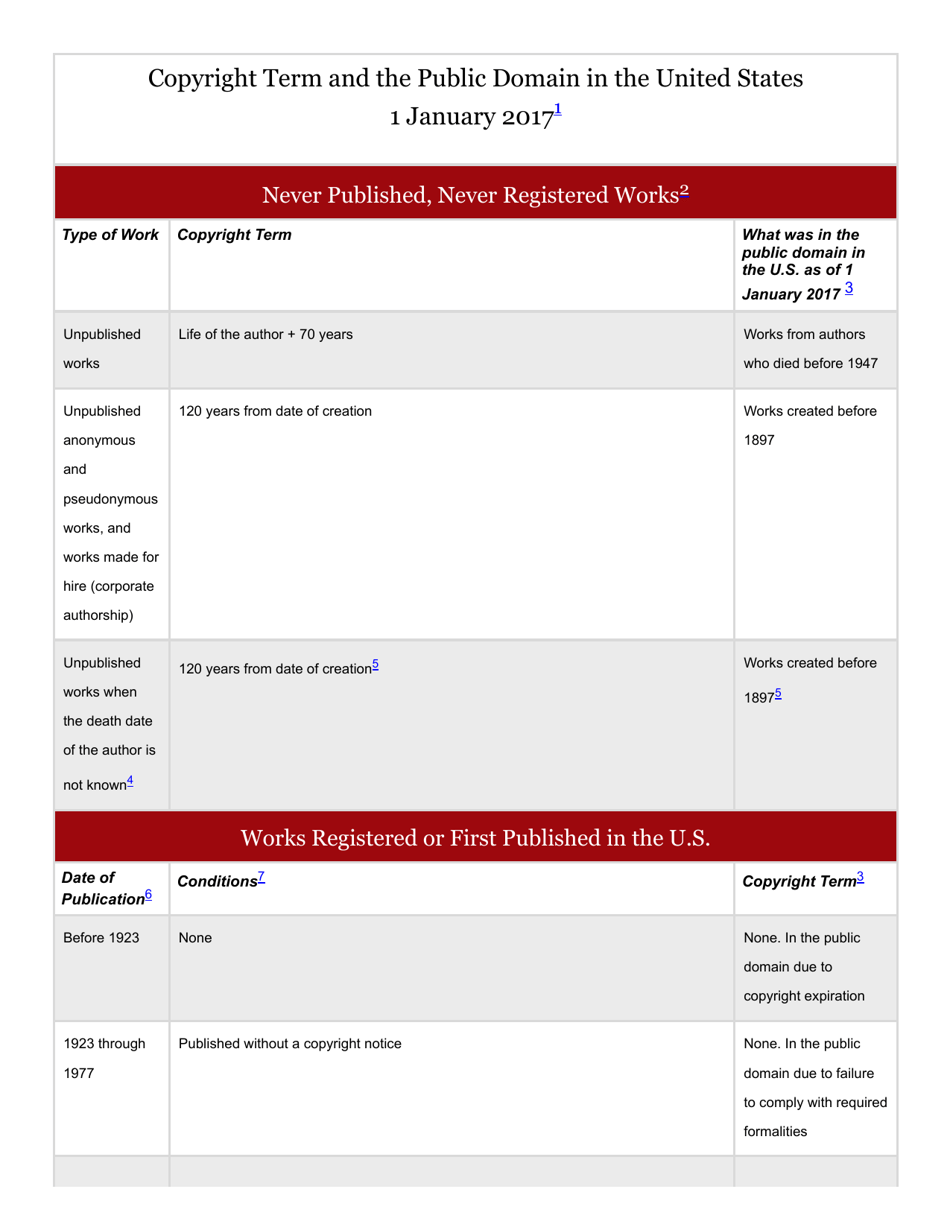
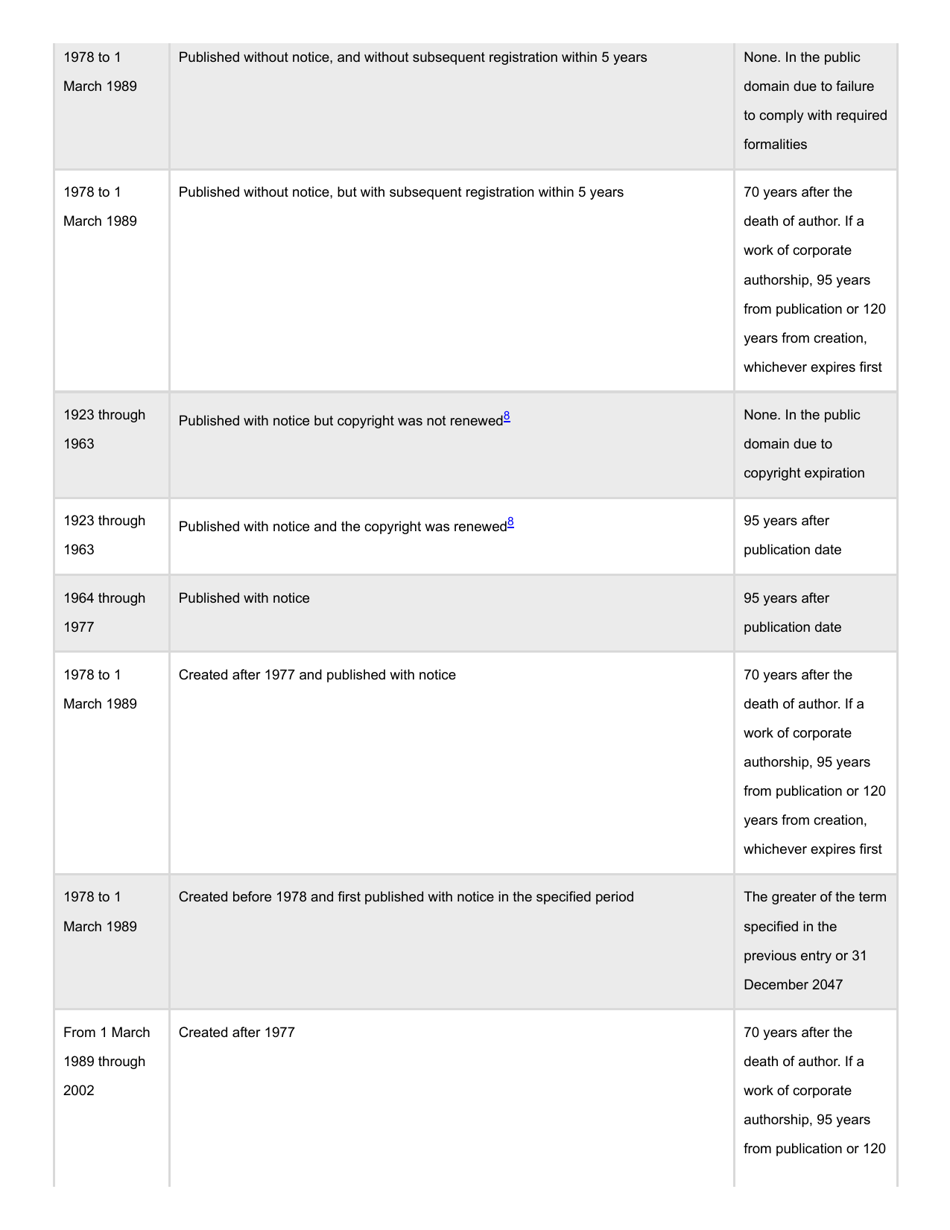
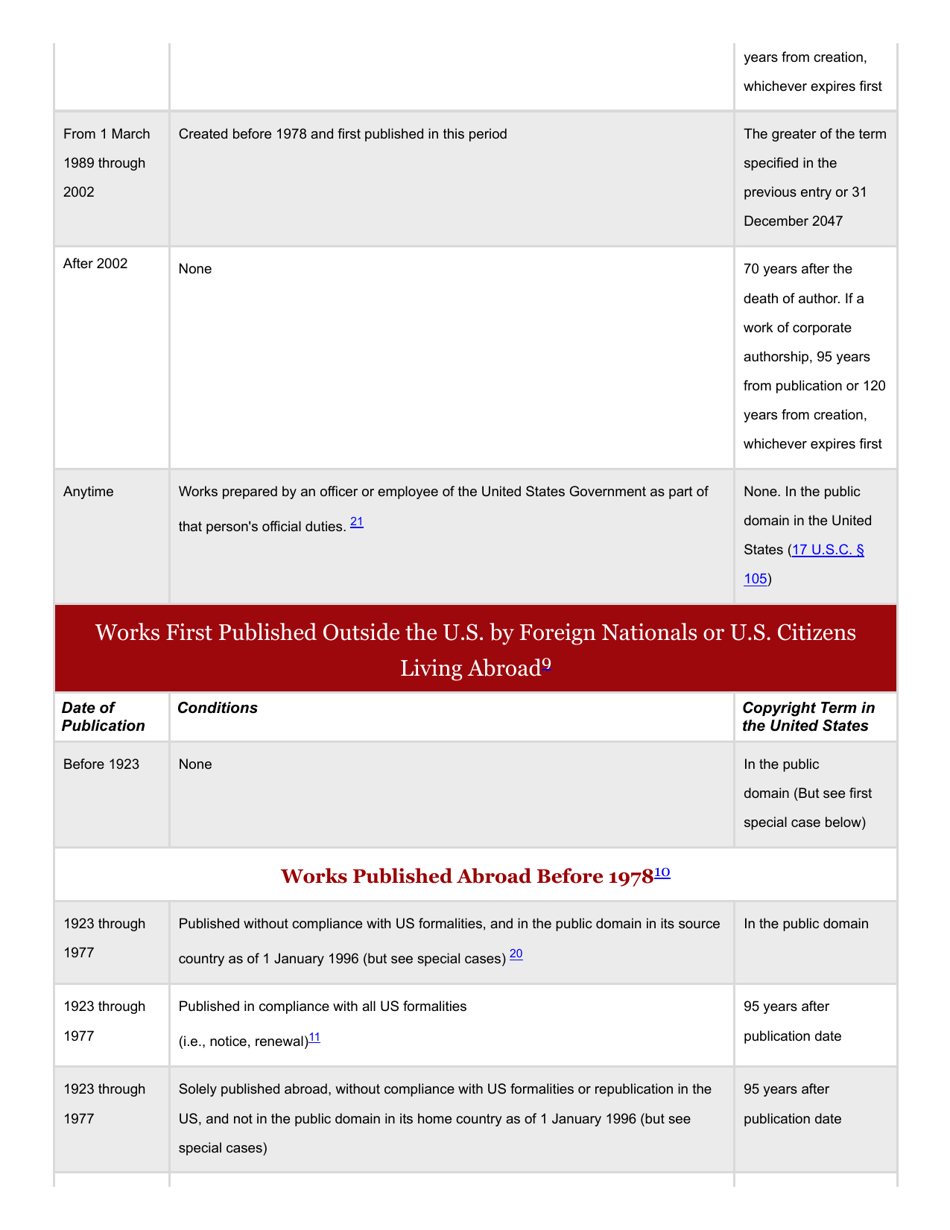
A: Copyright generally lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years.
Q: What is the Public Domain?
A: The Public Domain refers to works that are no longer protected by copyright and are freely available for use by the public.
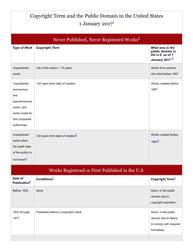
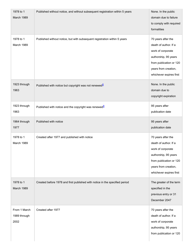
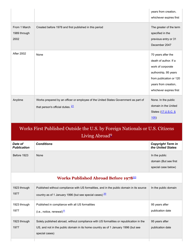
Q: When does a work enter the Public Domain?
A: Works published before 1926 are generally in the Public Domain, and works published between 1926 and 1977 may also be in the Public Domain depending on certain criteria.
Q: Can I use a work in the Public Domain without permission?
A: Yes, you can use a work in the Public Domain without seeking permission from the copyright holder.
Q: What is fair use?
A: Fair use is a legal doctrine that allows limited use of copyrighted materials without permission, for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, or research.
Q: How can I determine if a work is protected by copyright?
A: You can check the Copyright Office database or contact the copyright holder to find out if a work is protected by copyright.
Q: Can I use a copyrighted work without permission if I provide attribution?
A: Providing attribution alone does not necessarily allow you to use a copyrighted work without permission. You may still need to obtain permission from the copyright holder.
Q: What are some common exceptions to copyright protection?
A: Some common exceptions to copyright protection include works created by the U.S. government, facts and information, and works that are no longer protected by copyright.
Q: Can I use copyrighted music in my YouTube videos?
A: Using copyrighted music in YouTube videos may infringe upon the exclusive rights of the copyright holder unless you have obtained permission or the use falls under fair use.
Q: Can I use images from the Internet in my presentations?
A: Using images from the Internet in presentations may infringe upon the exclusive rights of the copyright holder unless you have obtained permission or the use falls under fair use.