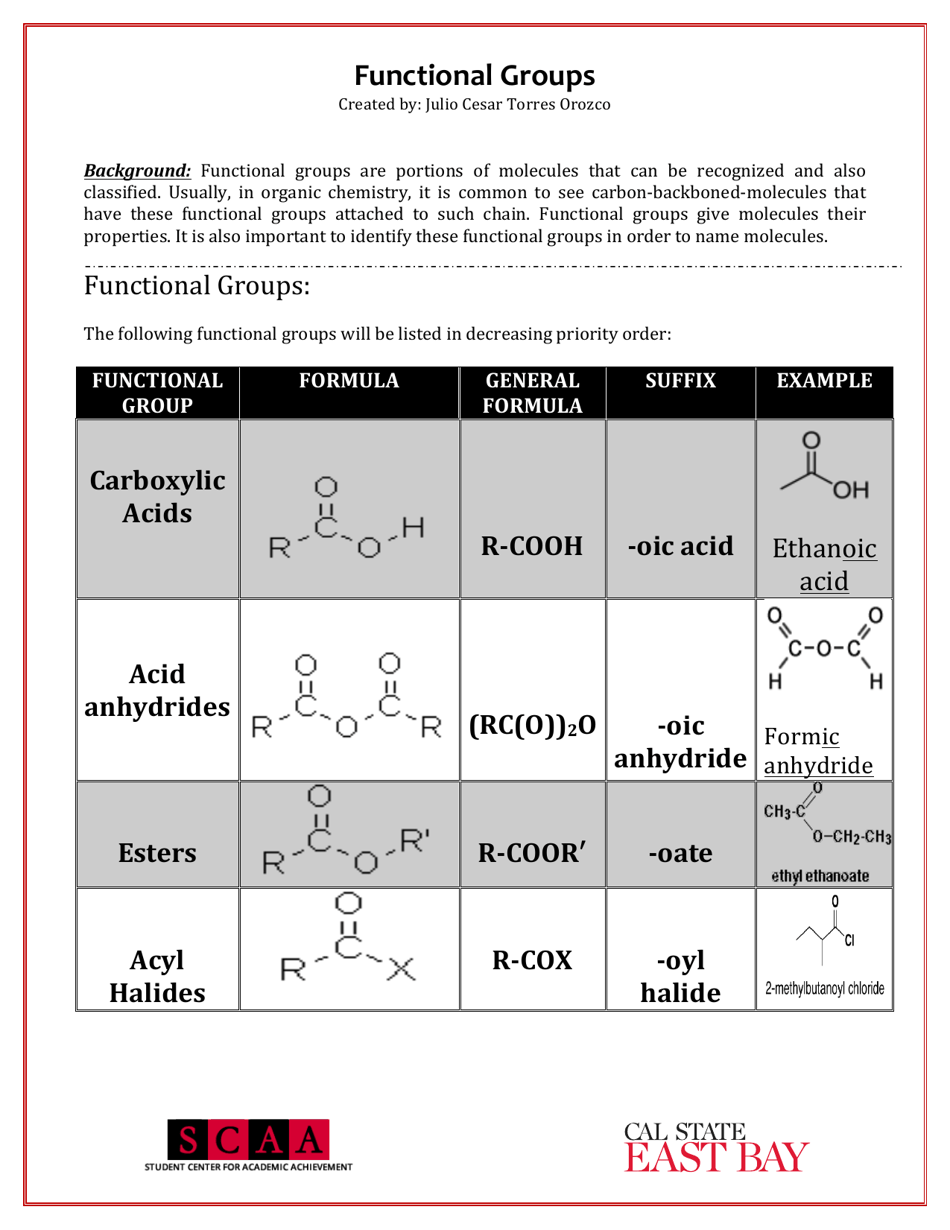
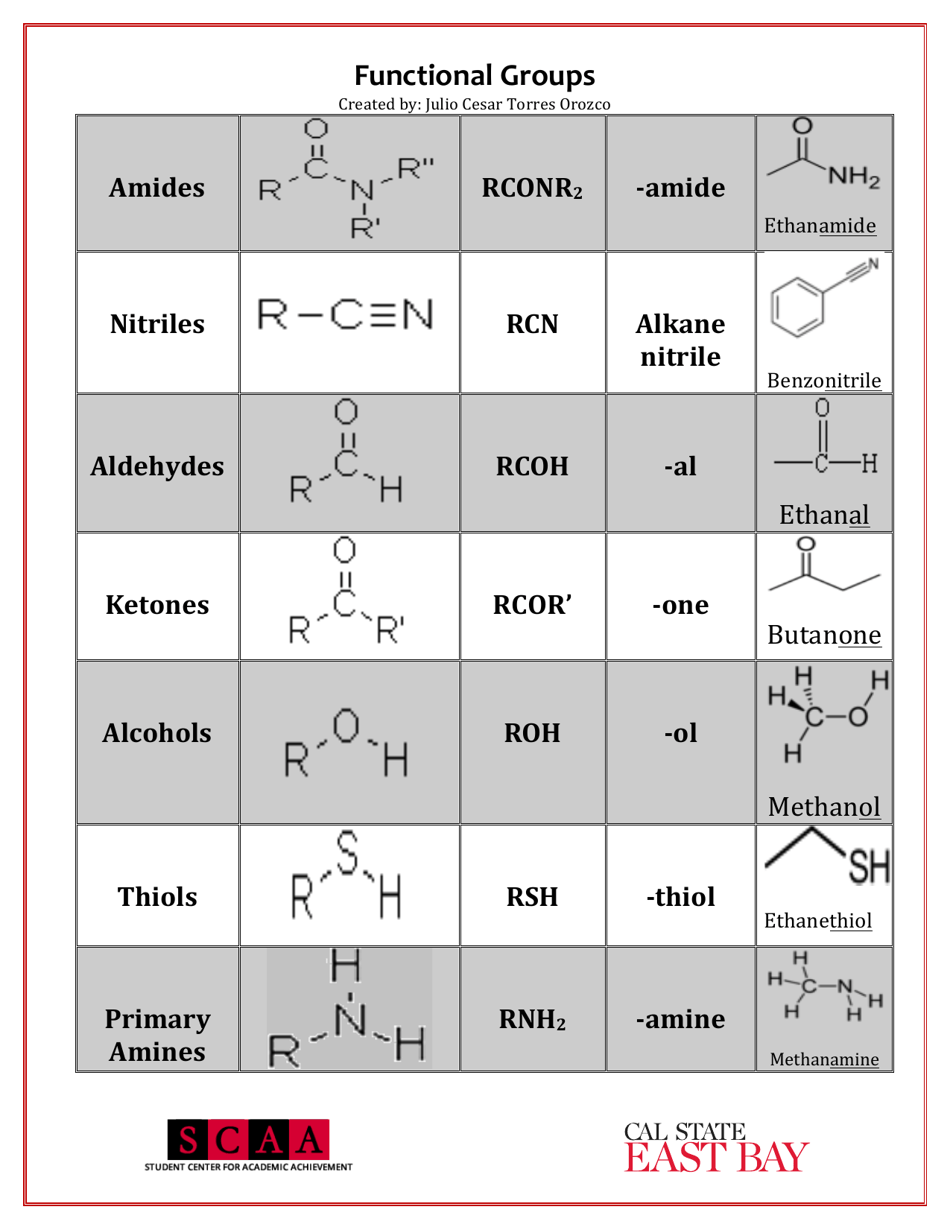
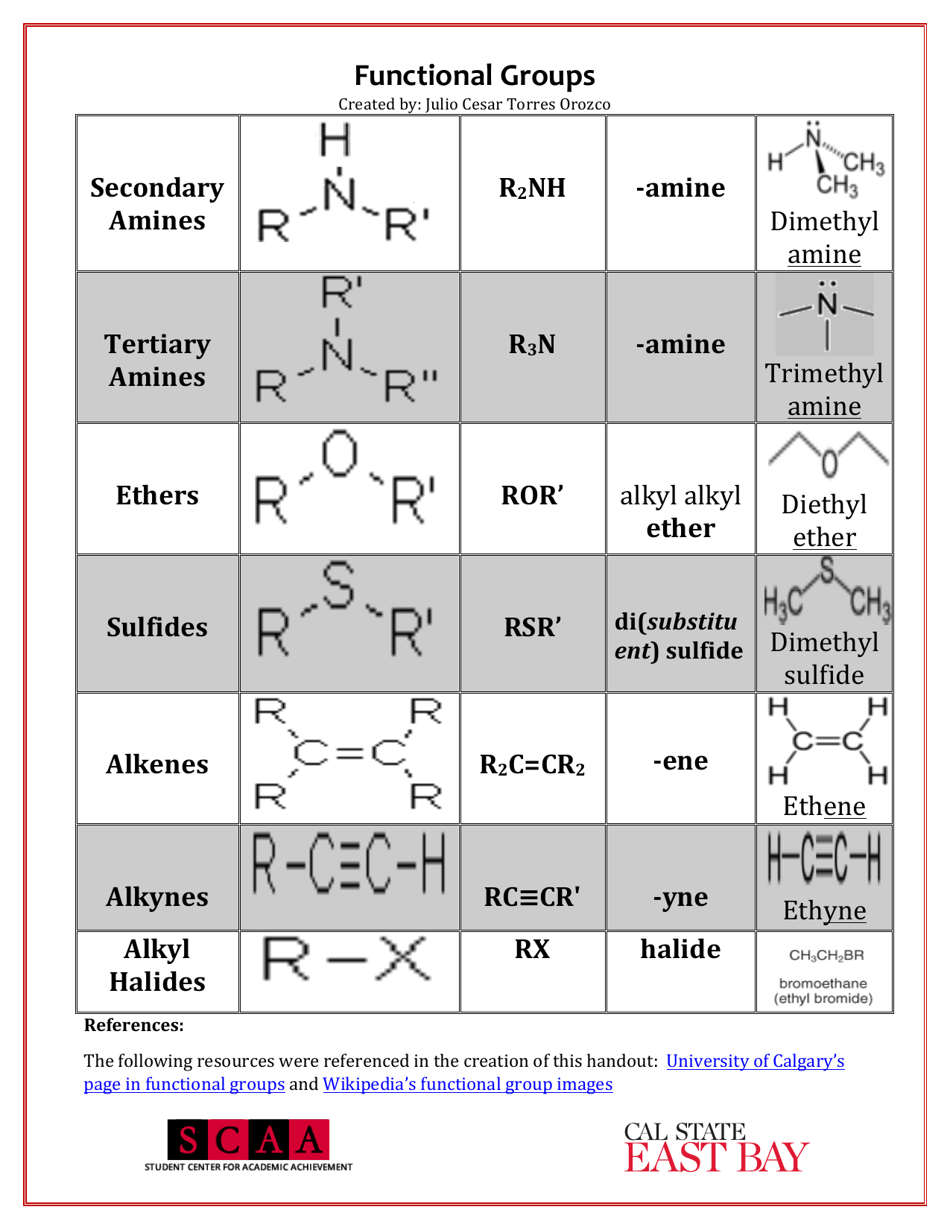
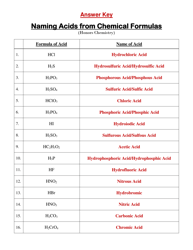
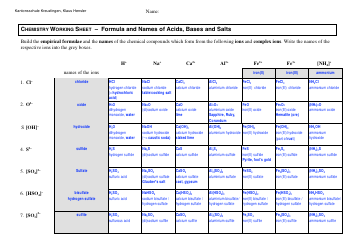
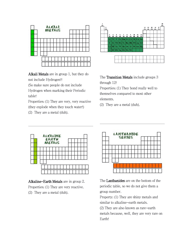
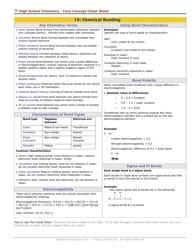
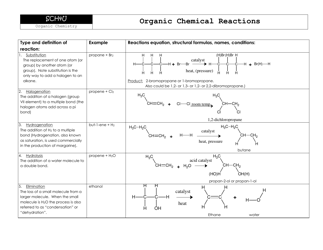
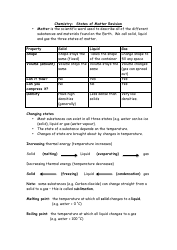
Chemistry Cheat Sheet - Functional Groups
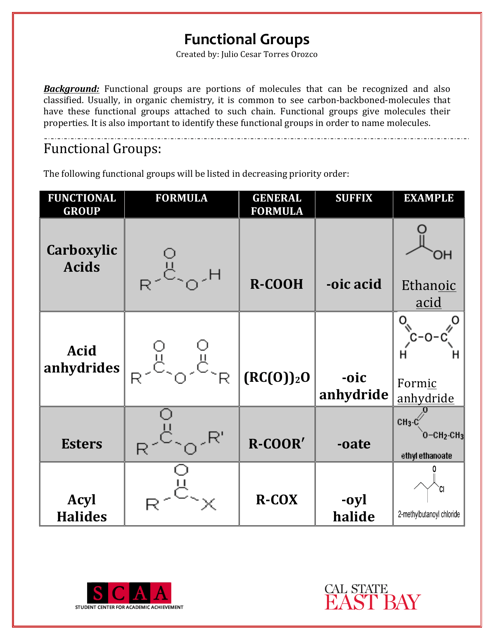
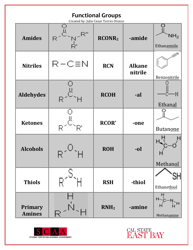
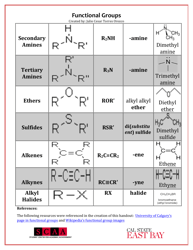
A Chemistry Cheat Sheet - Functional Groups is a quick reference guide that provides information about the various functional groups in organic chemistry. It helps students and professionals in quickly identifying and understanding the different functional groups and their characteristics.
FAQ
Q: What are functional groups in chemistry?
A: Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that determine the properties and reactivity of organic compounds.
Q: What are some examples of functional groups?
A: Some examples of functional groups include hydroxyl (-OH), carbonyl (C=O), amino (-NH2), and carboxyl (-COOH).
Q: What is the function of hydroxyl group?
A: Hydroxyl groups are polar and can form hydrogen bonds, making compounds more soluble in water.
Q: What is the function of carbonyl group?
A: Carbonyl groups provide compounds with structural integrity and play a role in the reactivity of the compound.
Q: What is the function of amino group?
A: Amino groups act as bases and can accept protons, making compounds basic.
Q: What is the function of carboxyl group?
A: Carboxyl groups are acidic and can donate protons, making compounds acidic.
Q: How do functional groups affect the properties of organic compounds?
A: Functional groups determine the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds, such as solubility, acidity/basicity, and reactivity.
Q: Why are functional groups important?
A: Functional groups allow chemists to predict the behavior and properties of organic compounds, aiding in the study and synthesis of new molecules.