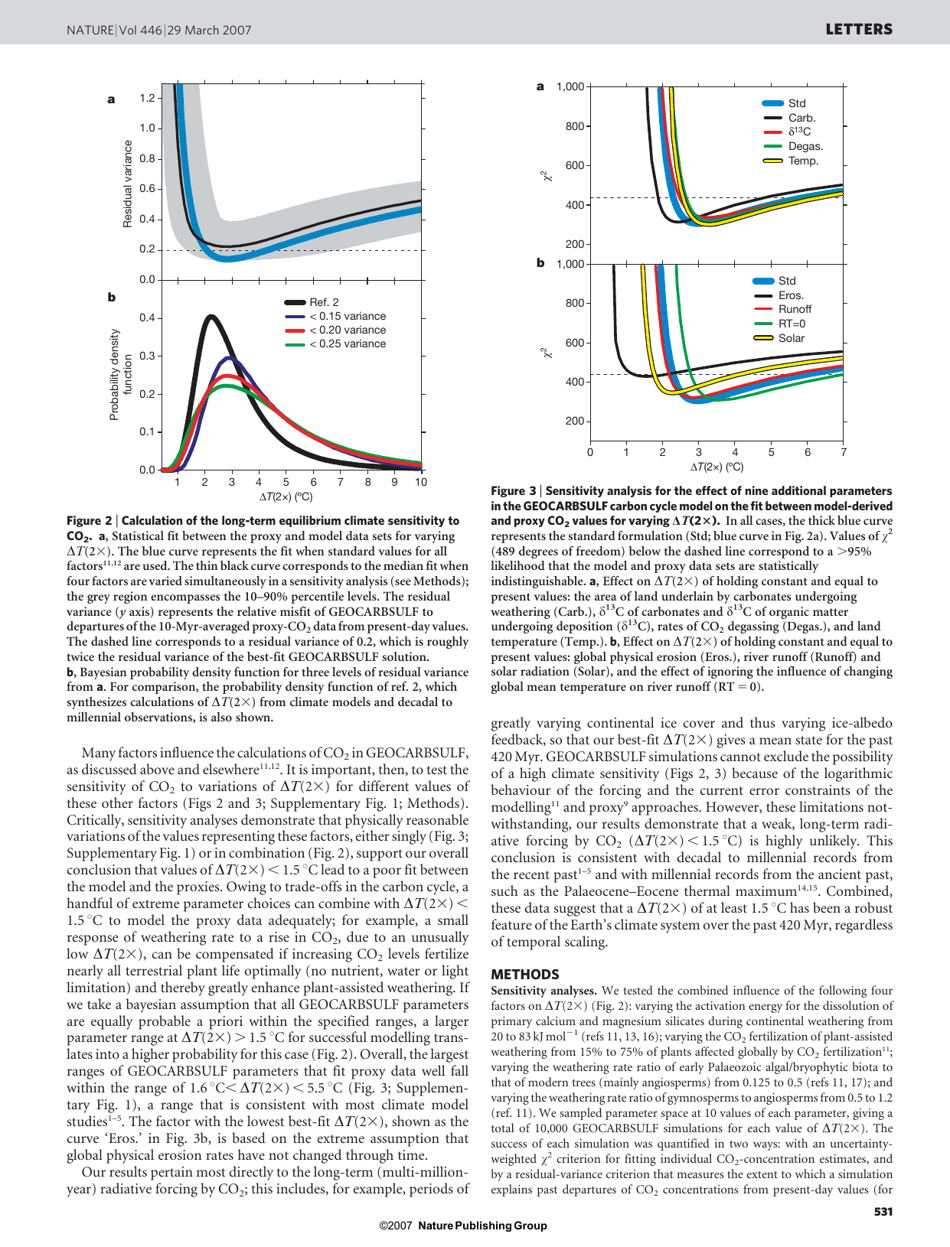
Climate Sensitivity Constrained by Co2 Concentrations Over the Past 420 Million Years
Climate sensitivity constrained by CO2 concentrations over the past 420 million years is important for studying and understanding the relationship between CO2 levels and global climate variability throughout Earth's history. It helps us assess the potential impacts of current and future CO2 emissions on the Earth's climate system.
The climate sensitivity constrained by CO2 concentrations over the past 420 million years is determined by scientists who study paleoclimatology and analyze fossil records.
FAQ
Q: What is the document about?
A: The document discusses climate sensitivity constrained by CO2 concentrations over the past 420 million years.
Q: What does climate sensitivity refer to?
A: Climate sensitivity refers to how much the Earth's temperature will change in response to changes in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Q: How far back does the document analyze CO2 concentrations?
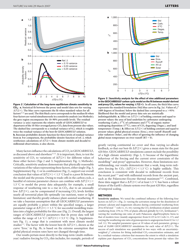
A: The document analyzes CO2 concentrations over the past 420 million years.
Q: Why is CO2 concentration important for climate sensitivity?
A: CO2 concentration is important because it is a greenhouse gas that influences the Earth's climate.
Q: What can past CO2 concentrations tell us about climate sensitivity?
A: Studying past CO2 concentrations can help us understand how the Earth's climate has responded to changes in CO2 levels in the past, which can inform predictions about future climate change.
Q: What is the significance of the timeframe of 420 million years?
A: The timeframe of 420 million years provides a long-term perspective on climate sensitivity and the relationship with CO2 concentrations.
Q: What does 'constrained' mean in the document title?
A: In this context, 'constrained' means that the study is limited or guided by the CO2 concentrations over the past 420 million years.
Q: How can understanding climate sensitivity help us?
A: Understanding climate sensitivity can help us make informed decisions about mitigating and adapting to climate change.
Q: What are some potential implications of the research findings?
A: The research findings could have implications for understanding the Earth's climate future, the effects of human activities on CO2 concentrations, and the potential for climate feedback loops.
Q: Why is studying CO2 concentrations over a long timeframe important?
A: Studying CO2 concentrations over a long timeframe allows us to see patterns and trends in climate sensitivity and gain a broader understanding of the Earth's climate system.