Review and Practice: Protein Synthesis Worksheet - Grade 12th, Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
The Review and Practice: Protein Synthesis Worksheet is designed for 12th grade students at Westgate Mennonite Collegiate to review and practice concepts related to protein synthesis. It is likely used as a study tool or homework assignment to reinforce learning in the subject.
FAQ
Q: What is the purpose of protein synthesis?
A: The purpose of protein synthesis is to create proteins, which are essential for various biological processes in the body.
Q: What are the two main steps of protein synthesis?
A: The two main steps of protein synthesis are transcription and translation.
Q: What happens during transcription?
A: During transcription, the DNA sequence is transcribed into a complementary mRNA sequence.
Q: What happens during translation?
A: During translation, the mRNA sequence is used as a template to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain.
Q: What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
A: mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes, where it is used as a template for protein synthesis.
Q: What is the role of tRNA in protein synthesis?
A: tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes, where they are assembled into a polypeptide chain based on the mRNA sequence.
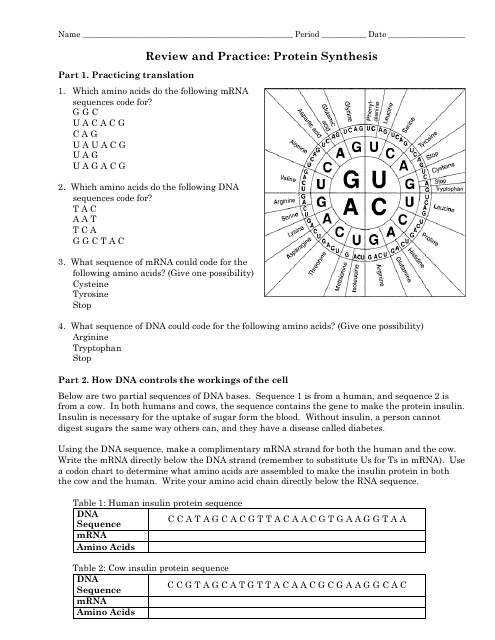
Q: What is a codon?
A: A codon is a three-letter sequence of mRNA nucleotides that corresponds to a specific amino acid.
Q: What is an anticodon?
A: An anticodon is a three-letter sequence of tRNA nucleotides that is complementary to a codon on the mRNA.
Q: What is the start codon?
A: The start codon (AUG) signals the beginning of protein synthesis and codes for the amino acid methionine.
Q: What are the three stop codons?
A: The three stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) signal the end of protein synthesis and do not code for any amino acid.
Q: What is a mutation?
A: A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence, which can alter the amino acid sequence and potentially affect protein function.
Q: What are the different types of mutations?
A: The different types of mutations include point mutations (substitutions), insertions, deletions, and frame shift mutations.
Q: What is a frameshift mutation?
A: A frameshift mutation is a mutation that shifts the reading frame of the genetic code, usually resulting in non-functional proteins.