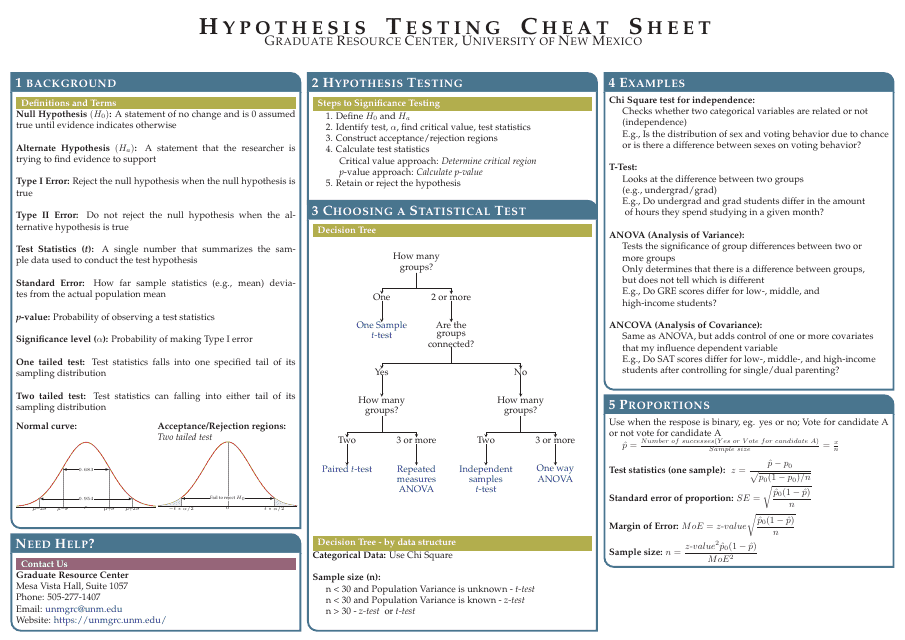
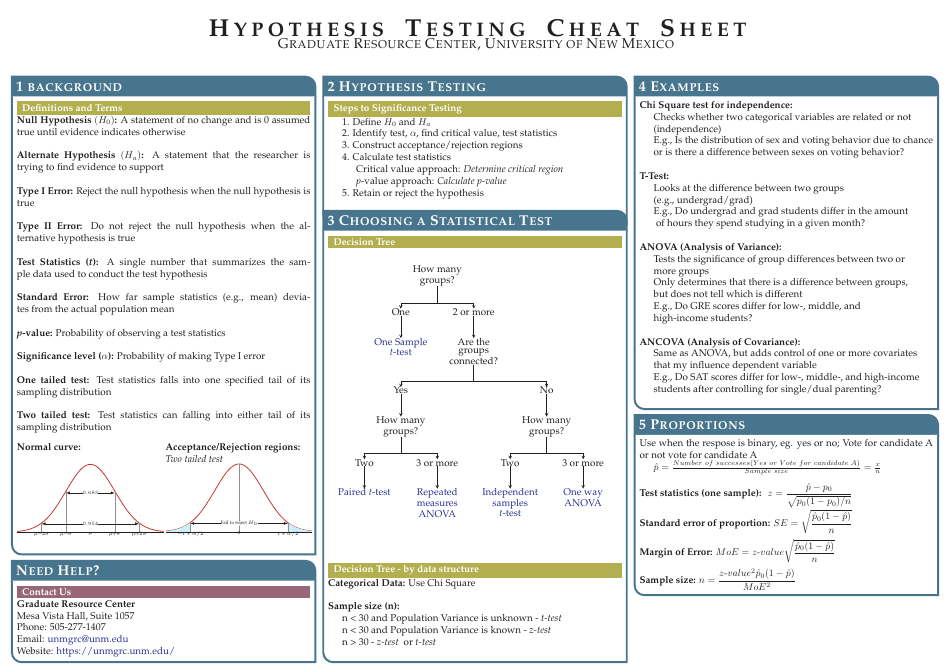
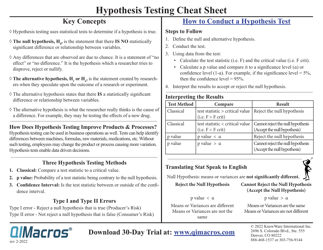
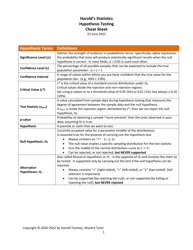
Hypothesis Testing Cheat Sheet - Graduate Resource Center, University of New Mexico
The Hypothesis Testing Cheat Sheet by the Graduate Resource Center at the University of New Mexico is a resource that provides a quick reference guide for graduate students on conducting hypothesis testing. It helps students understand and apply statistical concepts related to hypothesis testing in their research and data analysis.
FAQ
Q: What is hypothesis testing?
A: Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to make inferences about a population based on a sample of data.
Q: How does hypothesis testing work?
A: Hypothesis testing involves formulating a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, collecting data, and using statistical tests to determine the likelihood of accepting or rejecting the null hypothesis.
Q: What is a null hypothesis?
A: The null hypothesis is a statement of no effect or no difference. It is the hypothesis that we are trying to test and potentially reject.
Q: What is an alternative hypothesis?
A: The alternative hypothesis is a statement that contradicts or negates the null hypothesis. It is the hypothesis that we accept if we reject the null hypothesis.
Q: What is a p-value?
A: A p-value is a measure of the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis. It represents the probability of obtaining the observed data or more extreme results, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Q: What is the significance level?
A: The significance level, typically denoted as alpha (α), is the threshold used to determine whether the p-value is small enough to reject the null hypothesis. Commonly used significance levels are 0.05 and 0.01.
Q: What is type I error?
A: A type I error occurs when we reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true. It represents a false positive result.
Q: What is type II error?
A: A type II error occurs when we fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false. It represents a false negative result.
Q: What is a one-tailed test?
A: In a one-tailed test, the alternative hypothesis is defined in a specific direction. The test examines whether the sample evidence supports the claim of an effect in that direction only.
Q: What is a two-tailed test?
A: In a two-tailed test, the alternative hypothesis is defined in both directions. The test examines whether the sample evidence supports the claim of an effect in either direction.