A1c Test and the Estimated Average Glucose (Eag)
The A1c test, also known as the HbA1c or glycated hemoglobin test, is a blood test commonly used to diagnose and monitor individuals with type 1, type 2 or prediabetes. It provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. The test measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
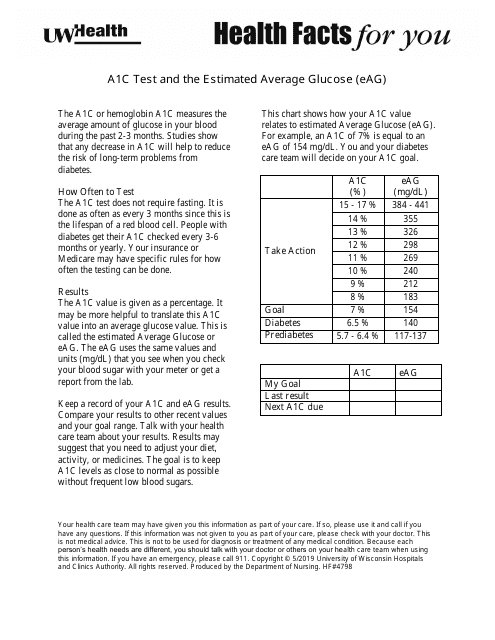
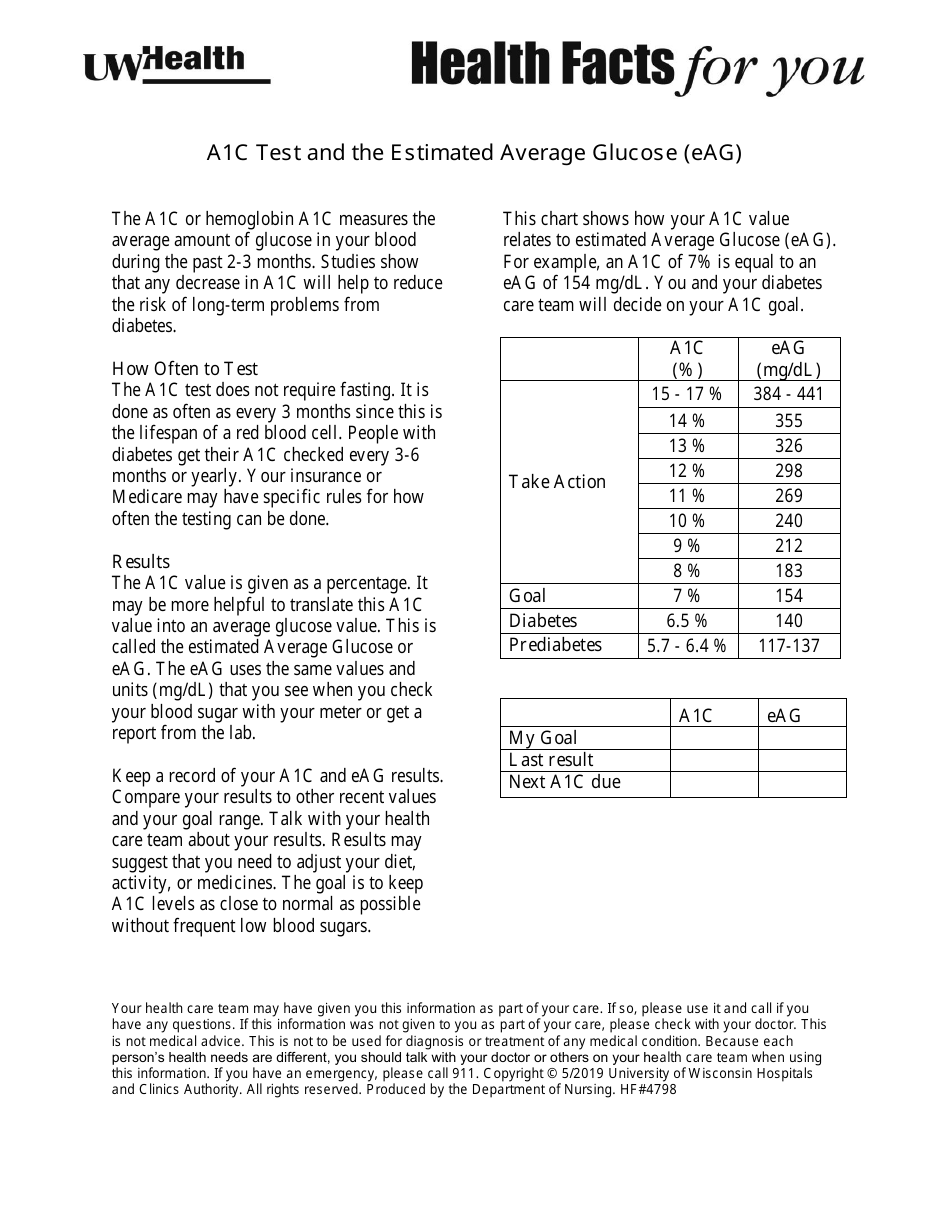
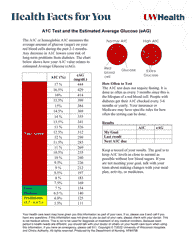
Estimated Average Glucose (EAG) is a measure derived from the A1c test result. It gives the same information as an A1c, but in units (mg/dl) that are more familiar to those who monitor their own blood sugars, thereby helping them to better understand their condition and how their doctor's recommendations will help them achieve good glucose control.
The A1C test and the Estimated Average Glucose (EAG) are not documents that are filed by a specific country or entity. Rather, they are medical tests that are conducted by healthcare providers.
The A1C test is a blood test that provides information about a person's average levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, over the past 3 months. The A1C test is the primary test used for diabetes management and diabetes research.
Similarly, EAG is a part of the results of the A1C test. It gives the patient a better idea of how well they are managing their diabetes, by translating the A1C percentage into a measurement more similar to what a patient would see on their glucose meter as they check their blood sugar levels at home.
This is not specific to a particular country and is a common practice in the healthcare field across the globe, including in the USA, Canada, India, and Australia. Healthcare providers in these countries perform these tests for patients who have diabetes or are at risk of it.
FAQ
Q: What is an A1C test?
A: An A1C test is a common blood test used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It also gauges how well you're managing your diabetes. The test results reflect your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months.
Q: What is Estimated Average Glucose (EAG)?
A: Estimated Average Glucose (EAG) gives the same information as an A1C test but in units similar to how daily blood sugar levels are measured. The EAG translates the A1C percentage into a number that better helps people with diabetes daily manage their blood sugars.
Q: How often should I have an A1C test?
A: If you have diabetes, it's recommended you have an A1C test at least twice per year. This frequency may increase if your doctor finds your diabetes is uncontrolled or if you change your diabetes treatment.
Q: What does it mean if my A1C level is too high?
A: If your A1C level is higher than your target, it means that your blood sugar levels have been too high in the past few months. High levels of blood sugar can damage your heart, blood vessels, kidneys, feet and eyes.
Q: How does the EAG correspond with A1C levels?
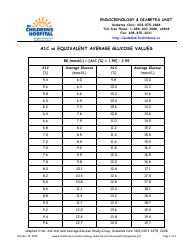
A: The EAG gives a clearer and more understandable number for diabetes management. For example, an A1C of 7 percent is equivalent to an EAG of 154 mg/dL. This can help individuals better understand their average blood glucose levels.
Q: Why is A1C test important for people with diabetes?
A: The A1C test is an important part of diabetes care because it provides information about a person’s average levels of blood glucose over the past 3 months. It helps healthcare providers understand how well a person's diabetes care plan is working.