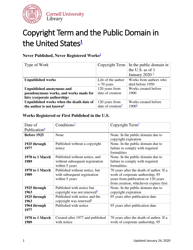
Copyright Term and the Public Domain in the United States - Cornell Copyright Information Center
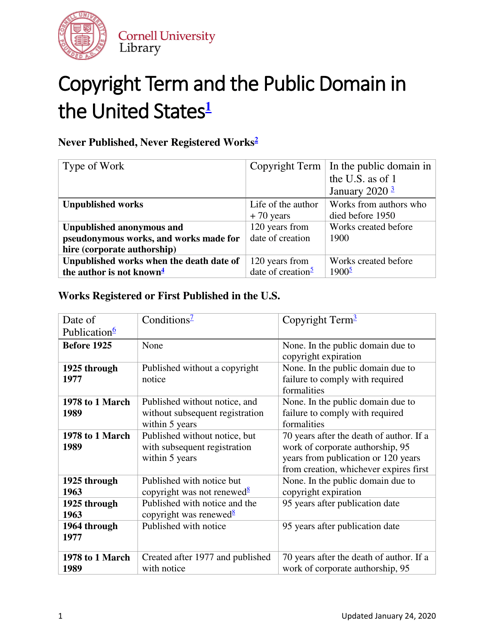
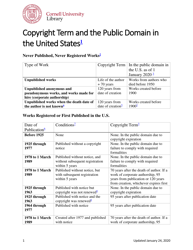
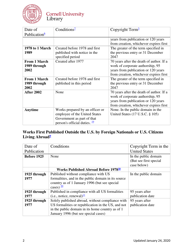
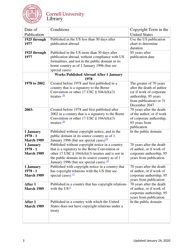
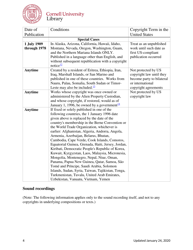
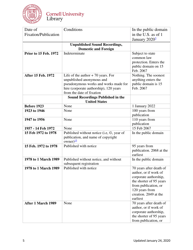
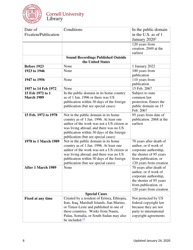
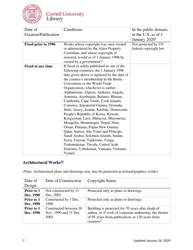
The Copyright Term and the Public Domain in the United States is a resource provided by the Cornell Copyright Information Center. It provides information about the duration of copyright protection for various types of works in the United States, as well as the conditions under which works enter the public domain.
The Cornell Copyright Information Center does not file the copyright term and the public domain in the United States.
Copyright Term and the Public Domain in the United States - Cornell Copyright Information Center - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the copyright term in the United States?
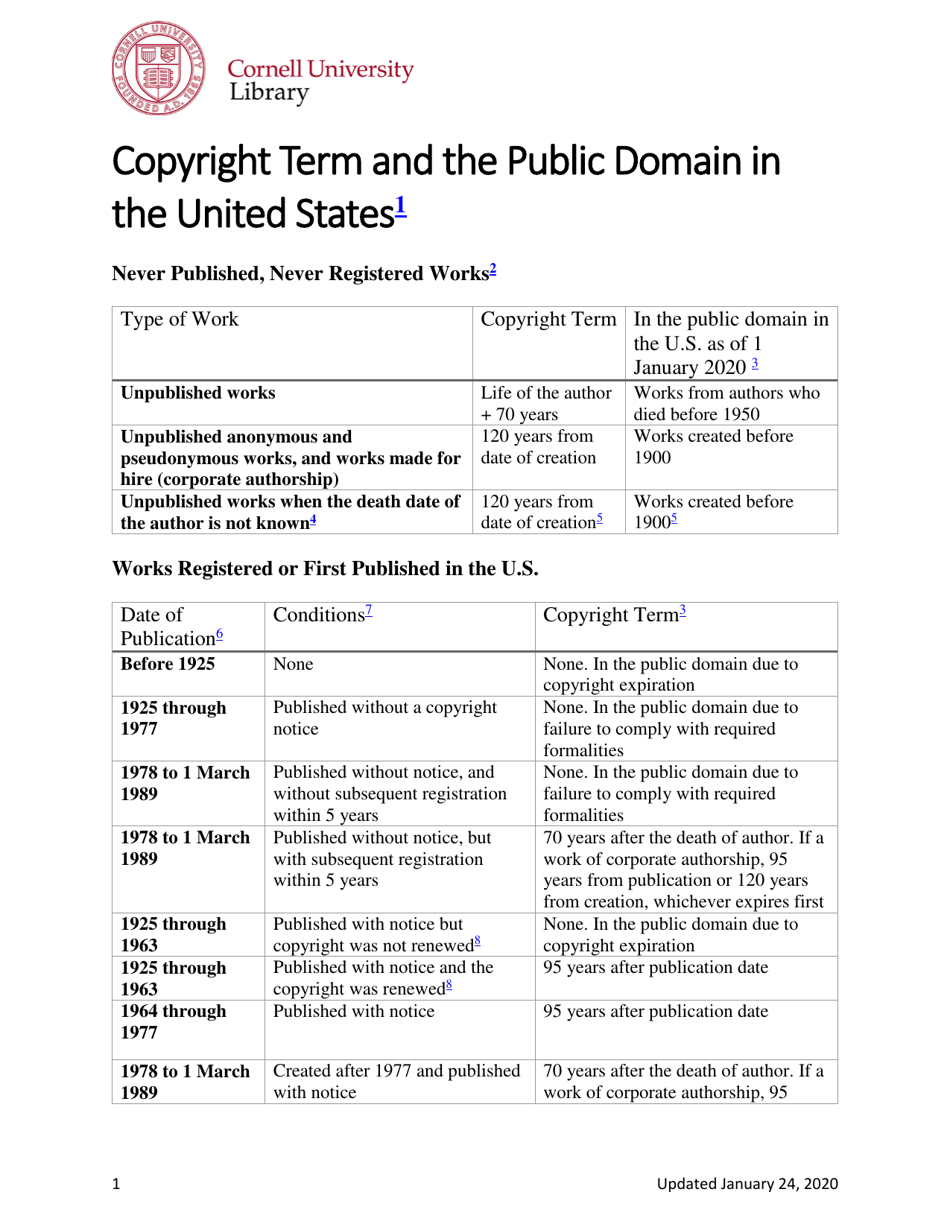
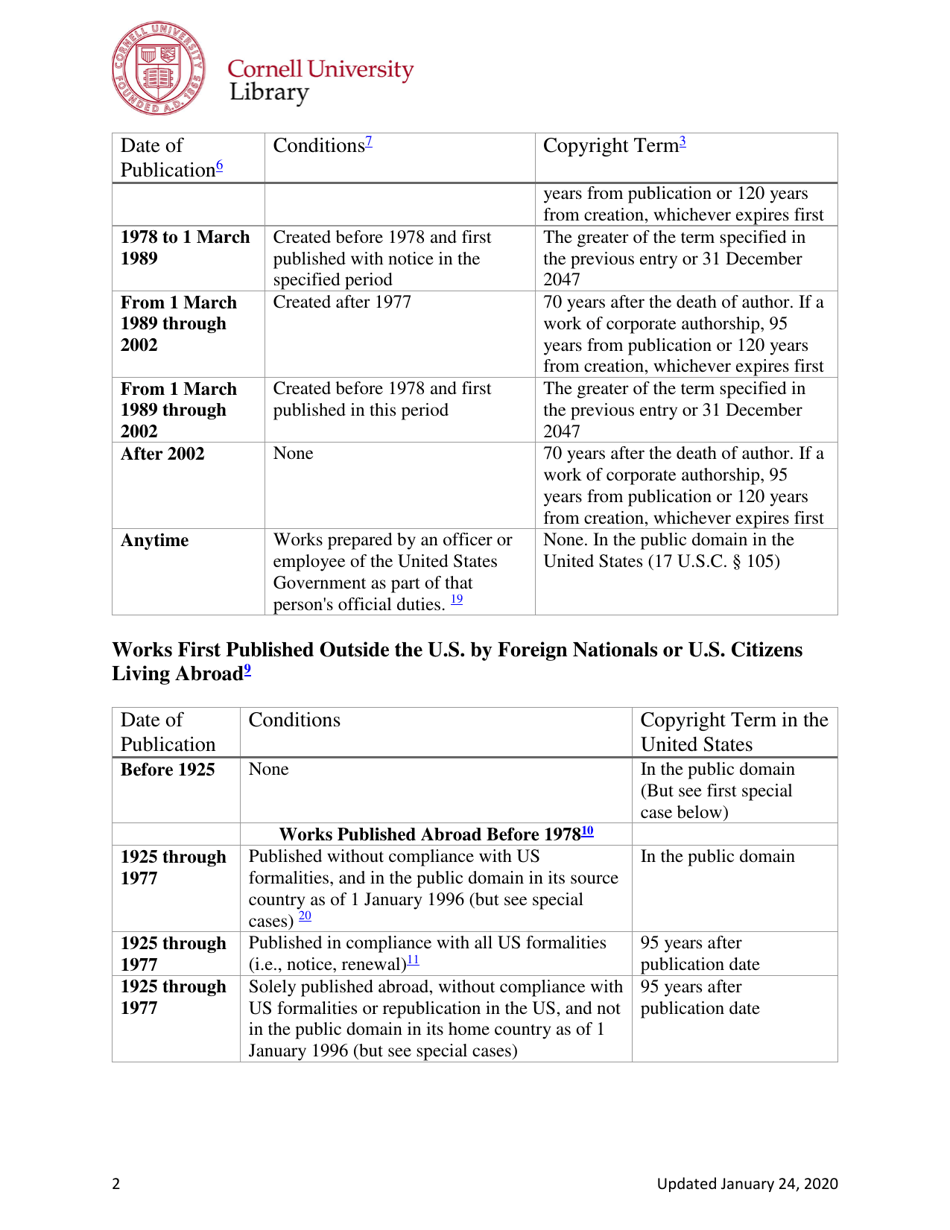
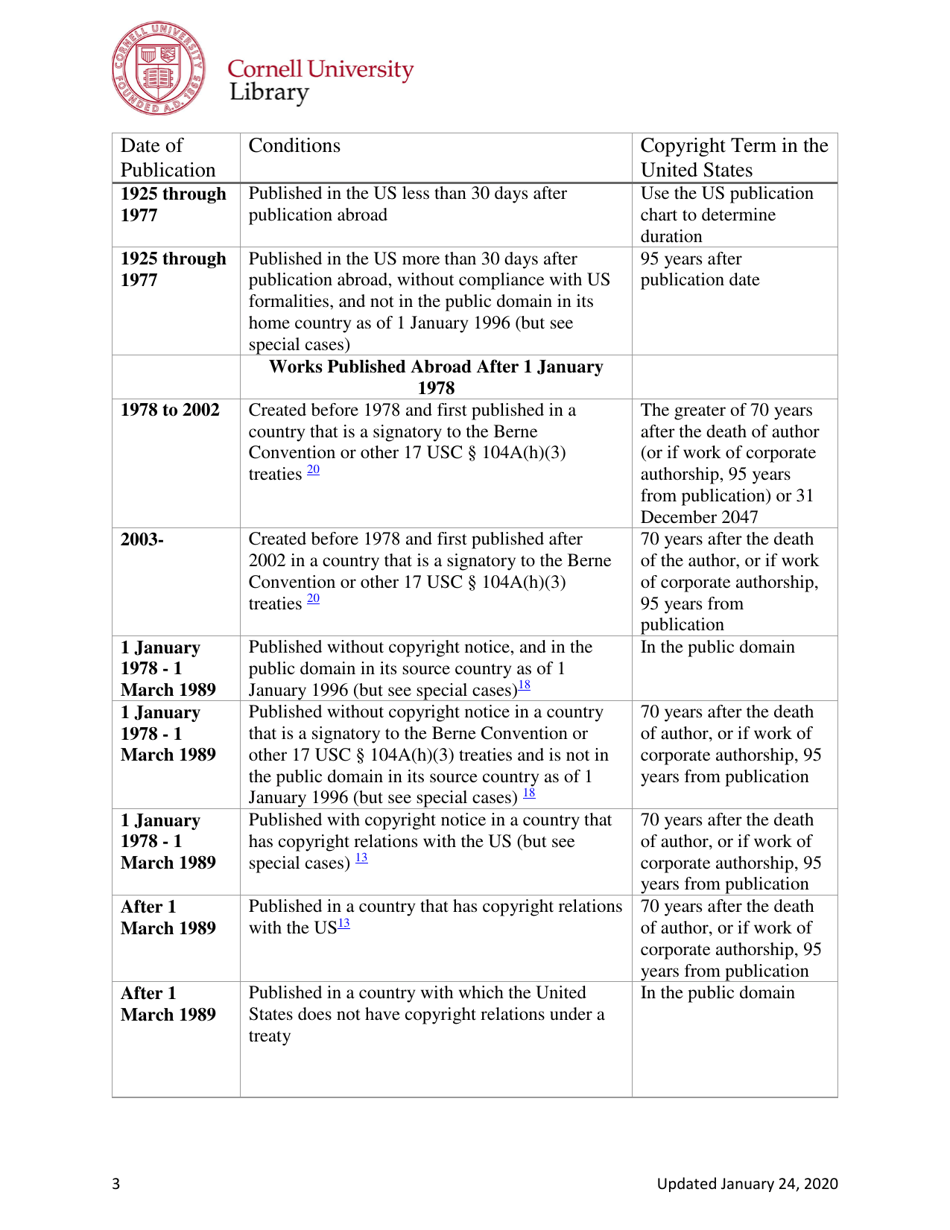
A: The copyright term in the United States can vary, but generally it lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years.
Q: What is the public domain?
A: The public domain refers to creative works that are not protected by copyright and can be freely used by anyone.
Q: How long does a work remain in the public domain?
A: In the United States, a work generally enters the public domain 70 years after the death of the author or the last surviving author.
Q: Can I use a work if it is in the public domain?
A: Yes, you can use a work that is in the public domain without permission or payment.
Q: What is fair use?
A: Fair use is a legal doctrine that allows for the limited use of copyrighted works without permission, for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, and research.
Q: Can I use copyrighted material under fair use?
A: Yes, you can use copyrighted material under fair use, but the specific circumstances and purpose of use will determine whether your use is considered fair.
Q: How can I determine if a work is still under copyright?
A: Determining the copyright status of a work can be complex, but you can start by researching the date of creation and the death date of the author.
Q: What are the consequences of infringing copyright?
A: Infringing copyright can result in legal consequences, such as being sued for damages and having to pay monetary penalties.
Q: Are government works copyrighted?
A: Government works are generally not copyrighted and are in the public domain, but there may be exceptions depending on the specific circumstances.
Q: What is the difference between copyright and trademark?
A: Copyright protects original creative works, while trademarks protect brands and symbols that distinguish goods or services.