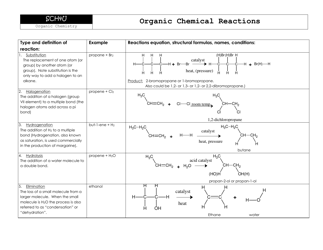
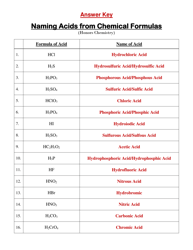
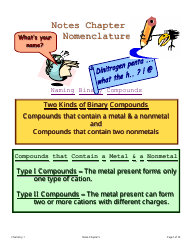
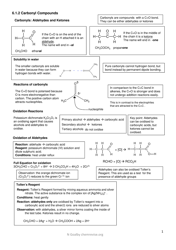
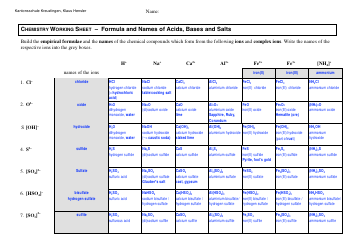
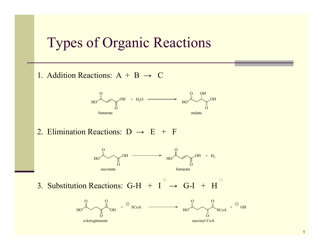
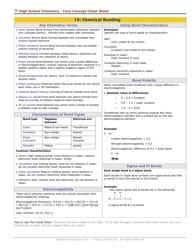
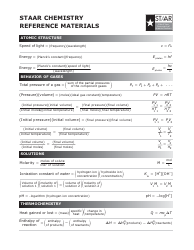
Chemistry Cheat Sheet - Naming Organic Compounds
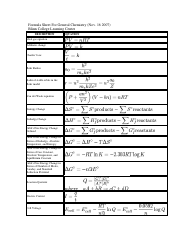
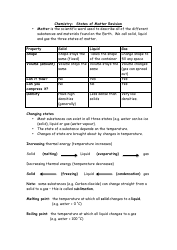
The Chemistry Cheat Sheet - Naming Organic Compounds is a reference guide that helps students and professionals in chemistry to understand and apply the rules for naming different organic compounds. It provides a concise summary of the naming rules, prefixes, and suffixes used in organic chemistry.
The Chemistry Cheat Sheet - Naming Organic Compounds may be filed by the publisher or the author of the cheat sheet.
FAQ
Q: What is an organic compound?
A: An organic compound is a compound that contains carbon atoms bonded to other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.
Q: What is the purpose of naming organic compounds?
A: Naming organic compounds helps us identify and communicate the structure and properties of different compounds.
Q: What are the different types of hydrocarbons?
A: The different types of hydrocarbons include alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Q: How do you name alkanes?
A: Alkanes are named using a prefix that corresponds to the number of carbon atoms and the suffix '-ane'. For example, methane (CH4) has one carbon atom, and ethane (C2H6) has two carbon atoms.
Q: What is the IUPAC system of nomenclature?
A: The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system of nomenclature is a set of rules for naming organic compounds.
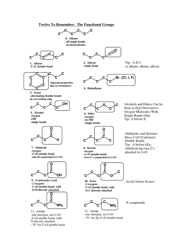
Q: What is a functional group?
A: A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that determine the chemical properties of a compound. It is usually attached to the carbon chain of the organic compound.
Q: How do you name compounds with functional groups?
A: Compounds with functional groups are named by identifying the longest carbon chain, numbering the carbons, and indicating the position of the functional group using a prefix or a number.
Q: What is a substituted hydrocarbon?
A: A substituted hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by a different atom or group of atoms.
Q: How do you name substituted hydrocarbons?
A: Substituted hydrocarbons are named by identifying the parent hydrocarbon chain, numbering the carbons, and indicating the position and name of the substituent using prefixes.
Q: What is a cyclic compound?
A: A cyclic compound is a compound in which the carbon atoms form a closed ring.
Q: How do you name cyclic compounds?
A: Cyclic compounds are named by identifying the parent hydrocarbon chain in the ring, numbering the carbons, and indicating the position and name of the substituent using prefixes or numbers.
Q: What are common functional groups?
A: Common functional groups include alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amines, amides, and halogens.