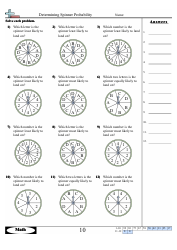
Basic Probability Worksheet With Answer Key
A Basic Probability Worksheet with Answer Key is a helpful educational resource designed to assess and enhance one's understanding of basic probability concepts. This worksheet typically consists of a series of questions accompanied by multiple-choice or short-answer options. The answer key provides the correct solutions for each question, allowing students to self-assess their progress and consolidate their knowledge in probability theory. This resource is commonly utilized by teachers, parents, or students as a supplementary tool for studying probability and improving problem-solving skills.
The basic probability worksheet with answer key is typically filed by the teacher or instructor who assigns it to students. This worksheet is commonly used in educational settings to assess students' understanding of probability concepts.
FAQ
Q: What is probability?
A: In simple terms, probability measures the likelihood of an event occurring. It is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, where 0 represents impossibility and 1 represents certainty.
Q: How is probability calculated?
A: Probability is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes.
Q: What is the difference between theoretical probability and experimental probability?
A: Theoretical probability is based on mathematical reasoning and assumes that all outcomes are equally likely. Experimental probability, on the other hand, is based on observed data and actual results from conducting experiments or trials.
Q: What is the addition rule of probability?
A: The addition rule states that the probability of the union of two events is equal to the sum of their individual probabilities, minus the probability of their intersection.
Q: What is the multiplication rule of probability?
A: The multiplication rule states that the probability of the joint occurrence of two independent events is equal to the product of their individual probabilities.
Q: What is conditional probability?
A: Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It is calculated using the formula: P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B), where P(A|B) represents the probability of event A given event B.
Q: What is a sample space in probability?
A: The sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment. It is usually represented by the letter 'S'.
Q: What are mutually exclusive events?
A: Mutually exclusive events are events that cannot occur at the same time. If one event happens, the other event cannot happen simultaneously.
Q: What are independent events?
A: Independent events are events whose occurrence or non-occurrence does not affect the probability of the other event happening.
Q: How is probability used in real life?
A: Probability is used in various fields such as statistics, finance, gaming, insurance, and weather forecasting. It helps in making informed decisions and predicting the likelihood of certain outcomes.