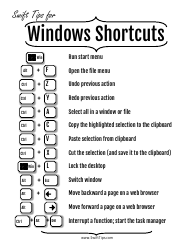
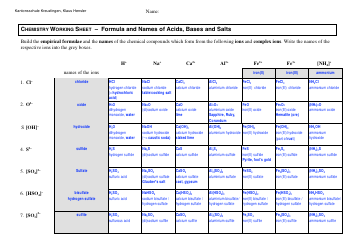
Vectors Cheat Sheet
The Vectors Cheat Sheet is a document that provides quick reference information and formulas for working with vectors in mathematics and physics. It is designed to help users understand and solve problems related to vector operations, such as addition, subtraction, dot product, cross product, and vector projection.
FAQ
Q: What is a vector?
A: A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Q: What are some examples of vectors?
A: Examples of vectors include displacement, velocity, force, and acceleration.
Q: How can vectors be represented?
A: Vectors can be represented using arrows or in terms of their components.
Q: What is the magnitude of a vector?
A: The magnitude of a vector is its length or size.
Q: What is the direction of a vector?
A: The direction of a vector is the angle it makes with a reference axis.
Q: What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
A: Scalar quantities have only magnitude, while vector quantities have both magnitude and direction.
Q: How are vectors added?
A: Vectors can be added by adding their corresponding components.
Q: What is the dot product of two vectors?
A: The dot product of two vectors is a scalar quantity that represents the projection of one vector onto the other.
Q: What is the cross product of two vectors?
A: The cross product of two vectors is a vector quantity that is perpendicular to both input vectors.
Q: What are unit vectors?
A: Unit vectors are vectors with a magnitude of 1 and are commonly used to represent directions.