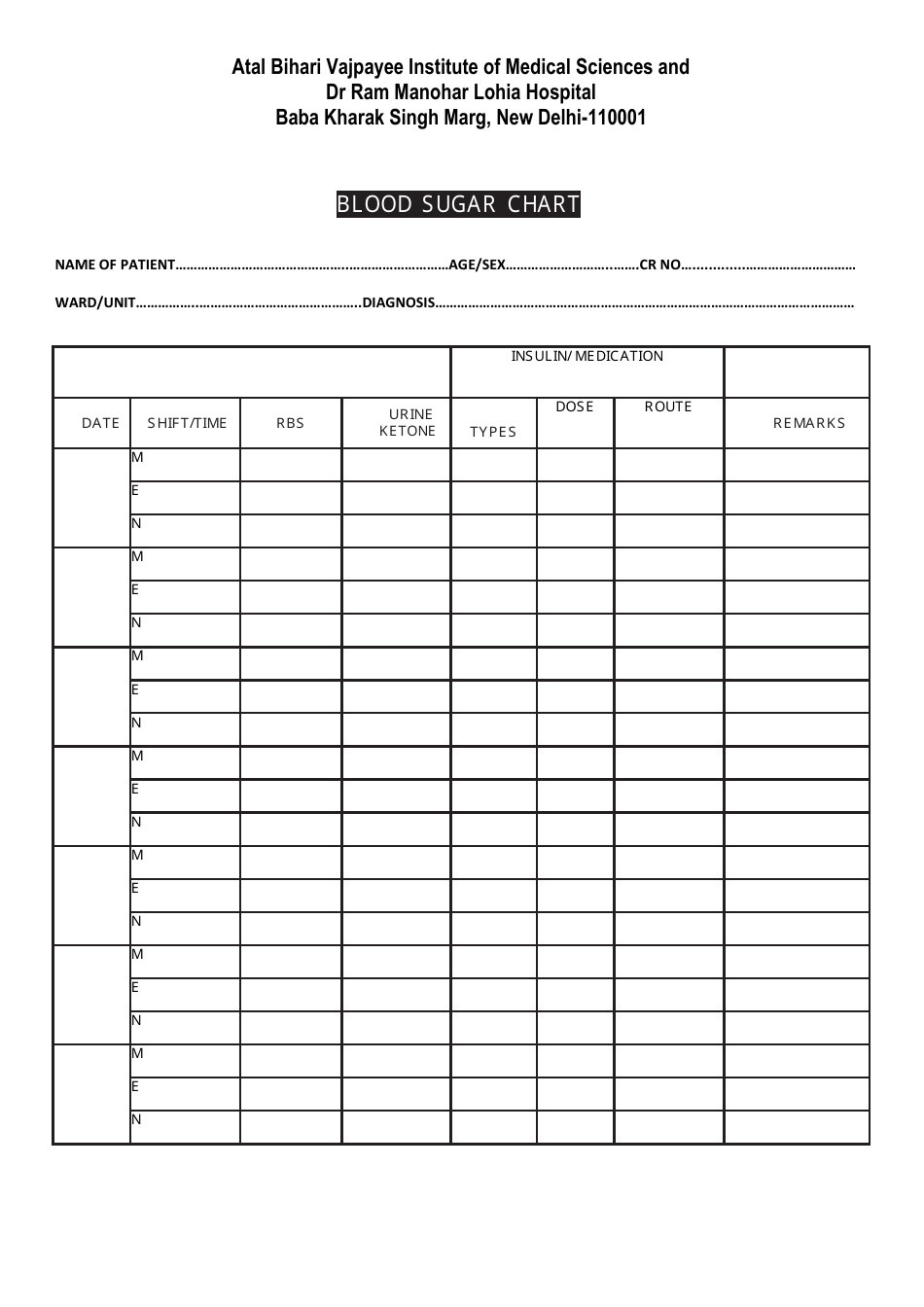
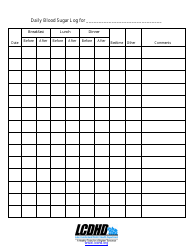
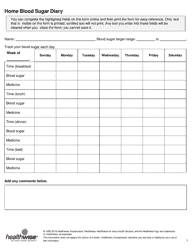
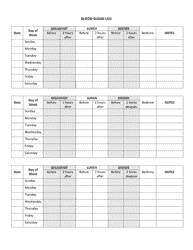
Blood Sugar Chart
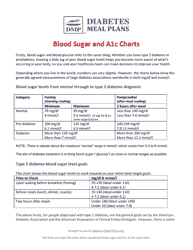
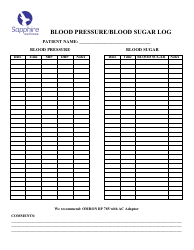
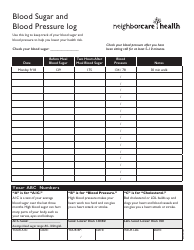
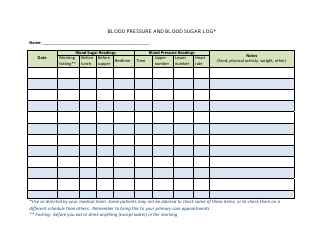
A blood sugar chart is used for tracking and managing the blood glucose levels of individuals with diabetes. It helps in understanding if the glucose levels are within the target range (which can differ depending on factors like age, overall health, etc.). This chart can assist individuals in managing their diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle choices to better control their diabetes. It's an essential tool for communicating effectively with healthcare professionals about the progress of diabetes management.
A Blood Sugar Chart is typically filed and maintained by an individual suffering from diabetes or individuals who need to monitor their blood sugar levels. It is also maintained by healthcare providers such as doctors, nurses, and medical professionals who are responsible for monitoring the health conditions of the patient. Further, in case of children or elderly people suffering from diabetes, their caregivers may maintain the chart.
In a broader context, organizations and institutions like hospitals, nursing homes, and care centers involved in the healthcare and management of people with diabetes or other blood sugar-related conditions also create, update and file these charts.
FAQ
Q: What is a blood sugar chart?
A: A blood sugar chart is a tool used to monitor and track blood glucose levels. It’s often used by individuals with diabetes to manage their condition. The chart typically includes points for tracking before and after meals, at bedtime, and possibly other times during the day, depending on the individual’s treatment plan.
Q: How are blood sugar levels measured?
A: Blood sugar levels are usually measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) in the United States. Other countries, like Canada and Australia, measure levels in millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
Q: What is a normal blood sugar level?
A: In a person without diabetes, a normal blood sugar level is generally between 70 mg/dL and 100 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L) when fasting, and up to 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating.
Q: What is considered high blood sugar?
A: Blood sugar is typically considered high if it is above 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L) when fasting, or above 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) two hours after eating. However, what's considered 'high' can vary depending on individual health situations.
Q: What are the dangers of having high or low blood sugar?
A: Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to damage in various organs, nerves, and blood vessels. But extremely low blood sugar levels can cause confusion, dizziness, unconsciousness, and in severe cases, even death.
Q: What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
A: Symptoms of high blood sugar may include frequent urination, increased thirst, headaches, difficulty concentrating, blurred vision, and fatigue.
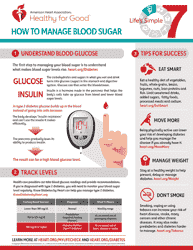
Q: How can blood sugar be managed?
A: Blood sugar levels can be managed through a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, weight management, and, if needed, medication prescribed by a healthcare provider.