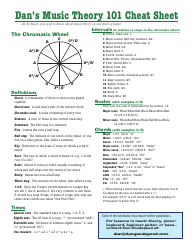
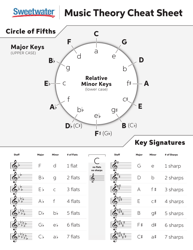
Probability Cheat Sheet - Theory
The Probability Cheat Sheet - Theory is a document that provides a concise summary of the key concepts and formulas related to probability theory. It is a helpful reference guide for understanding and applying the principles of probability in various mathematical and statistical problems.
FAQ
Q: What is probability?
A: Probability is a measure of the likelihood that an event will occur.
Q: How is probability expressed?
A: Probability is usually expressed as a number between 0 and 1, where 0 represents impossibility and 1 represents certainty.
Q: What is the difference between experimental probability and theoretical probability?
A: Experimental probability is based on data from actual trials or experiments, while theoretical probability is based on mathematical calculations.
Q: What is the law of large numbers?
A: The law of large numbers states that as the number of trials or experiments increases, the experimental probability approaches the theoretical probability.
Q: What is the addition rule of probability?
A: The addition rule of probability states that the probability of the union of two events is the sum of their individual probabilities, minus the probability of their intersection.
Q: What is the multiplication rule of probability?
A: The multiplication rule of probability states that the probability of the intersection of two independent events is the product of their individual probabilities.
Q: What are independent events?
A: Independent events are events that do not affect each other's outcomes.
Q: What is conditional probability?
A: Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
Q: What is Bayes' theorem?
A: Bayes' theorem is a mathematical formula that calculates the probability of an event based on prior knowledge or information.