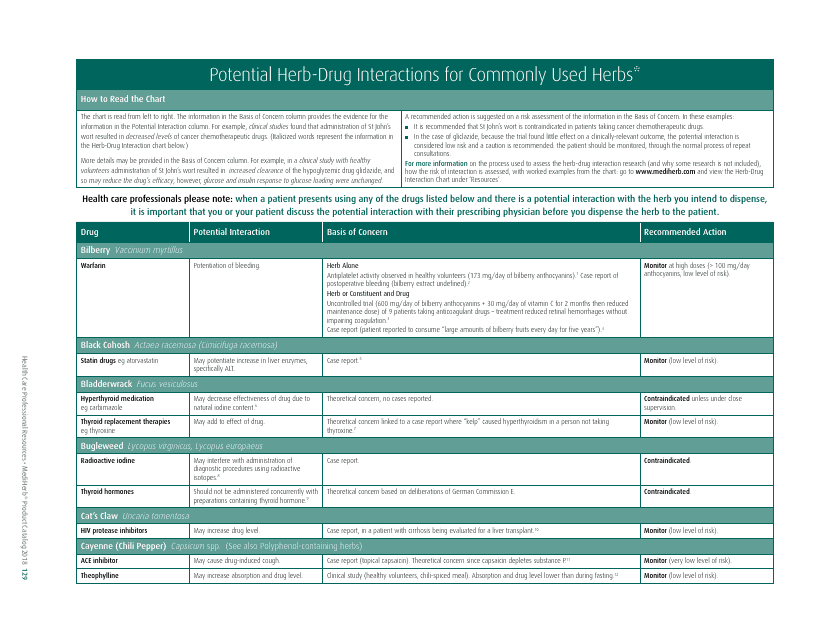
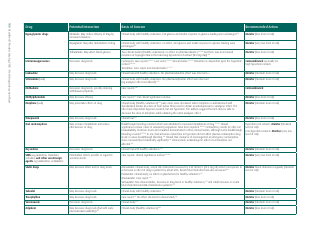
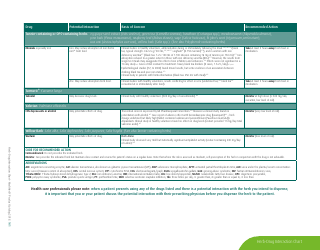
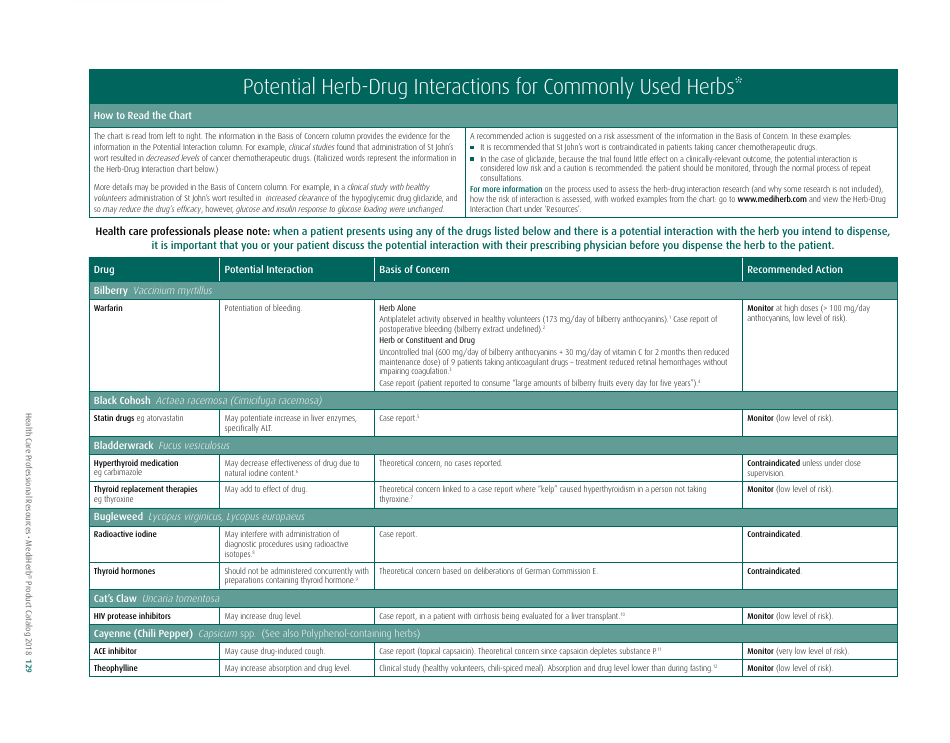
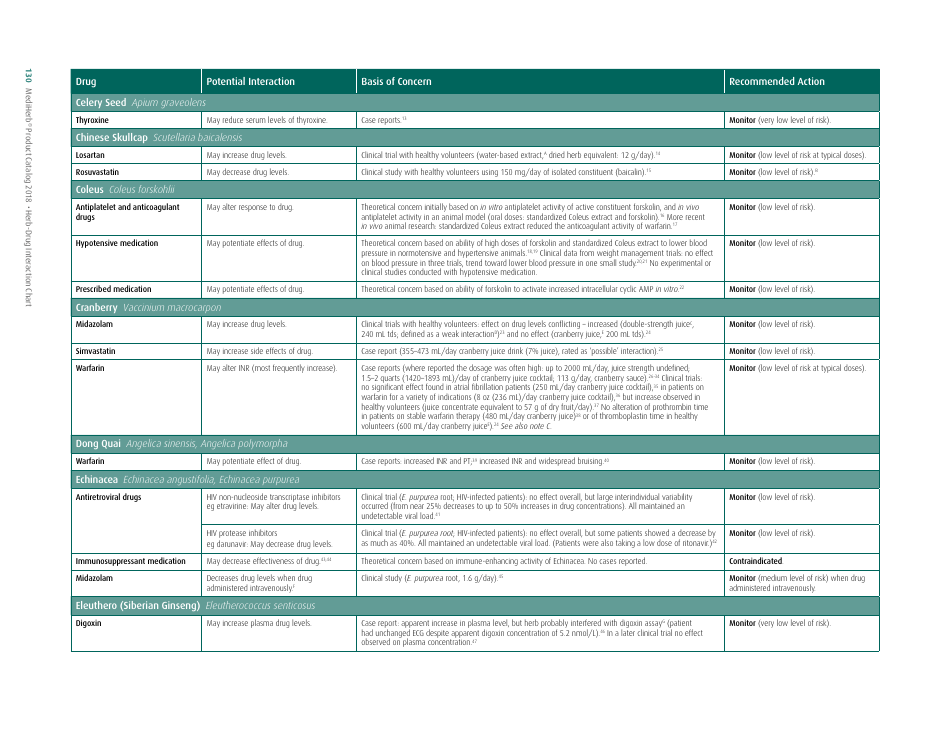
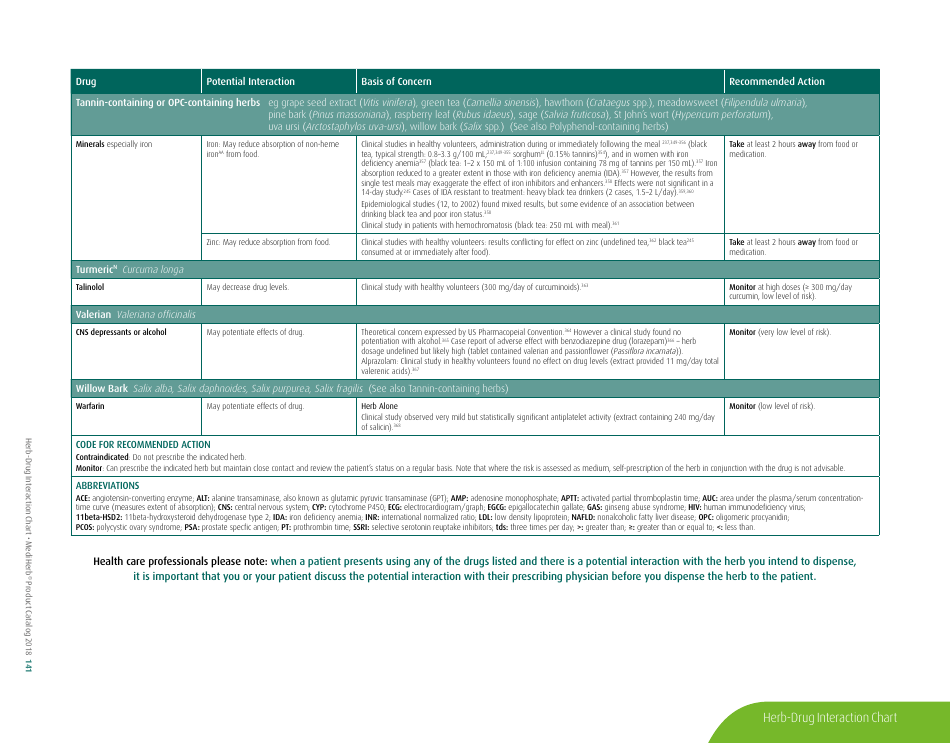
Potential Herb-Drug Interactions for Commonly Used Herbs
The document "Potential Herb-Drug Interactions for Commonly Used Herbs" is essentially used as a guide to educate healthcare providers, patients, or individuals who might be using traditional herbal remedies along with their prescribed medication.
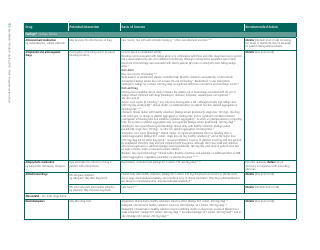
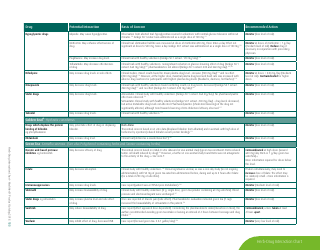
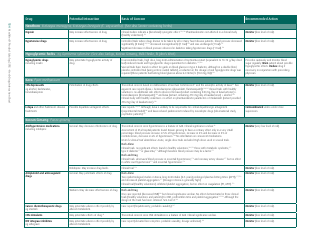
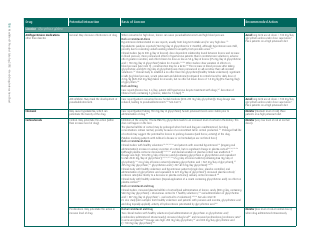
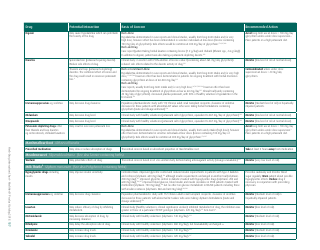
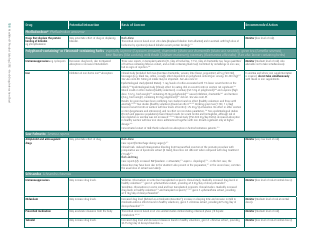
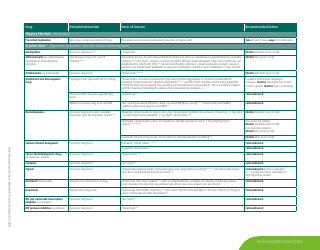
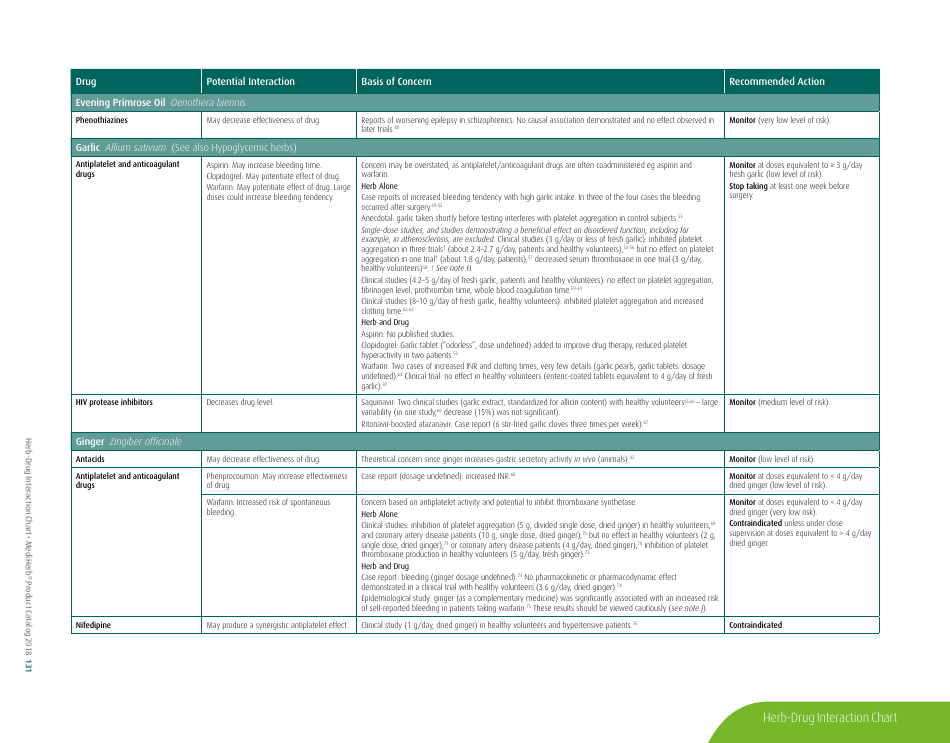
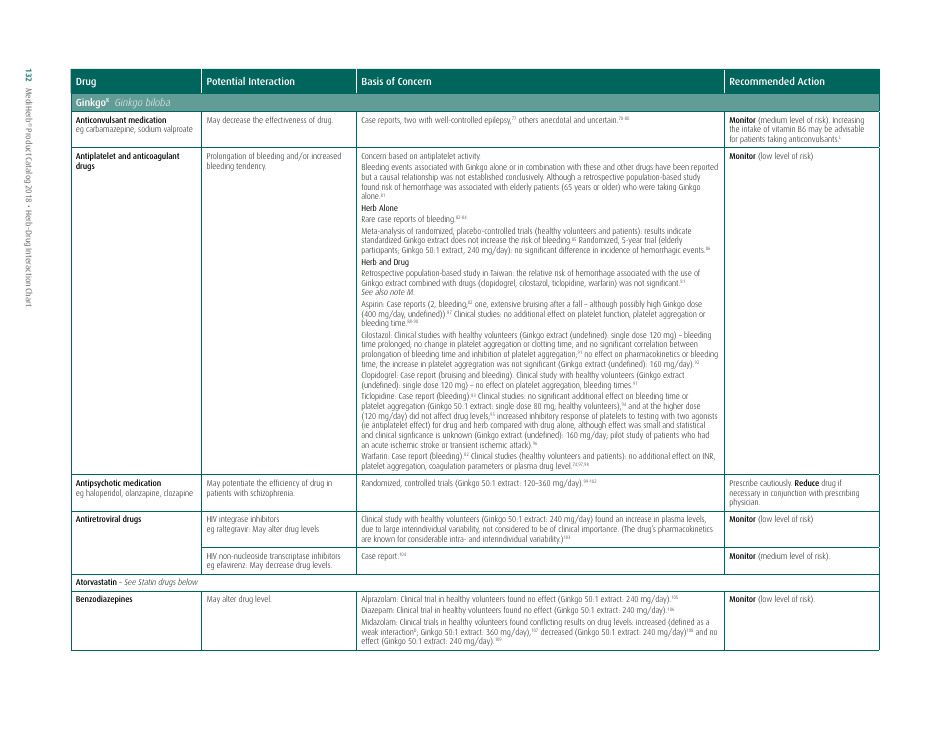
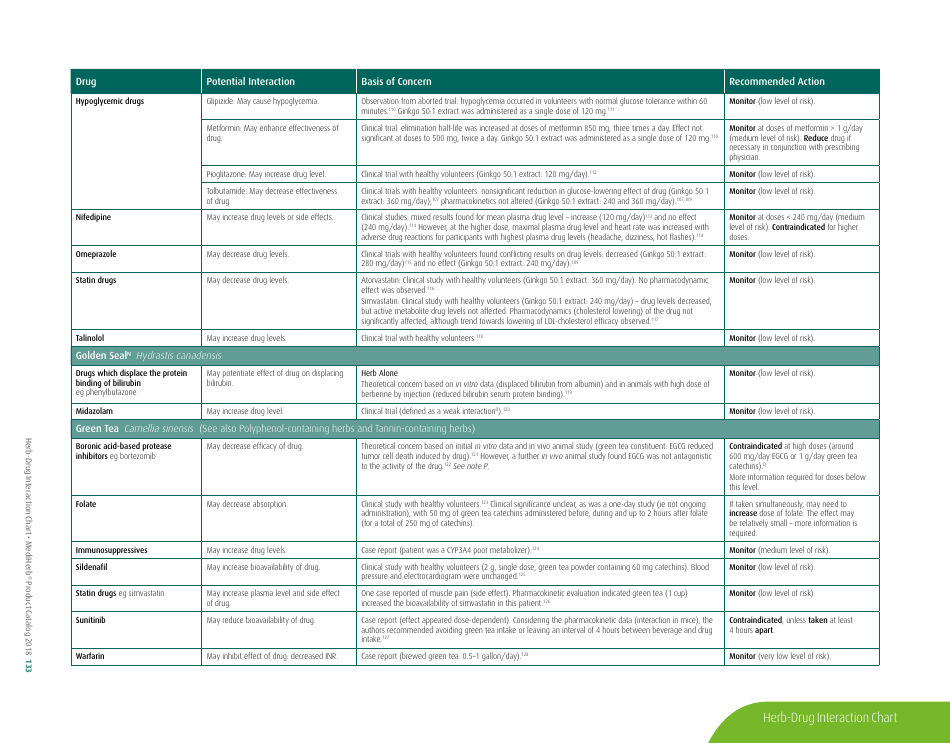
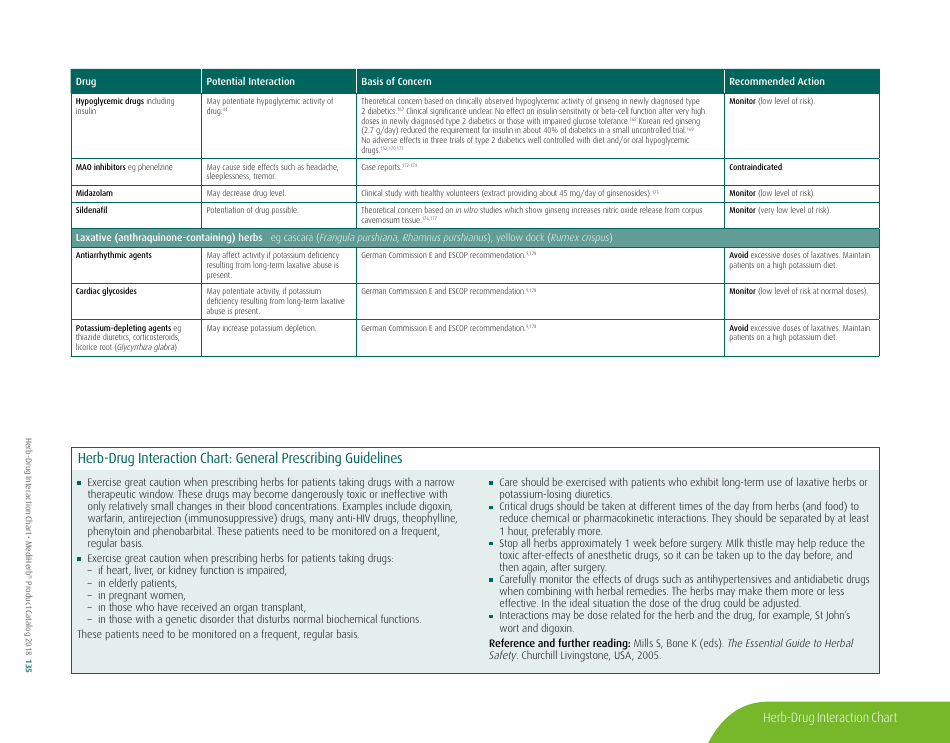
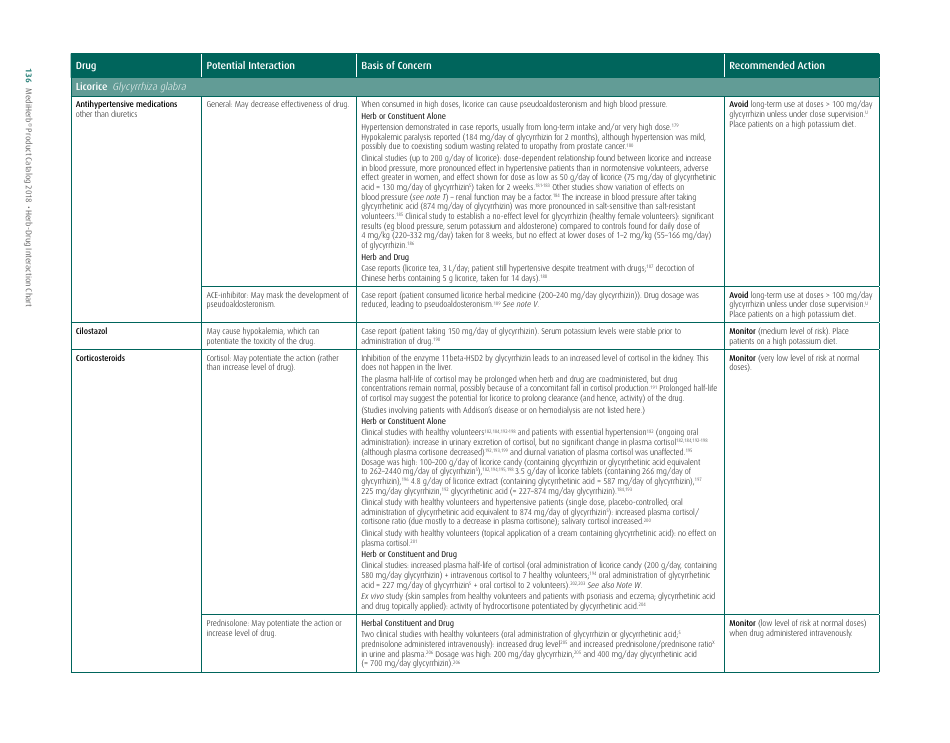
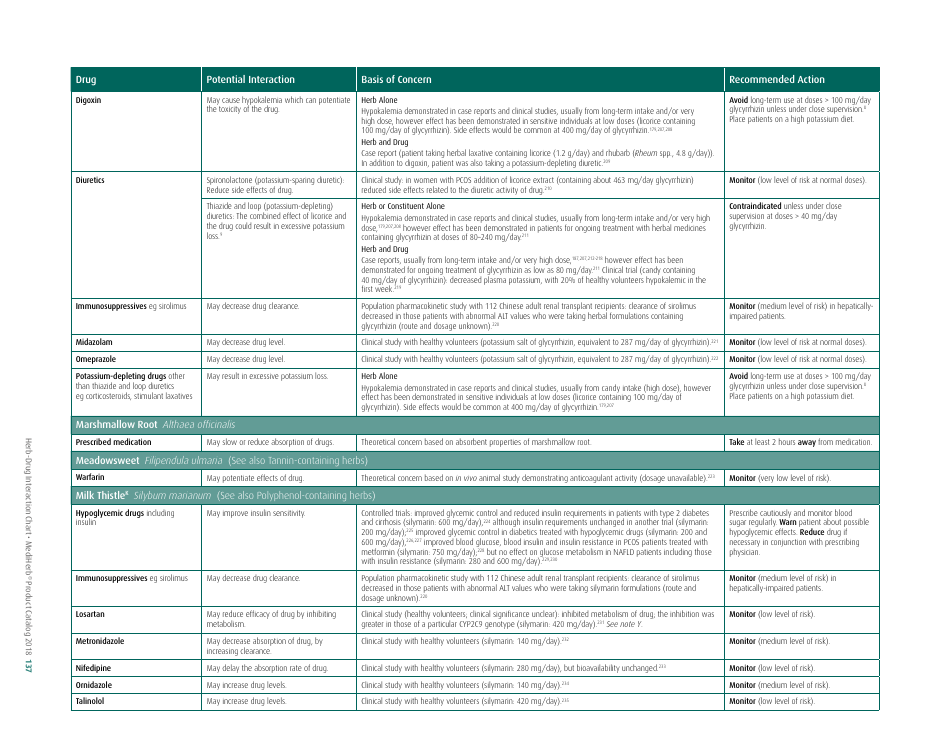
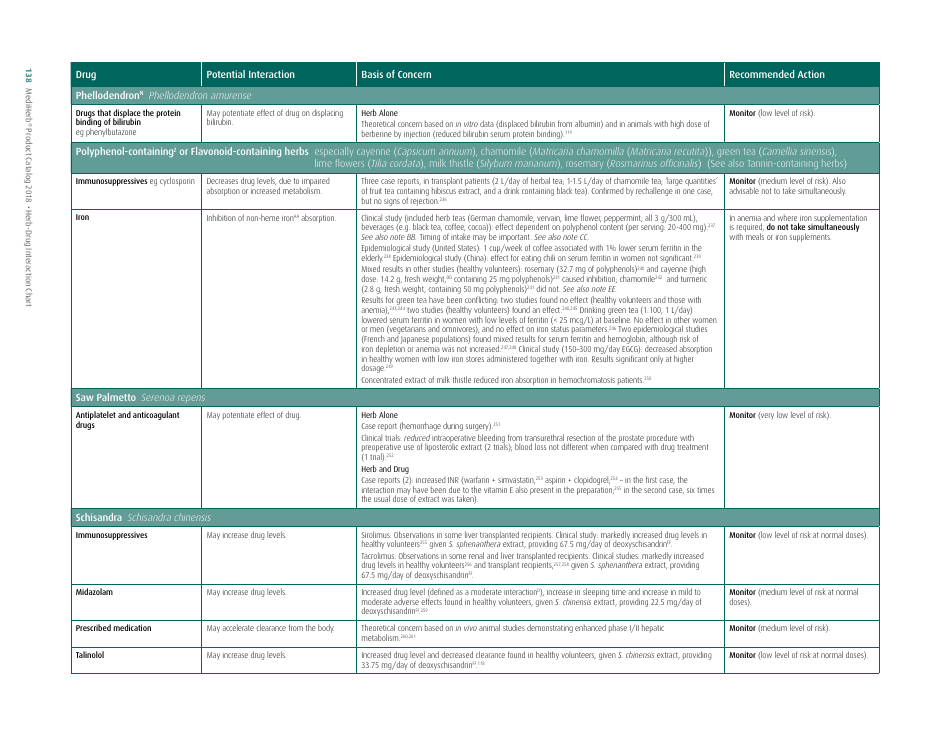
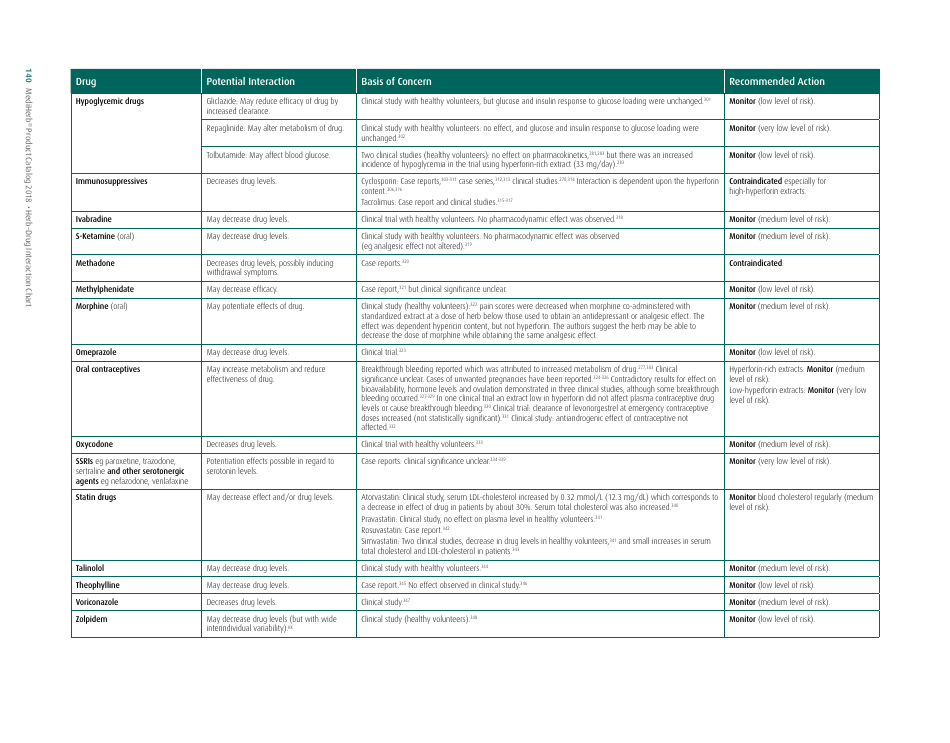
The document generally contains a list of commonly used herbs and their possible interactions with different types of drugs. This resource can assist in identifying possible harmful combinations or interactions that can cause side effects, reduce the effectiveness of medications, or alter the way a drug works in the body.
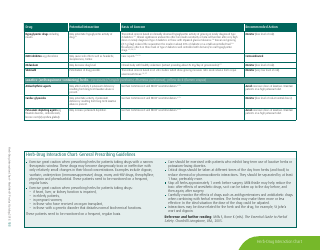
Its purpose is to encourage safe and effective use of herbal remedies and drugs and reduce the potential risks associated with herb-drug interactions. It is essential to provide this information for people who use both herbs and medications, so they can better manage their health and inform their healthcare provider about their herbal use.
The potential Herb-Drug Interactions for commonly used herbs are usually documented by authoritative health bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health under the National Institutes of Health (NIH). In Canada, this responsibility lies with Health Canada, while in India, the Ayurvedic, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homoeopathy (AYUSH) Ministry handles it. On the other hand, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) manages such documentation in Australia. Likewise, educational institutions, hospitals, and research centers may also contribute to maintaining records of herb-drug interactions.
FAQ
Q: What are some common herbs that could interact with drugs?
A: Common herbs that may interact with drugs include Echinacea, ginkgo biloba, garlic, St. John's wort, and ginseng.
Q: What are some potential herb-drug interactions for Echinacea?
A: Echinacea can interact with medications that suppress the immune system, medications that can harm the liver, as well as some antifungal drugs and antiviral medications.
Q: What medications could ginkgo biloba potentially interfere with?
A: Ginkgo biloba can interact with anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs, anticonvulsants, certain antidepressants, and medications for diabetes and high blood pressure.
Q: How can garlic supplements affect medication efficacy?
A: Garlic may interfere with the effectiveness of medications such as HIV drugs, drugs to prevent organ transplant rejection, contraceptive drugs, and certain anticancer drugs.
Q: What could come of combining St. John's wort with other medications?
A: St. John's wort can reduce the effectiveness of many drugs, including antidepressants, birth control pills, cyclosporine, digoxin, indinavir, irinotecan, and anticoagulants.
Q: How can ginseng affect the way other drugs work?
A: Ginseng can interfere with medications like antidiabetic drugs, anticoagulants, immune suppressants, and drugs used to treat high blood pressure and heart disease.