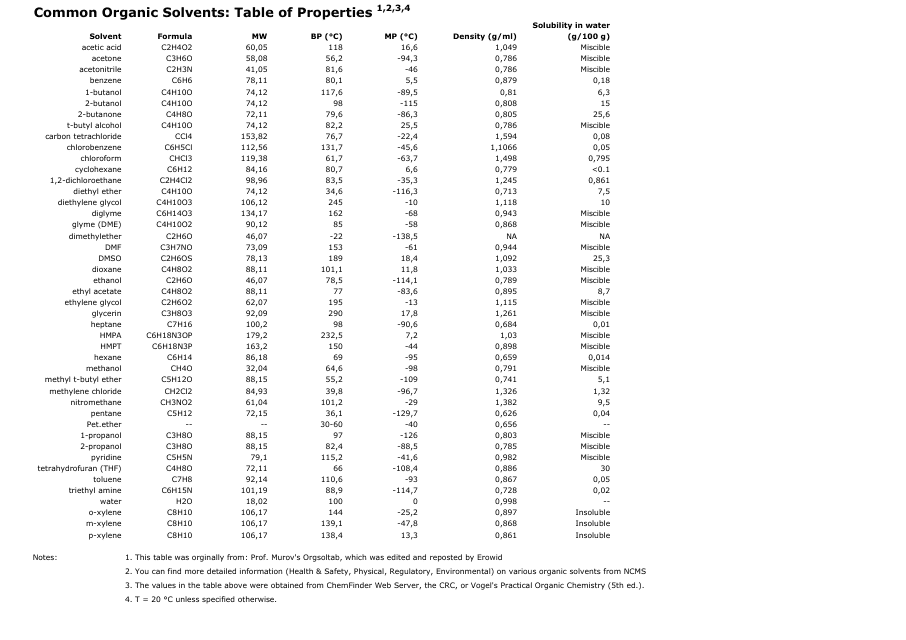
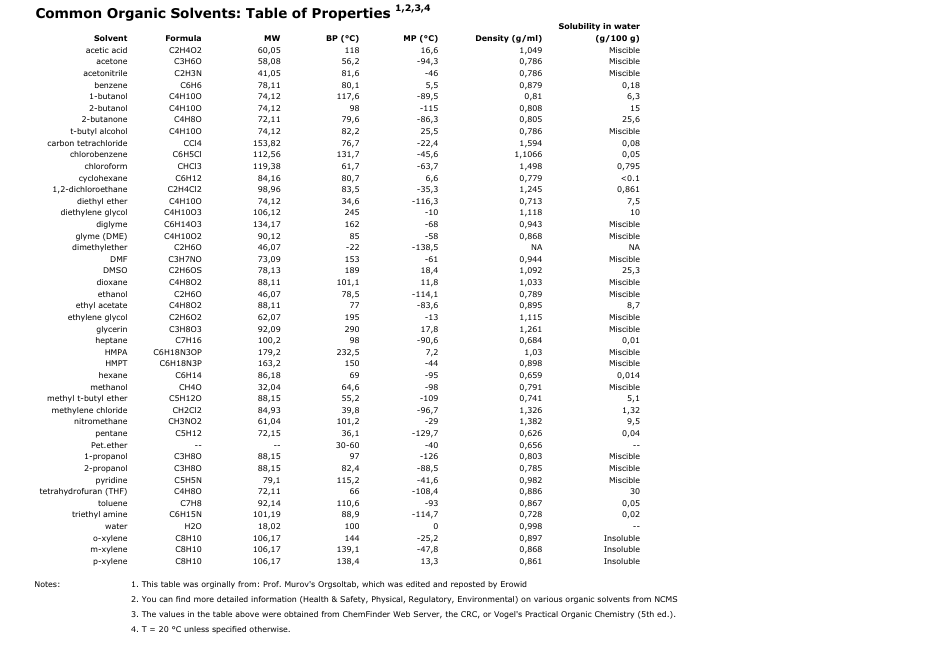
Common Organic Solvents Table of Properties - White
The Common Organic Solvents Table of Properties - White is a document that provides information about various organic solvents commonly used in chemical processes. It includes details such as boiling points, melting points, and other important properties of these solvents. This information is useful for scientists, researchers, and professionals working in fields like chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. It helps them determine the appropriate solvent for specific applications and understand how different solvents may behave in different conditions.
FAQ
Q: What is an organic solvent?
A: An organic solvent is a type of chemical compound that is capable of dissolving other substances.
Q: What are some examples of organic solvents?
A: Examples of organic solvents include ethanol, methanol, acetone, and toluene.
Q: What are the properties of organic solvents?
A: The properties of organic solvents can vary, but some common properties include high volatility, low boiling point, and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
Q: What is the purpose of using organic solvents?
A: Organic solvents are commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, paints and coatings, and cleaning products for purposes such as dissolving, cleaning, and extracting substances.
Q: Are organic solvents safe to use?
A: Some organic solvents can be toxic or flammable, so it is important to handle them with caution and follow safety guidelines when using them.