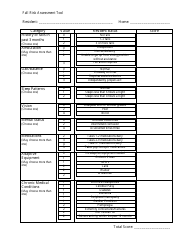
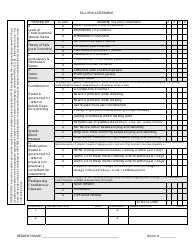
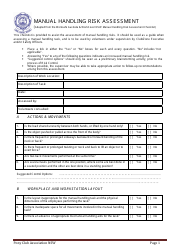
Wrist Examination Checklist
A Wrist Examination Checklist is typically utilized by healthcare professionals for conducting a methodical and comprehensive inspection of a patient's wrist. The purpose of this checklist is to detect any abnormality, injury, or disease related to the wrist and to subsequently guide the appropriate treatment.
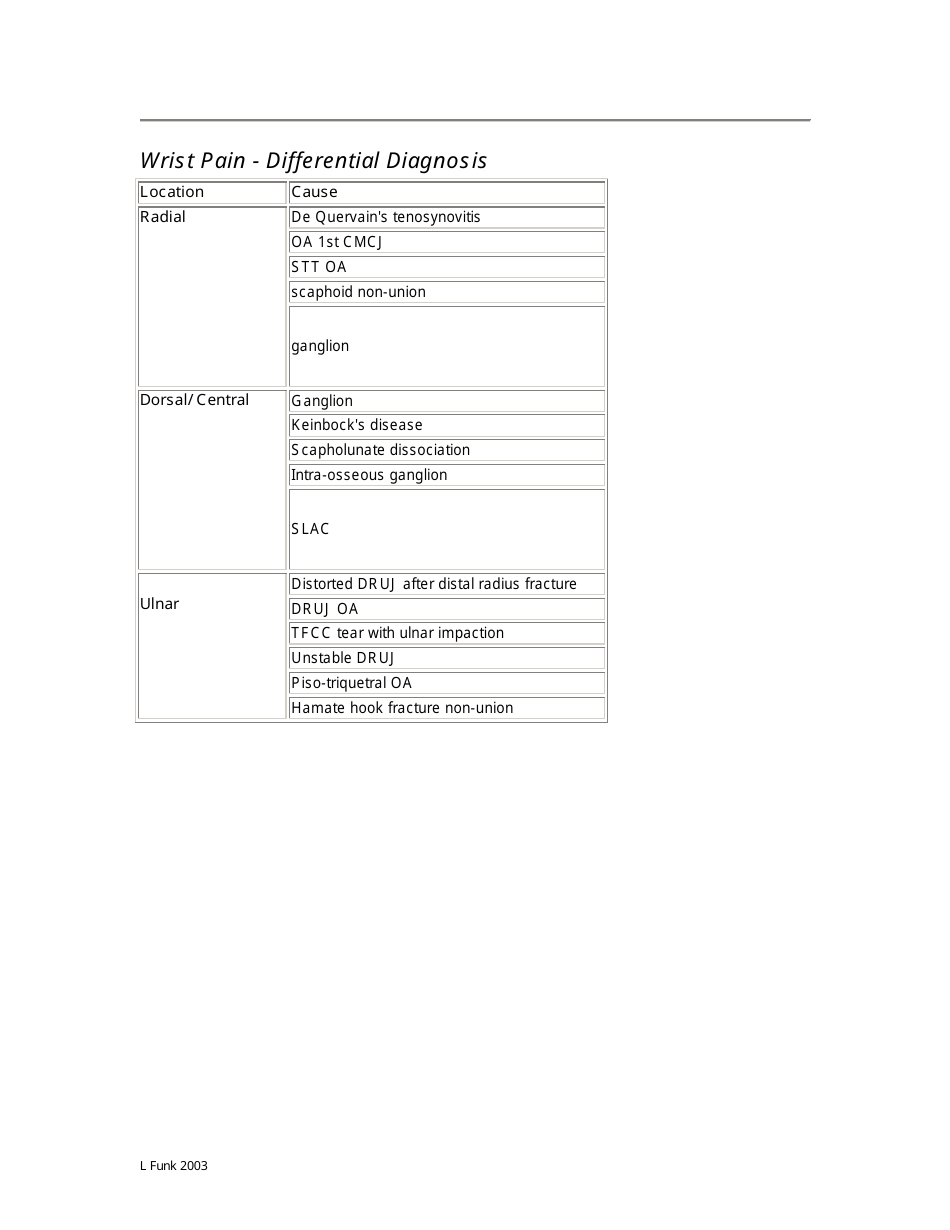
The checklist typically includes the assessment of several aspects such as:
-
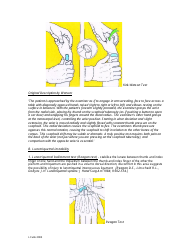
Observations: Looking for deformities, swelling, redness or any other visible abnormality.
-
Palpation: Touching the wrist to check for tenderness, heat, nodules, lumps or bumps.
-
Range of Motion: Checking the ability of the wrist joint to move in different directions.
-
Neurovascular Examination: Assessing the nerves and blood vessels around the wrist.
-
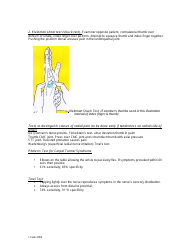
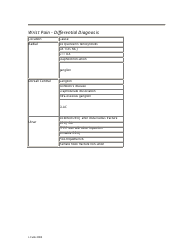
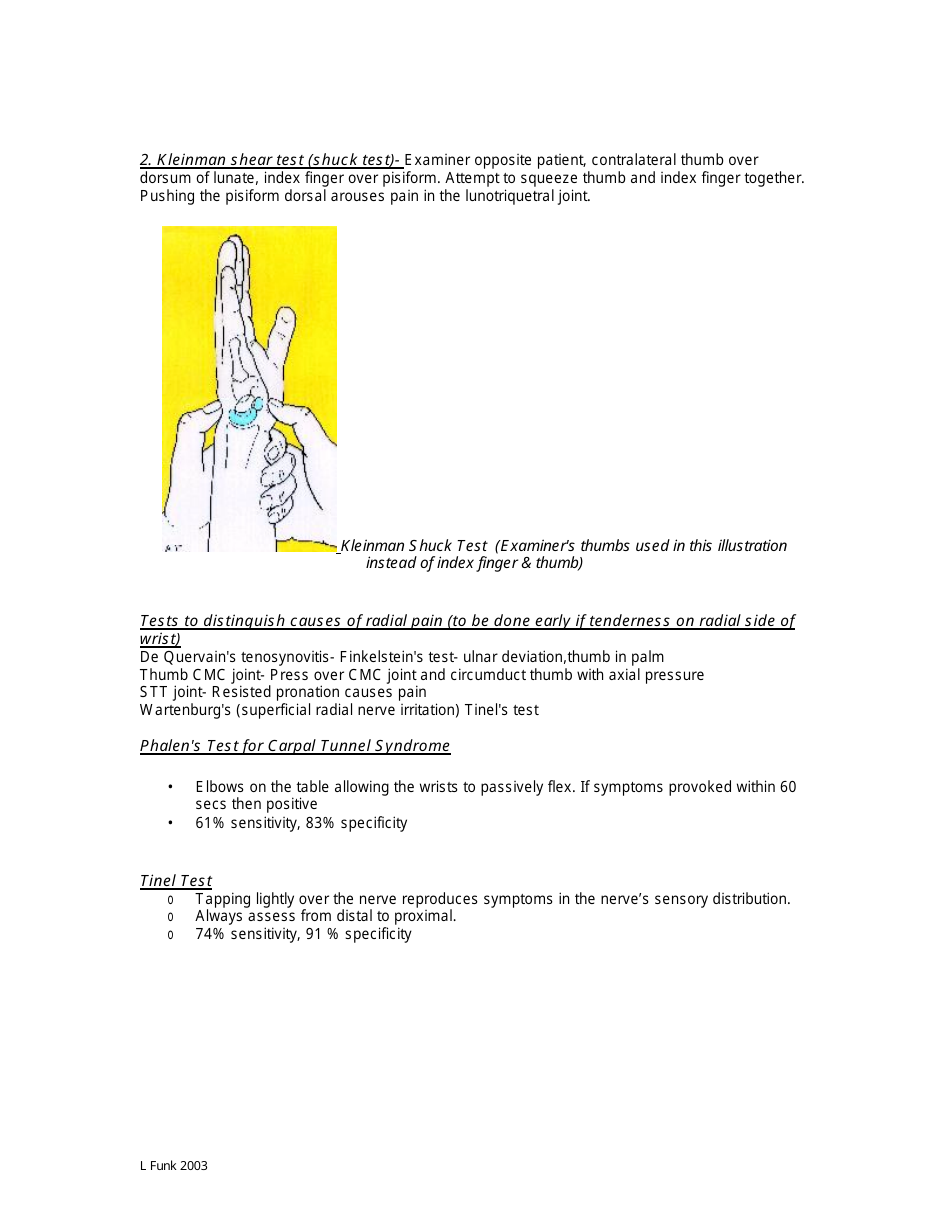
Special Tests: Performing specific tests to diagnose certain conditions such as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Wrist Tendonitis, etc.
However, please note the actual content of a Wrist Examination Checklist can vary depending on the guidelines followed by the specific health institution or the healthcare provider.
The Wrist Examination Checklist is usually filed by a healthcare professional, such as a physician, physical therapist, or other medical specialist. This document is used during the physical examination of a patient's wrist to evaluate its condition, noting any symptoms like pain, swelling, deformity, or limited motion. The information gathered from this checklist helps in diagnosing potential health issues such as fractures, carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, etc.
FAQ
Q: What are the main components of a wrist examination checklist?
A: The main components of a wrist examination checklist include the inspection of the wrist, palpation for any tenderness, checking the range of motion for flexibility, strength testing, and specific tests for injury or conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Q: What does inspection of the wrist in an examination involve?
A: Inspection of the wrist involves looking at the wrist for any visible abnormalities such as deformity, swelling, redness, or any sign of injury. The physician may check it for symmetry, comparing it to the other wrist.
Q: What does palpation in a wrist examination mean?
A: Palpation in a wrist examination means that the doctor will use their hands to feel the wrist. They will check for areas of tenderness, swelling, warmth, or deformity. The physician may look for any sign of fractures, masses, or joint irregularities.
Q: What does range of motion for flexibility mean in a wrist examination?
A: Range of motion for flexibility in a wrist examination is a series of tests where the doctor will ask you to move your wrist in different directions such as bending it forward and backward (flexion and extension), moving it side to side (radial and ulnar deviation), and rotating it (pronation and supination). These are done to check the flexibility of the wrist and to detect if there's any stiffness or discomfort while moving.
Q: What is strength testing in a wrist examination?
A: Strength testing in a wrist examination involves the doctor assessing your ability to hold or grip things without experiencing pain. This can help indicate if there is any weakness in the muscles, which may be a sign of injury or conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Q: What kind of specific tests might be performed in a wrist examination?
A: Specific tests in a wrist examination might include the Phalen's test and the Tinel sign for carpal tunnel syndrome, the Finkelstein test for DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis, and many others. These tests are designed to provoke symptoms of specific issues, helping the doctor diagnose the condition.