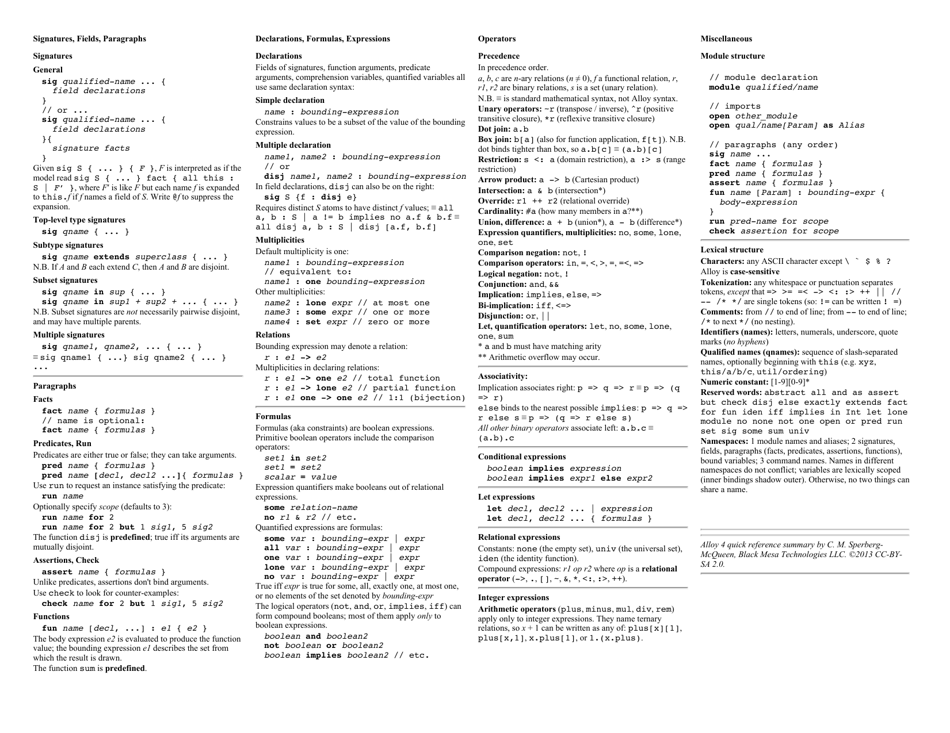
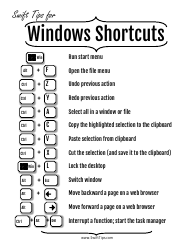
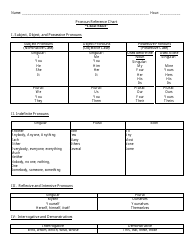
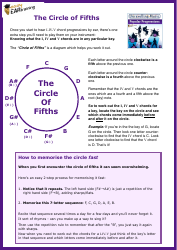
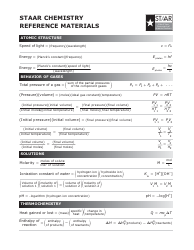
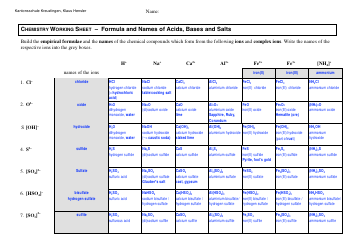
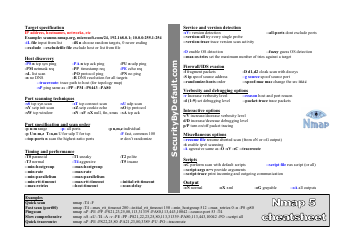
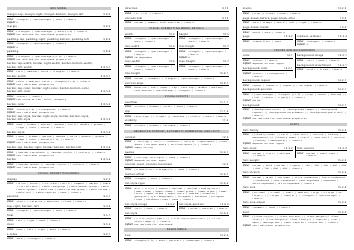
Alloy Cheat Sheet
The Alloy Cheat Sheet is a reference guide that provides quick and concise information about the Alloy specification language. It helps users understand and utilize the various features and constructs of Alloy, which is a modeling language used in software engineering and formal methods.
FAQ
Q: What is an alloy?
A: An alloy is a mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.
Q: What are some examples of alloys?
A: Some examples of alloys include steel, bronze, and brass.
Q: What is the purpose of creating alloys?
A: Creating alloys can enhance the properties of metals, such as strength or resistance to corrosion.
Q: How are alloys made?
A: Alloys are made by melting the base metals together and then cooling and solidifying the mixture.
Q: Are alloys stronger than pure metals?
A: In many cases, alloys are stronger than pure metals due to their improved properties.
Q: Can alloys be customized for specific uses?
A: Yes, alloys can be customized by adjusting the proportions of the different metals or adding additional elements.
Q: What are some applications of alloys?
A: Alloys are used in a wide range of applications, including construction, transportation, and electronics.
Q: Do alloys have specific names?
A: Yes, alloys often have specific names based on their composition, such as stainless steel or bronze.