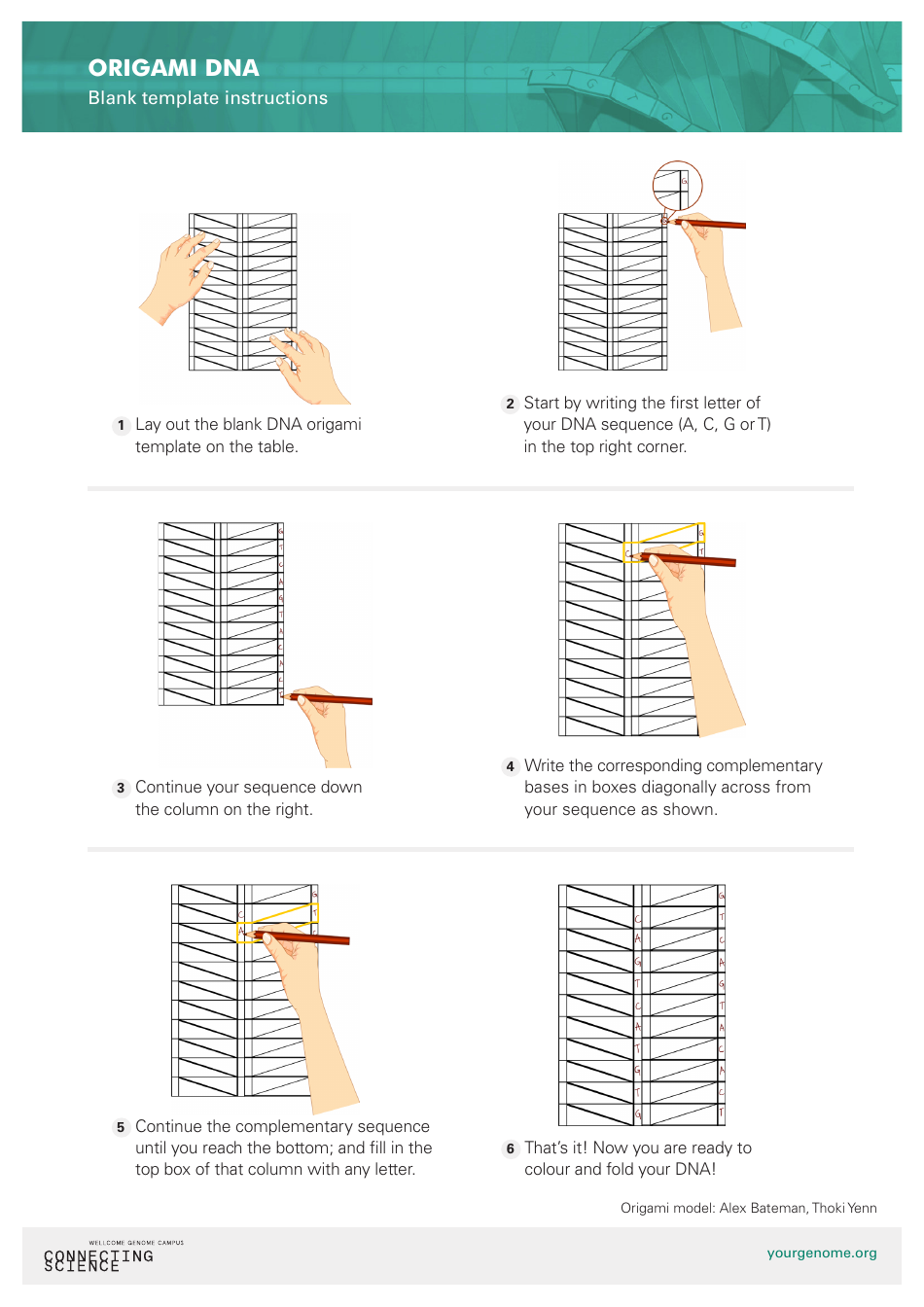
Origami Dna
Origami DNA refers to a method in Nanotechnology where DNA molecules are manipulated to self-assemble into various shapes and structures. This principle is akin to the art of Origami where a single sheet of paper is folded into different forms.
Origami DNA is used primarily for biomedical research and applications. It aids in the development of nanoscale devices like nanorobots, drug delivery systems, and molecular computers. Additionally, it provides an opportunity to study and understand biological processes on a molecular level.
For example, in the healthcare sector, nanorobots made from DNA Origami can carry and deliver drugs directly to specific cancer cells, thus making treatments more efficient and reducing side effects.
However, this field is still in its nascent stage, and further research and testing are needed to fully realize its potential.
The term "Origami DNA" typically refers to a method of DNA folding where DNA is manipulated into shapes or structures, just like the art of paper origami. This is a field of study and research done by scientists, particularly in the area of nanotechnology and molecular biology. It's not something that a person or a country would typically file. Therefore, it may not be accurate to say a specific country or person files 'Origami DNA.' It's more of a scientific technique used in research. However, specific research papers or patents relating to techniques or advancements in Origami DNA could be filed by researchers or organizations from any country, including the USA, Canada, India, or Australia.
FAQ
Q: What is origami DNA?
A: Origami DNA is a method used in nanotechnology where DNA is folded into specific shapes or structures. These shapes are potentially useful in fields like drug delivery and biosensing.
Q: How does DNA origami work?
A: It works by using a long single strand of DNA, combined with several shorter 'staple' strands. These staple strands are designed to match with certain sections of the long strand, and when they bind together, they pull the long strand into the desired shape.
Q: Is origami DNA related to the traditional Japanese art of origami?
A: Yes, the technique of folding DNA into useful shapes is reminiscent of the Japanese art of folding paper into aesthetic shapes, thus the name 'origami'.
Q: What applications does DNA origami have?
A: DNA origami has potential applications in various fields such as drug delivery where it can be used to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells, bio-engineering for building cellular machines, data storage, and biosensing where it helps in detecting diseases and contaminants.
Q: Is DNA origami used in medicine?
A: Yes, DNA origami is considered to be hugely promising in the field of medicine. It could help with targeted drug delivery, diagnostic devices, and the construction of synthetic tissues.
Q: Who invented origami DNA?
A: DNA Origami was proposed by Paul Rothemund at Caltech (California Institute of Technology) in 2006.
Q: How is DNA origami engineered?
A: DNA origami is engineered using a long, single strand of DNA, typically from the M13mp18 virus. This strand is mixed with smaller synthetic oligonucleotide staple strands that guide the long strand to fold into a specific shape, such as a rectangle, square, or even more complex shapes.
Q: Can DNA origami spontaneously self-assemble?
A: Yes, with the correct set of staple strands, the DNA origami structure can spontaneously self-assemble when the strands are mixed together and slowly cooled.