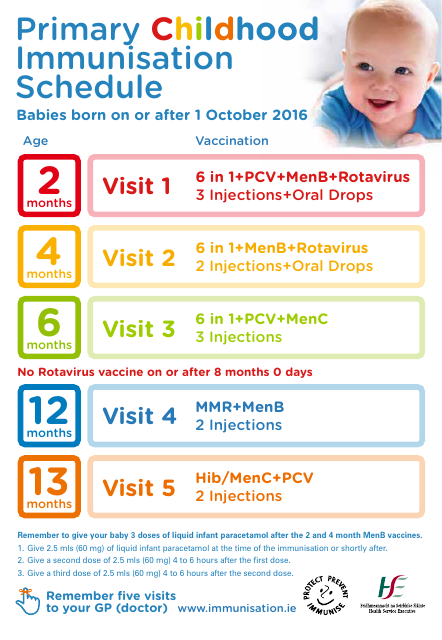
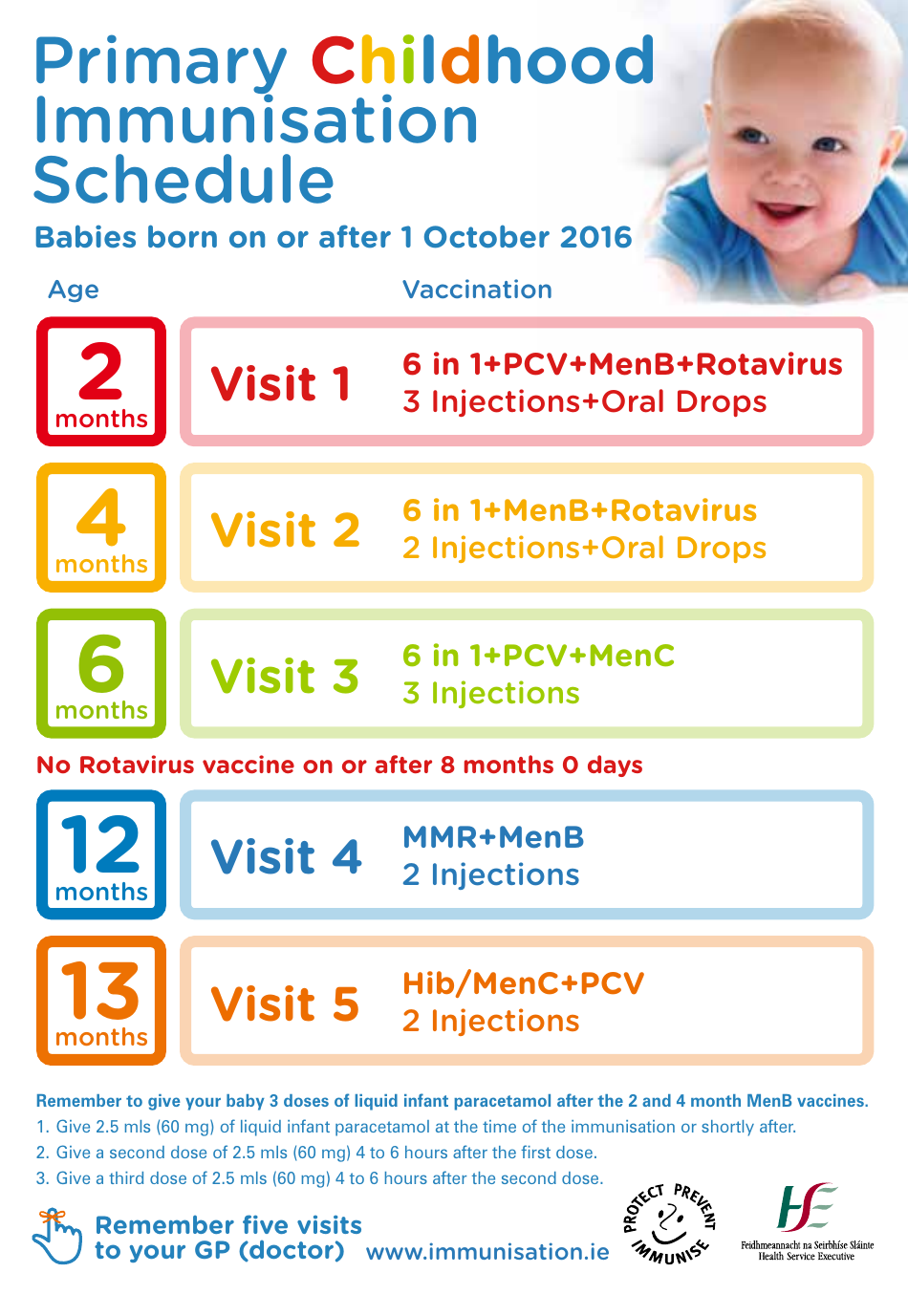
Primary Childhood Immunisation Schedule
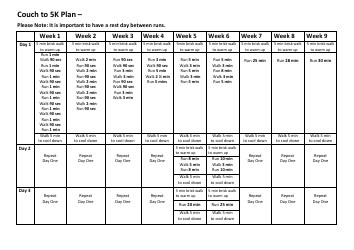
The Primary Childhood Immunisation Schedule is a recommended schedule of vaccines that helps protect children from serious diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, and more. It helps build immunity and prevent the spread of these illnesses among children.
In the United States, the primary childhood immunization schedule is developed and maintained by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), which is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
FAQ
Q: What is the primary childhood immunisation schedule?
A: The primary childhood immunisation schedule is a set of recommended vaccines that children should receive to protect them from various diseases.
Q: What vaccines are included in the primary childhood immunisation schedule?
A: The vaccines included in the primary childhood immunisation schedule may vary slightly depending on the country, but common vaccines include those for measles, mumps, rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, hepatitis B, and varicella (chickenpox).
Q: At what age should children receive their primary childhood immunisations?
A: Children should receive their primary childhood immunisations according to the recommended schedule, which usually starts shortly after birth and continues through early childhood.
Q: Are the primary childhood immunisations mandatory?
A: In most countries, primary childhood immunisations are not mandatory, but they are strongly recommended by healthcare authorities and often required for school entry.
Q: Are primary childhood immunisations safe?
A: Yes, primary childhood immunisations are considered to be safe and have undergone rigorous testing before being approved for use. Vaccines are continually monitored for safety by healthcare authorities.
Q: What are the benefits of primary childhood immunisations?
A: Primary childhood immunisations help protect children from serious diseases and their complications. They also contribute to reducing the spread of infectious diseases in the community.