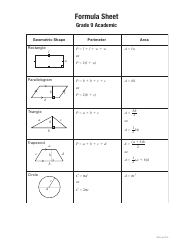
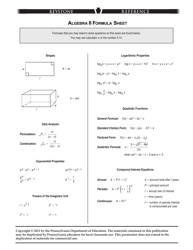
Applied Math Formula Sheet
An Applied Math Formula Sheet is a document that contains a comprehensive collection of mathematical formulas and equations that are commonly used in practical applications. It serves as a reference guide for individuals studying or working in fields such as engineering, physics, computer science, and economics, among others. The formula sheet allows users to quickly access and apply relevant mathematical concepts to solve real-life problems and make calculations. It is often used during exams, projects, and day-to-day problem-solving in various technical and scientific disciplines.
The Applied Math Formula Sheet is not filed by a specific entity or organization. It is typically provided to students or individuals who are studying or working in the field of applied mathematics. The formula sheet serves as a reference guide, containing various mathematical formulas and equations that are commonly used in applied math problems and calculations. It may be provided by educational institutions, online resources, or textbooks.
FAQ
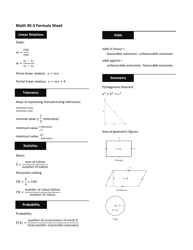
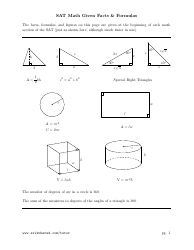
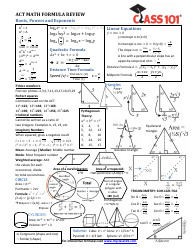
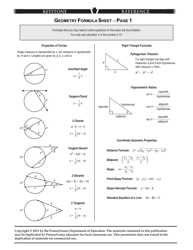
Q: What is the Pythagorean theorem?
A: The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
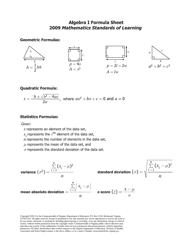
Q: What is the quadratic formula?
A: The quadratic formula is used to find the roots of a quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants. It states that the roots are given by x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac))/(2a).
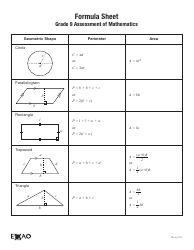
Q: What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
A: The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis).
Q: What is the distance formula?
A: The distance formula calculates the distance between two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) in a coordinate plane. It is given by √((x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²).
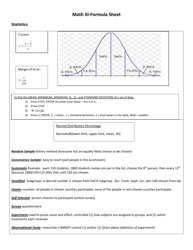
Q: What is the formula for exponential growth or decay?
A: The formula for exponential growth or decay is given by A = P(1 + r)^t, where A is the final amount, P is the initial amount, r is the growth or decay rate, and t is the time period.