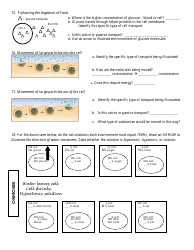
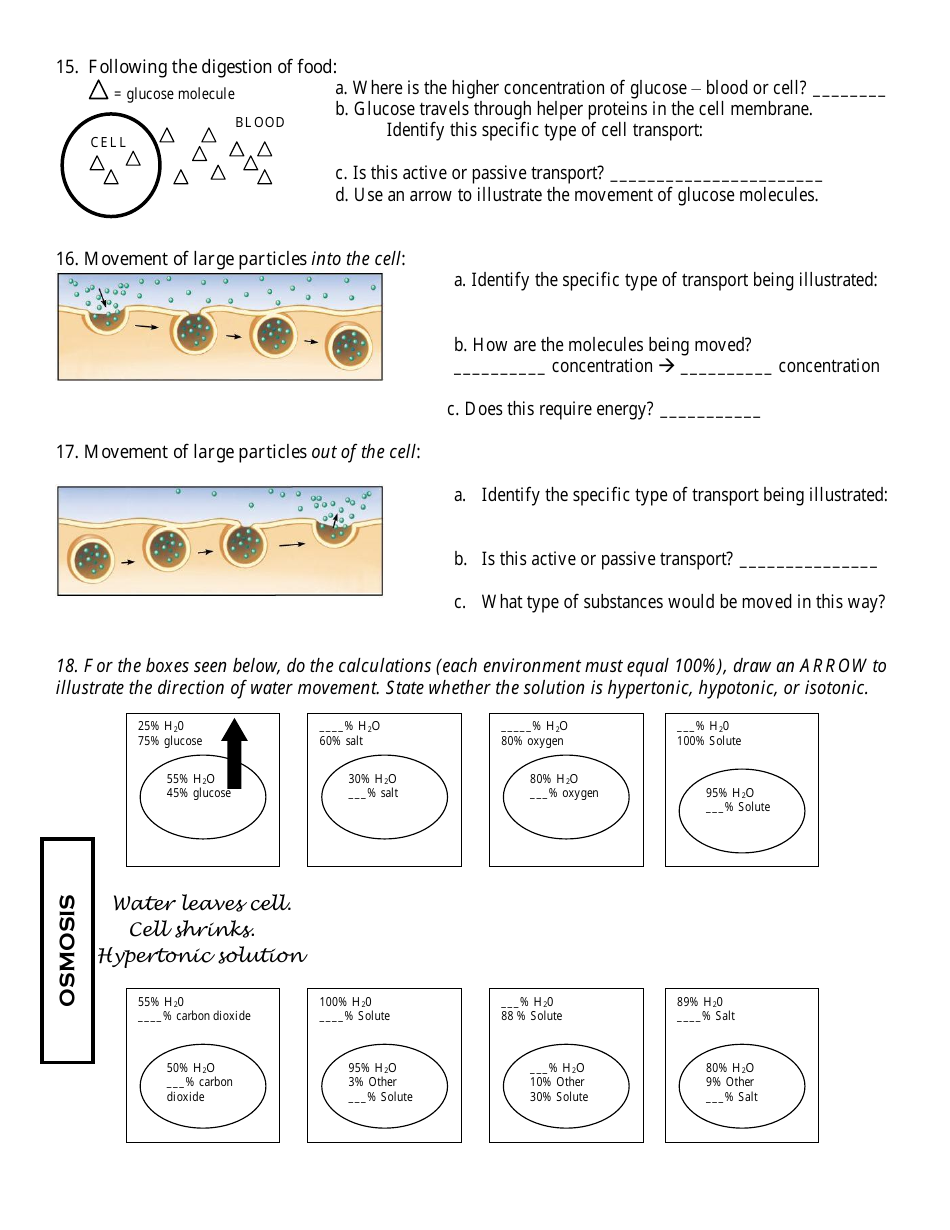
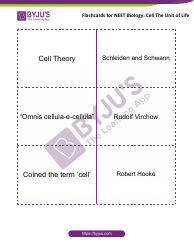
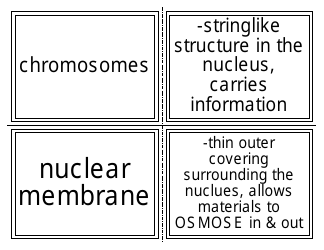
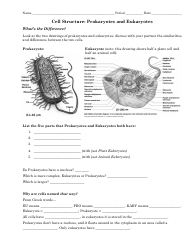
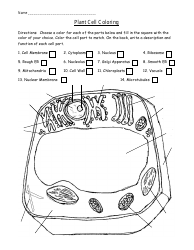
Cell Transport Biology Worksheet
The Cell Transport Biology Worksheet is a learning tool used in biology to help students understand the various mechanisms by which molecules and ions move across cell membranes. It allows students to practice and test their understanding of concepts such as diffusion, osmosis, and active transport.
FAQ
Q: What is cell transport?
A: Cell transport refers to the movement of substances in and out of cells.
Q: What are the two main types of cell transport?
A: The two main types of cell transport are passive transport and active transport.
Q: What is passive transport?
A: Passive transport is the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy.
Q: What are the three types of passive transport?
A: The three types of passive transport are diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Q: What is diffusion?
A: Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Q: What is osmosis?
A: Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
Q: What is facilitated diffusion?
A: Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane with the help of transport proteins.
Q: What is active transport?
A: Active transport is the movement of substances across a cell membrane using energy.
Q: What is endocytosis?
A: Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances by engulfing them in a vesicle.
Q: What is exocytosis?
A: Exocytosis is the process by which cells release substances by fusing a vesicle with the cell membrane.