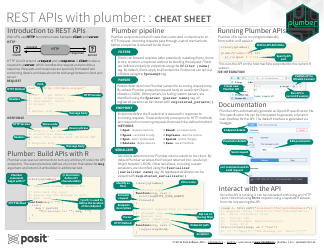
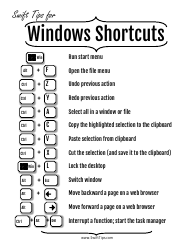
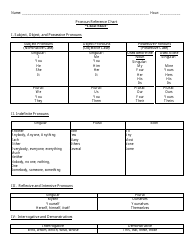
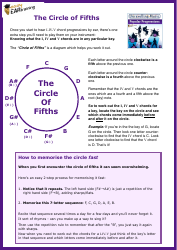
Webgl 1.0 Api Cheat Sheet
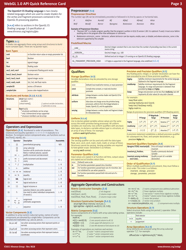
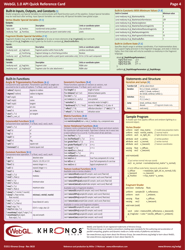
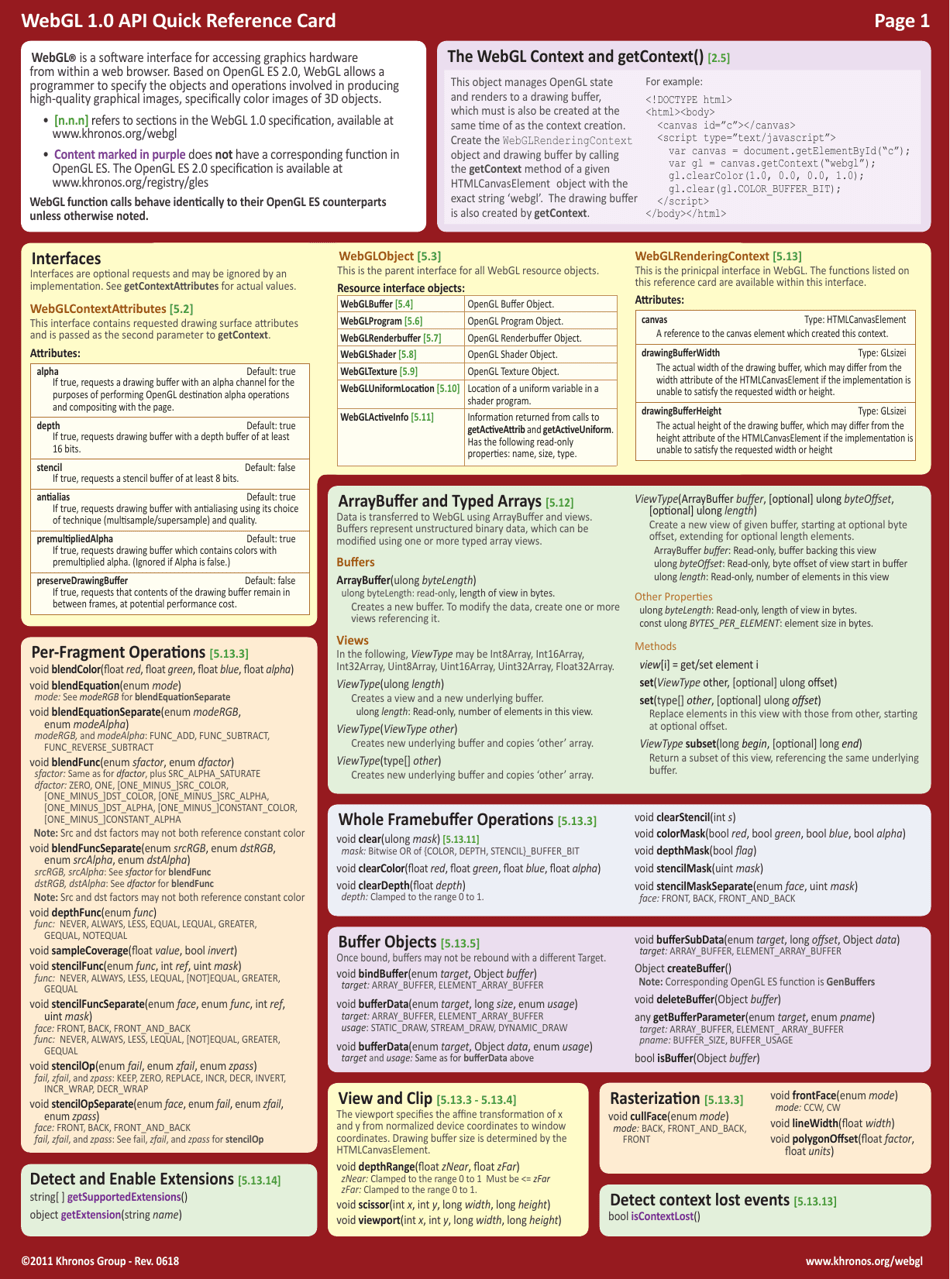
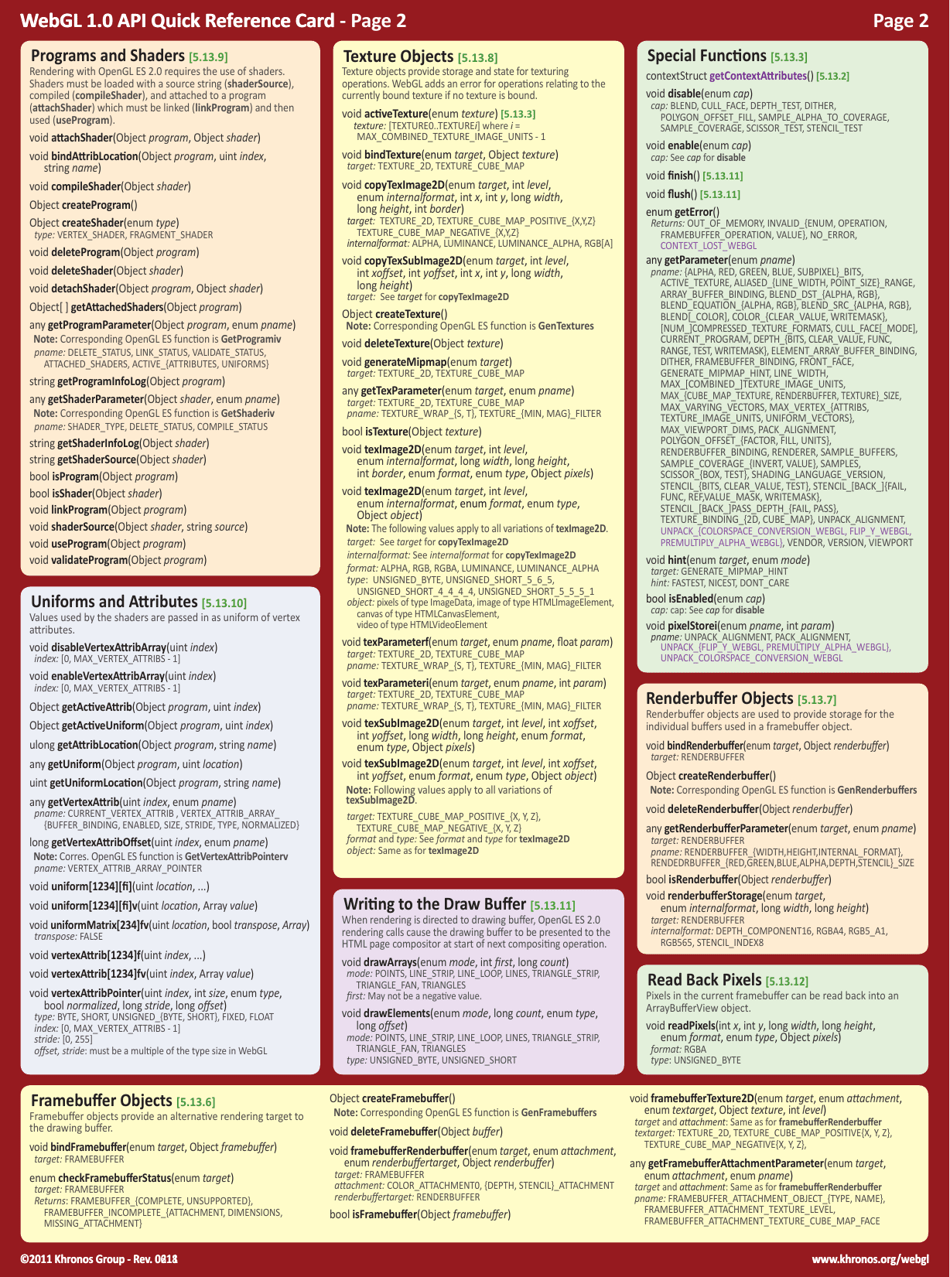
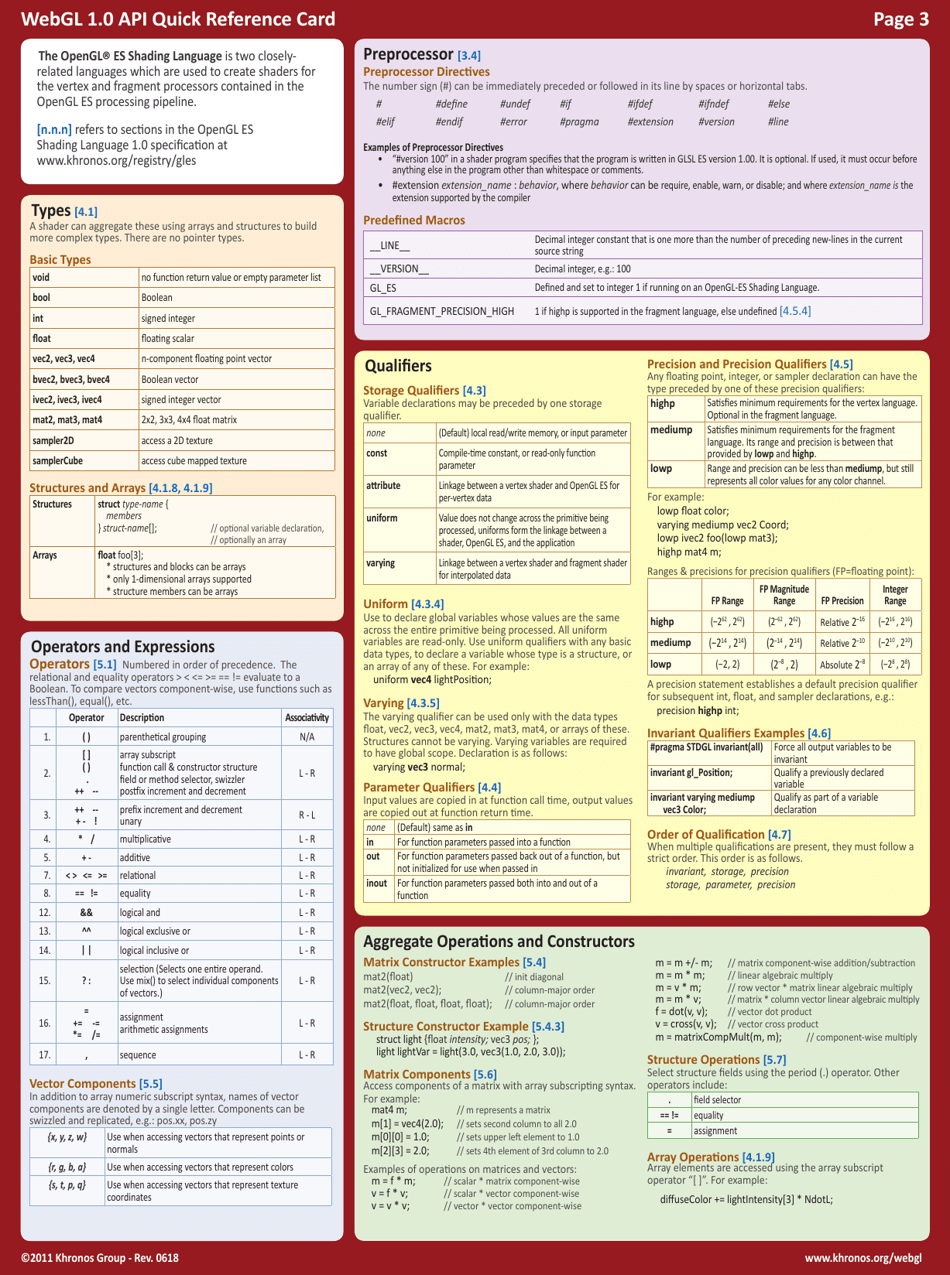
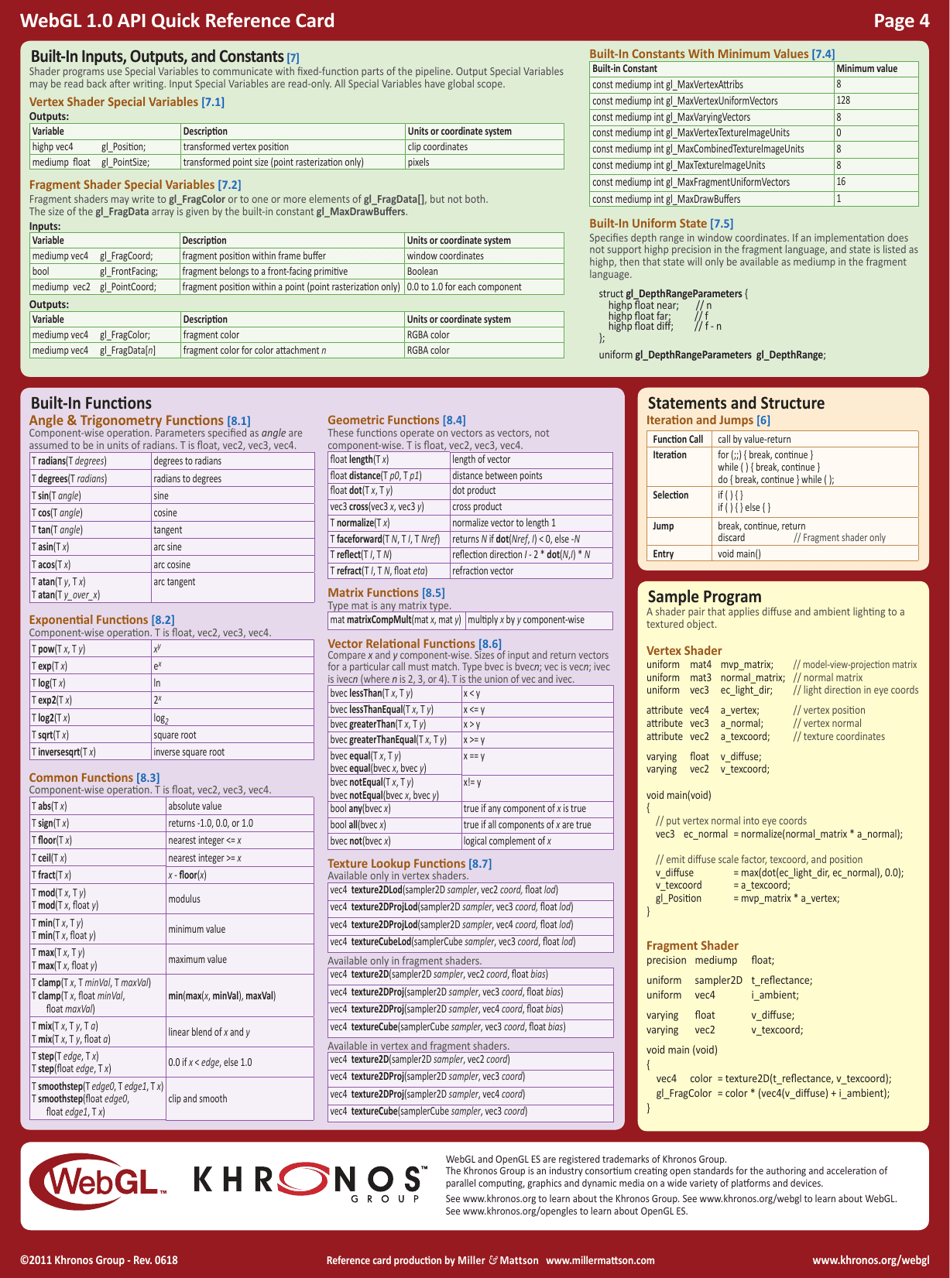
The WebGL 1.0 API Cheat Sheet is a quick reference guide used for creating and rendering interactive 3D graphics on the web. It provides a summary of the functions, attributes, and properties available in WebGL 1.0, making it easier for developers to work with and understand the API.
FAQ
Q: What is WebGL 1.0 API?
A: WebGL 1.0 API is a JavaScript API that allows rendering of interactive 2D and 3D graphics within a web browser.
Q: What can I do with WebGL 1.0 API?
A: With WebGL 1.0 API, you can create and manipulate 3D models, apply textures, shaders, and other effects, and render them in real-time on a web page.
Q: Which web browsers support WebGL 1.0 API?
A: Most modern web browsers, including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari, support WebGL 1.0 API. However, Internet Explorer does not support WebGL.
Q: Do I need any special plugins or extensions to use WebGL 1.0 API?
A: No, WebGL 1.0 API is natively supported by compatible web browsers and does not require any additional plugins or extensions.
Q: Is WebGL 1.0 API only for desktop computers?
A: No, WebGL 1.0 API can be used on a variety of devices, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and even smartphones, as long as the web browser supports it.
Q: Can I use WebGL 1.0 API for commercial projects?
A: Yes, WebGL 1.0 API can be used for commercial projects, as long as you adhere to the licensing requirements of any third-party libraries or frameworks you may use.
Q: Is WebGL 1.0 API secure?
A: WebGL 1.0 API is designed with security in mind, but like any web technology, it is important to follow best practices to ensure the security of your application.
Q: Can I use WebGL 1.0 API to create games?
A: Yes, WebGL 1.0 API is commonly used for creating browser-based games, as it provides the necessary tools and performance for real-time 3D graphics.
Q: Are there any alternatives to WebGL 1.0 API?
A: Yes, there are alternatives to WebGL 1.0 API, such as WebGL 2.0 API, which provides additional features and improvements, and other graphics libraries like Three.js or Babylon.js.