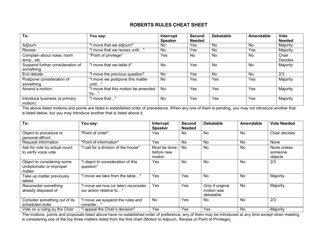
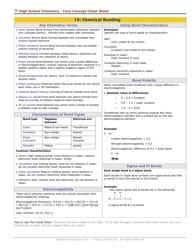
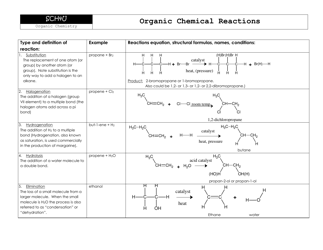
Net Ionic Equations and Solubility Rules Cheat Sheet
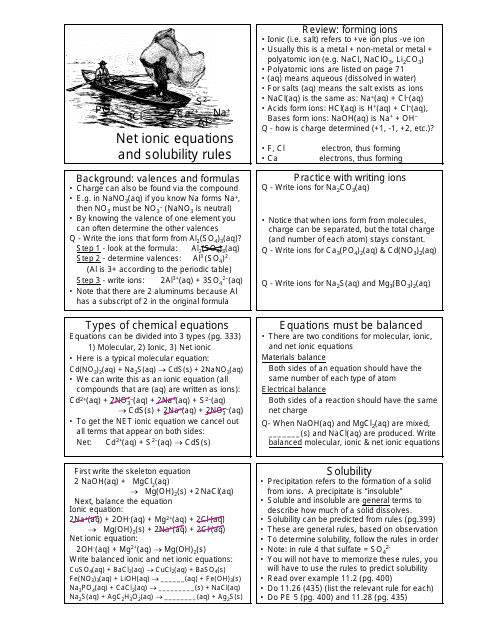
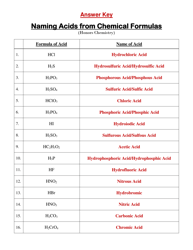
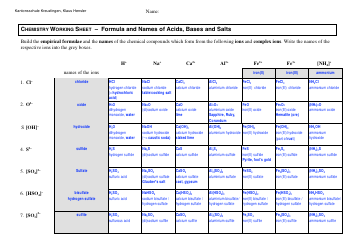
The Net Ionic Equations and Solubility Rules Cheat Sheet is a tool that helps to determine which compounds are soluble or insoluble in water and how to write net ionic equations. It can be used in chemistry to quickly reference the solubility rules and write balanced chemical equations.
The net ionic equations and solubility rules cheat sheet is typically filed by individual students or teachers for their personal use. There is no specific entity or organization that files it.
FAQ
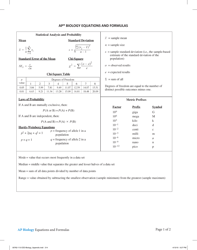
Q: What is a net ionic equation?
A: A net ionic equation shows only the species that are changed during a chemical reaction.
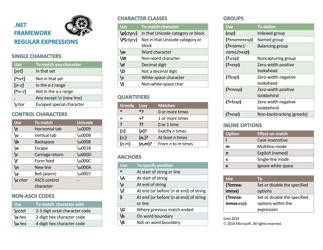
Q: What are solubility rules?
A: Solubility rules are guidelines that predict whether a compound will dissolve or precipitate in water.
Q: What is a solubility rule example?
A: An example of a solubility rule is that most sulfate compounds are soluble, except for those of calcium, strontium, barium, and lead.
Q: Why are solubility rules important?
A: Solubility rules are important because they help determine the state of a compound in a solution and predict the formation of precipitates.
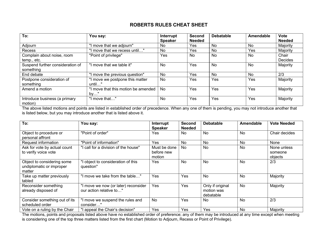
Q: How can you use solubility rules?
A: You can use solubility rules to identify the products of a chemical reaction and determine whether a precipitate will form.
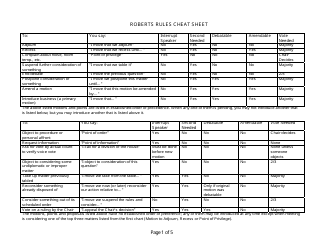
Q: What is a precipitation reaction?
A: A precipitation reaction is a reaction in which a solid substance, known as a precipitate, is formed when two aqueous solutions are mixed.
Q: What is a spectator ion?
A: A spectator ion is an ion that does not participate in a chemical reaction and remains unchanged.
Q: Why are spectator ions important?
A: Spectator ions are important because they help balance the charges in a net ionic equation and provide a more accurate representation of the reaction.
Q: How do you write a net ionic equation?
A: To write a net ionic equation, you must first write the balanced molecular equation and then eliminate the spectator ions to show only the species involved in the reaction.