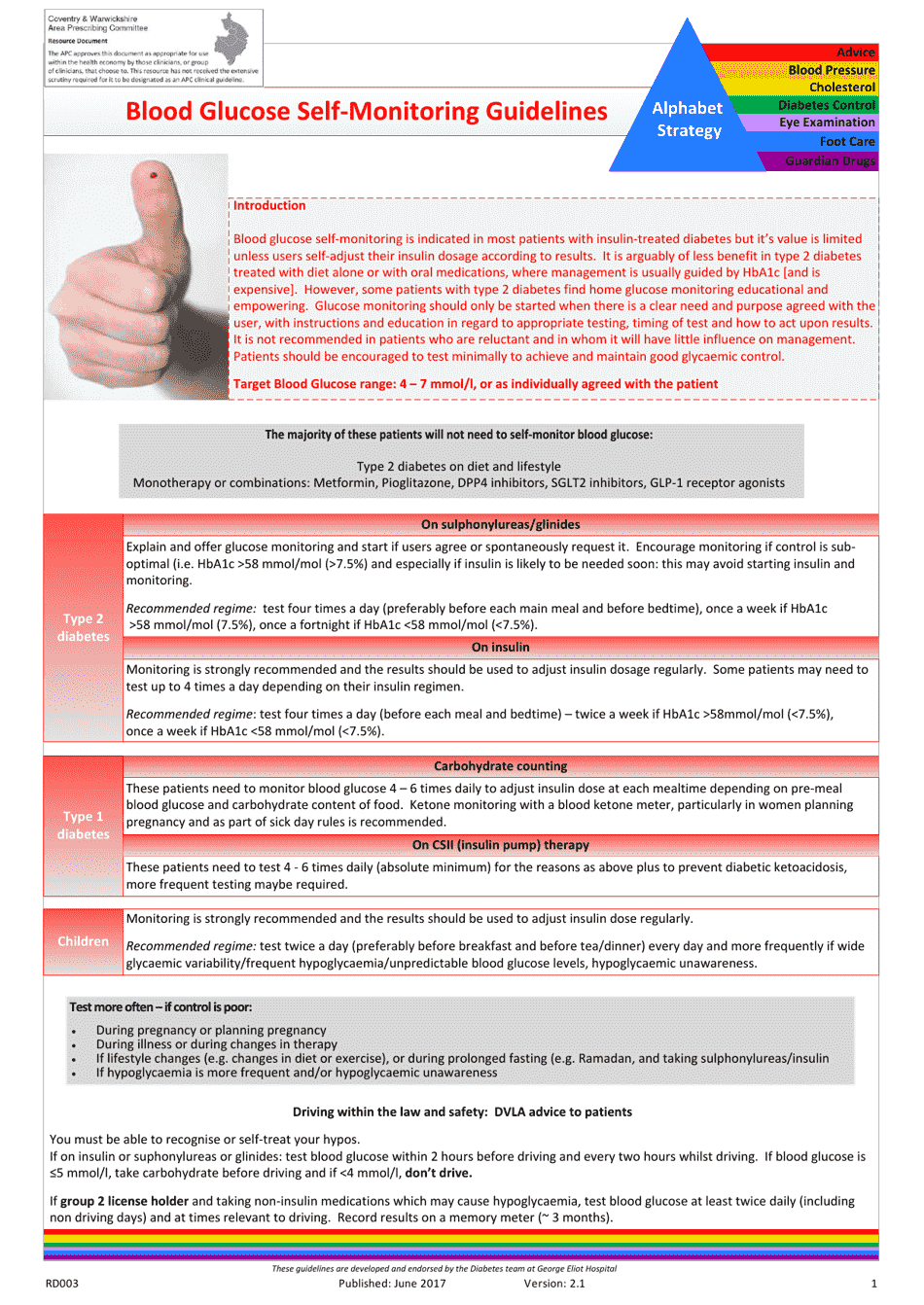
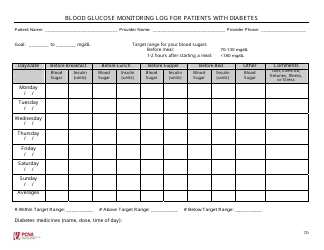
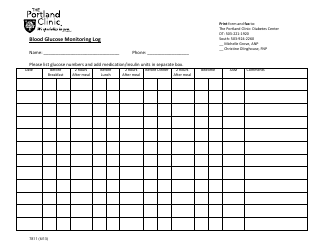
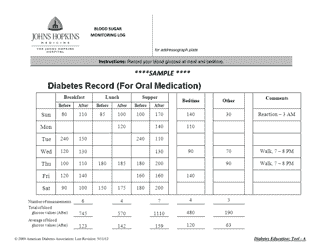
Blood Glucose Self-monitoring Guidelines
Blood Glucose Self-monitoring Guidelines are used to provide instructions and recommendations on how to measure and track your blood glucose levels at home. This helps people with diabetes to manage their condition, understand the effects of food, exercise, and medications on their blood sugar, and make informed decisions about their health.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) files the Blood Glucose Self-monitoring Guidelines in the United States.
FAQ
Q: Why is blood glucose self-monitoring important?
A: Blood glucose self-monitoring helps individuals with diabetes to track their blood sugar levels.
Q: Who should perform blood glucose self-monitoring?
A: People with diabetes should perform blood glucose self-monitoring.
Q: How often should blood glucose self-monitoring be done?
A: The frequency of blood glucose self-monitoring varies depending on a person's diabetes management plan. It is best to consult with a healthcare provider for specific guidelines.
Q: What are the different ways to perform blood glucose self-monitoring?
A: There are several methods to test blood glucose levels, including using a blood glucose meter, continuous glucose monitoring system, or glucose testing strips.
Q: Are there any specific guidelines for blood glucose self-monitoring?
A: Yes, it is important to follow the instructions provided by the blood glucose monitoring device manufacturer and consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidelines.
Q: What can affect blood glucose levels?
A: Factors such as food, physical activity, stress, medications, and illness can all impact blood glucose levels.
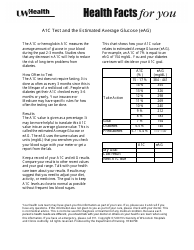
Q: What is the target blood glucose range?
A: The target blood glucose range can vary depending on individual circumstances. It is typically recommended to maintain blood glucose levels between 80 and 130 mg/dL before meals and below 180 mg/dL two hours after eating.
Q: What should I do if my blood glucose levels are consistently outside the target range?
A: If blood glucose levels are consistently too high or too low, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to adjust the diabetes management plan.
Q: Can blood glucose self-monitoring help prevent complications of diabetes?
A: Regular blood glucose self-monitoring, along with proper diabetes management, can help reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Q: What other lifestyle factors are important for blood glucose control?
A: Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting enough sleep are all important for blood glucose control in addition to self-monitoring.