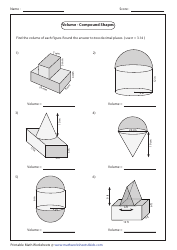
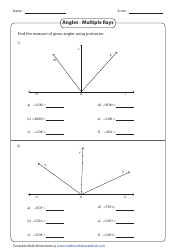
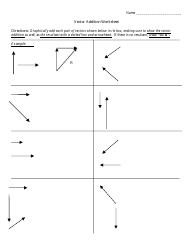
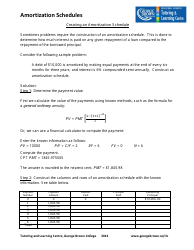
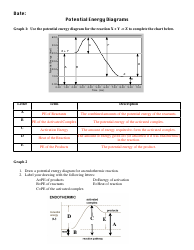
Calculating Ph and Poh Worksheet With Answers
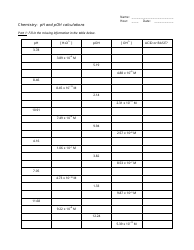
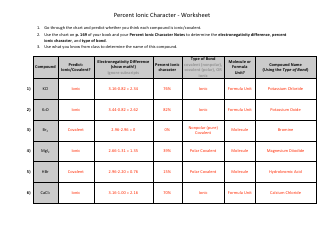
Calculating pH and pOH worksheet with answers is a learning tool that helps students understand and practice the calculation of pH and pOH values. pH and pOH are measures of acidity and alkalinity, respectively, in a solution. This worksheet provides a set of questions and problems that require students to calculate the pH or pOH values of different solutions, given the concentration of hydrogen or hydroxide ions. The answers provided in the worksheet assist students in understanding the correct approach and solution to these calculations. The purpose of this worksheet is to enhance students' knowledge and skills in pH and pOH calculations, which are fundamental concepts in chemistry.
The document "Calculating pH and pOH Worksheet with Answers" is typically filed by students or teachers in educational settings. It is not usually filed with any specific organization or government agency.
FAQ
Q: What is pH?
A: pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) present in a solution.
Q: How is pH calculated?
A: pH is calculated using the formula: pH = -log[H+]. It is a logarithmic scale, ranging from 0 to 14, where a pH of 7 is considered neutral, pH below 7 is acidic, and pH above 7 is alkaline (basic).
Q: How do I calculate pOH?
A: pOH is calculated using the formula: pOH = -log[OH-]. It is another way to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, but it focuses on the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) instead of hydrogen ions.
Q: What is the relationship between pH and pOH?
A: The relationship between pH and pOH is inverse. In other words, as the pH of a solution increases, the pOH decreases, and vice versa. The sum of pH and pOH is always equal to 14 in a neutral solution.
Q: How can I convert pH to hydrogen ion concentration?
A: To convert pH to hydrogen ion concentration, you can use the formula: [H+] = 10^(-pH).
Q: How can I convert pOH to hydroxide ion concentration?
A: To convert pOH to hydroxide ion concentration, you can use the formula: [OH-] = 10^(-pOH).
Q: How can pH and pOH be used to determine whether a solution is acidic, neutral, or alkaline?
A: If the pH of a solution is less than 7, it is considered acidic. If the pH is equal to 7, it is neutral. And if the pH is greater than 7, it is alkaline (basic). Similarly, if the pOH of a solution is less than 7, it is alkaline. If the pOH is equal to 7, it is neutral. And if the pOH is greater than 7, it is acidic.
Q: Why is it important to calculate pH and pOH?
A: Calculating pH and pOH is essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, environmental science, and medicine. It helps in understanding the acidity or alkalinity of solutions, which is crucial for determining their properties and impacts.