9.1 Cellular Respiration: an Overview
9.1 Cellular Respiration: an Overview is a document that provides information and an overview of the process of cellular respiration, which is how cells generate energy from glucose and other molecules.
FAQ
Q: What is cellular respiration?
A: Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
Q: Why is cellular respiration important?
A: Cellular respiration is important because it is the primary way by which cells generate energy to carry out their functions.
Q: What are the main stages of cellular respiration?
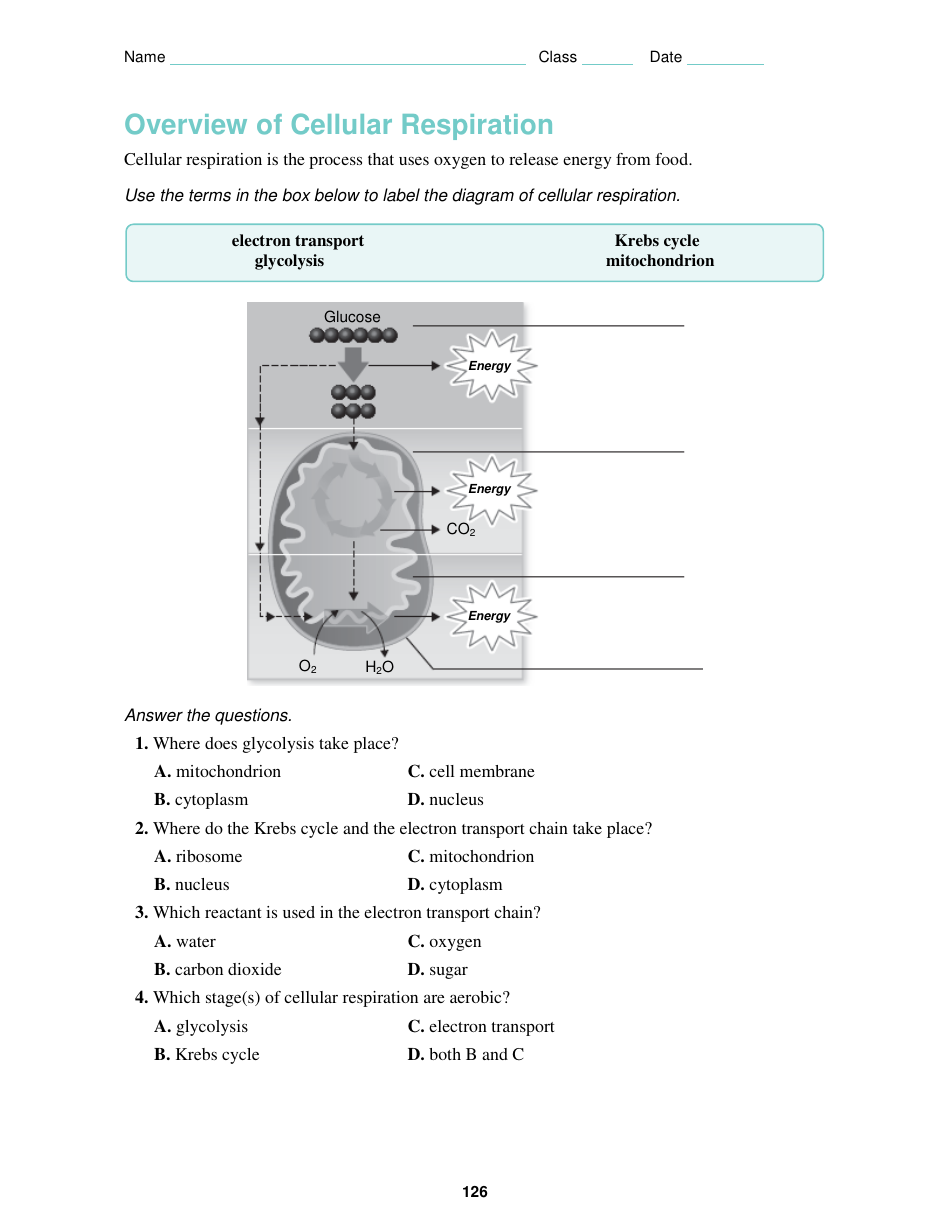
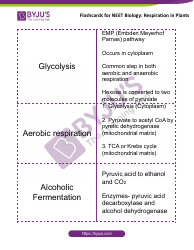
A: The main stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Q: What is glycolysis?
A: Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration, where glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate.
Q: What is the citric acid cycle?
A: The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is the second stage of cellular respiration, where pyruvate is further broken down to release energy.
Q: What is oxidative phosphorylation?
A: Oxidative phosphorylation is the final stage of cellular respiration, where the bulk of ATP production occurs.
Q: What is the role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
A: Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain during oxidative phosphorylation, allowing for the production of ATP.
Q: What are the waste products of cellular respiration?
A: The waste products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide and water.
Q: Is cellular respiration the same as breathing?
A: No, cellular respiration is the process by which cells generate energy, while breathing is the process of taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.