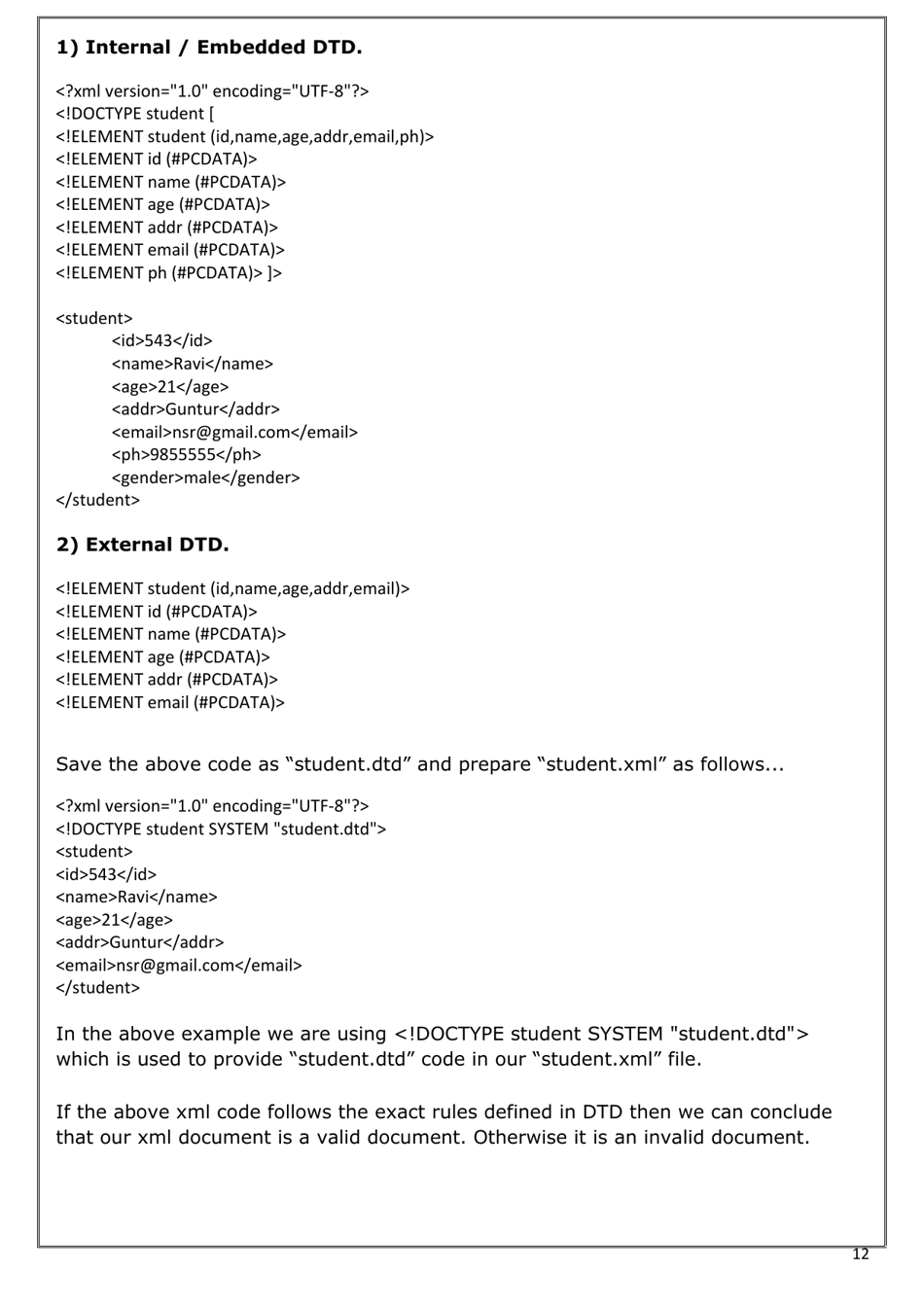
Xml Basics Cheat Sheet
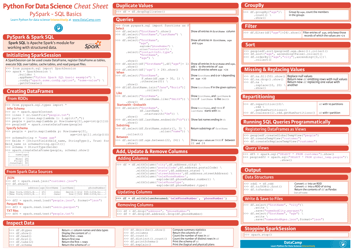
The XML Basics Cheat Sheet is a quick reference guide that provides an overview of the basic elements and syntax used in XML (eXtensible Markup Language). It is designed to help individuals understand and use XML to structure and store data in a standardized way. The cheat sheet usually includes information on how to define tags, attributes, and nested elements, as well as the rules for well-formed XML documents.
FAQ
Q: What is XML?
A: XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language. It is a markup language that is used to encode documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable.
Q: What is a markup language?
A: A markup language is a system for annotating a document in a way that is distinguishable from the text itself. Markup is typically indicated by specific tags or codes.
Q: How is XML structured?
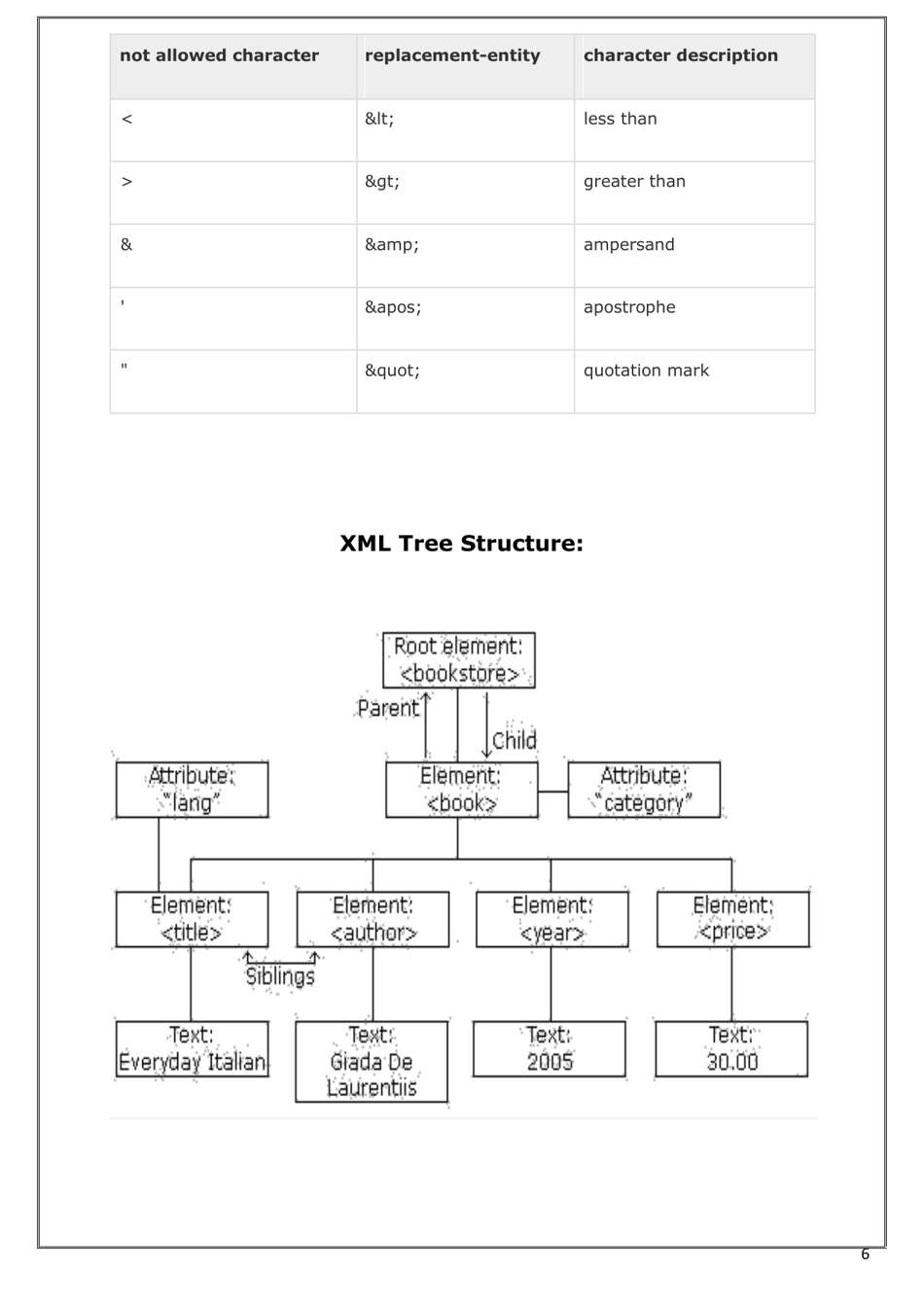
A: XML documents are structured as a hierarchy of elements. Each element has a start tag, content, and an end tag. Elements can contain other elements, forming a tree-like structure.
Q: What are XML attributes?
A: XML attributes provide additional information about an element. They are part of the start tag and consist of a name-value pair.
Q: Can XML be used for data exchange?
A: Yes, XML is widely used for data exchange between different systems and platforms. Its flexibility and extensibility make it suitable for various data formats.
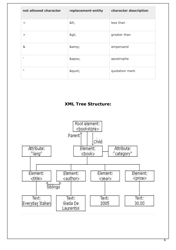
Q: What is a well-formed XML document?
A: A well-formed XML document follows the basic syntax rules of XML, such as having a root element, properly nested tags, and correctly encoded entities.
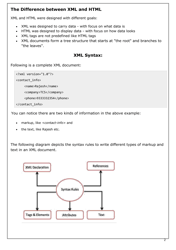
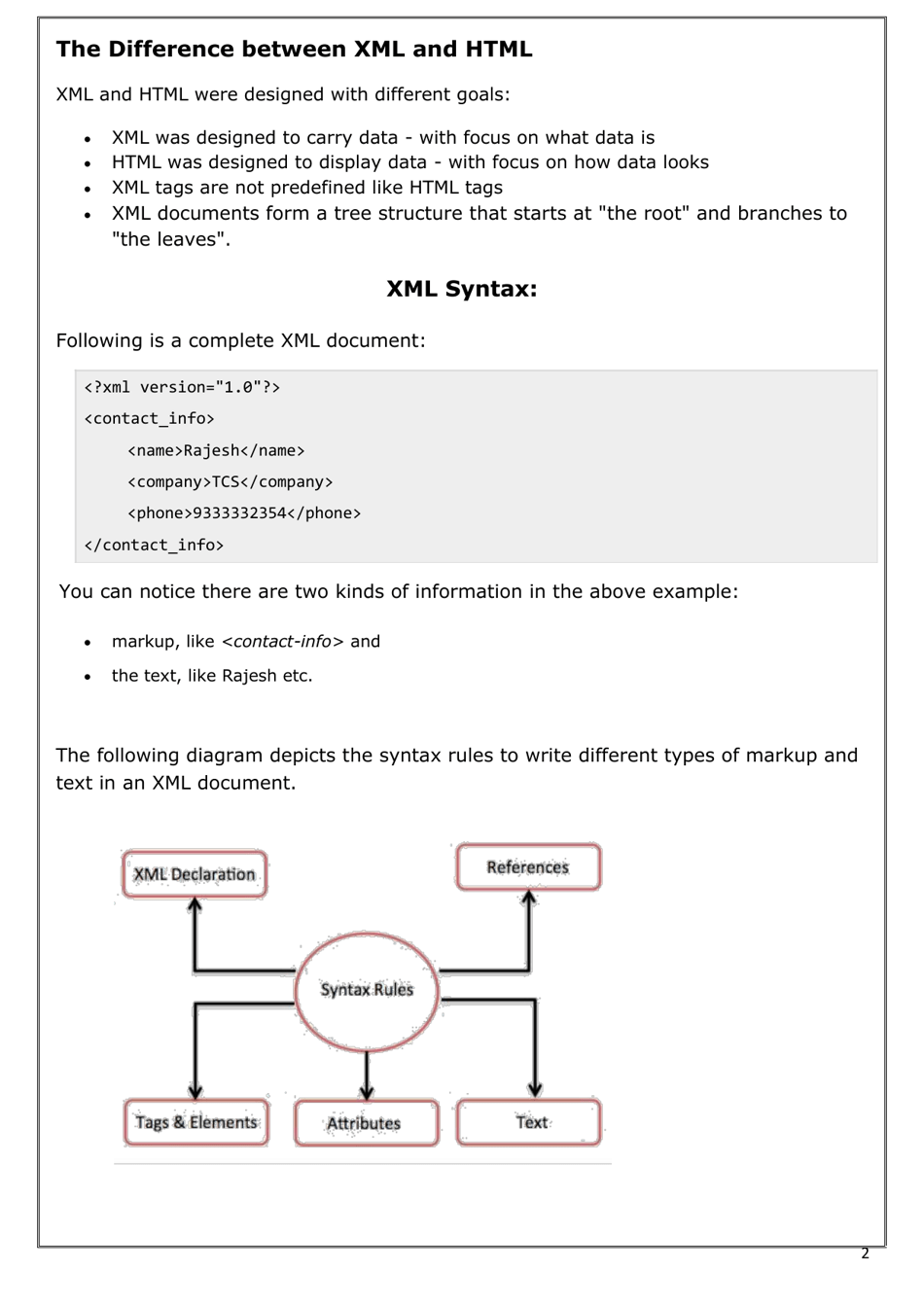
Q: What is the difference between XML and HTML?
A: XML is a general-purpose markup language used for storing and transporting data, while HTML is a markup language specifically designed for creating web pages.