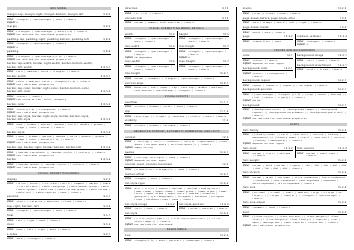
Moles & Stoichiometry Cheat Sheet
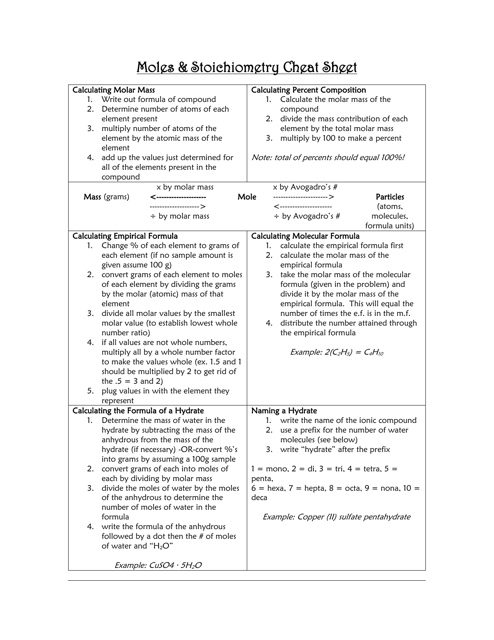
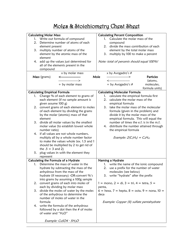
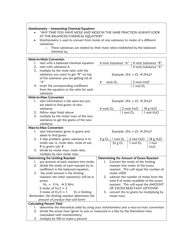
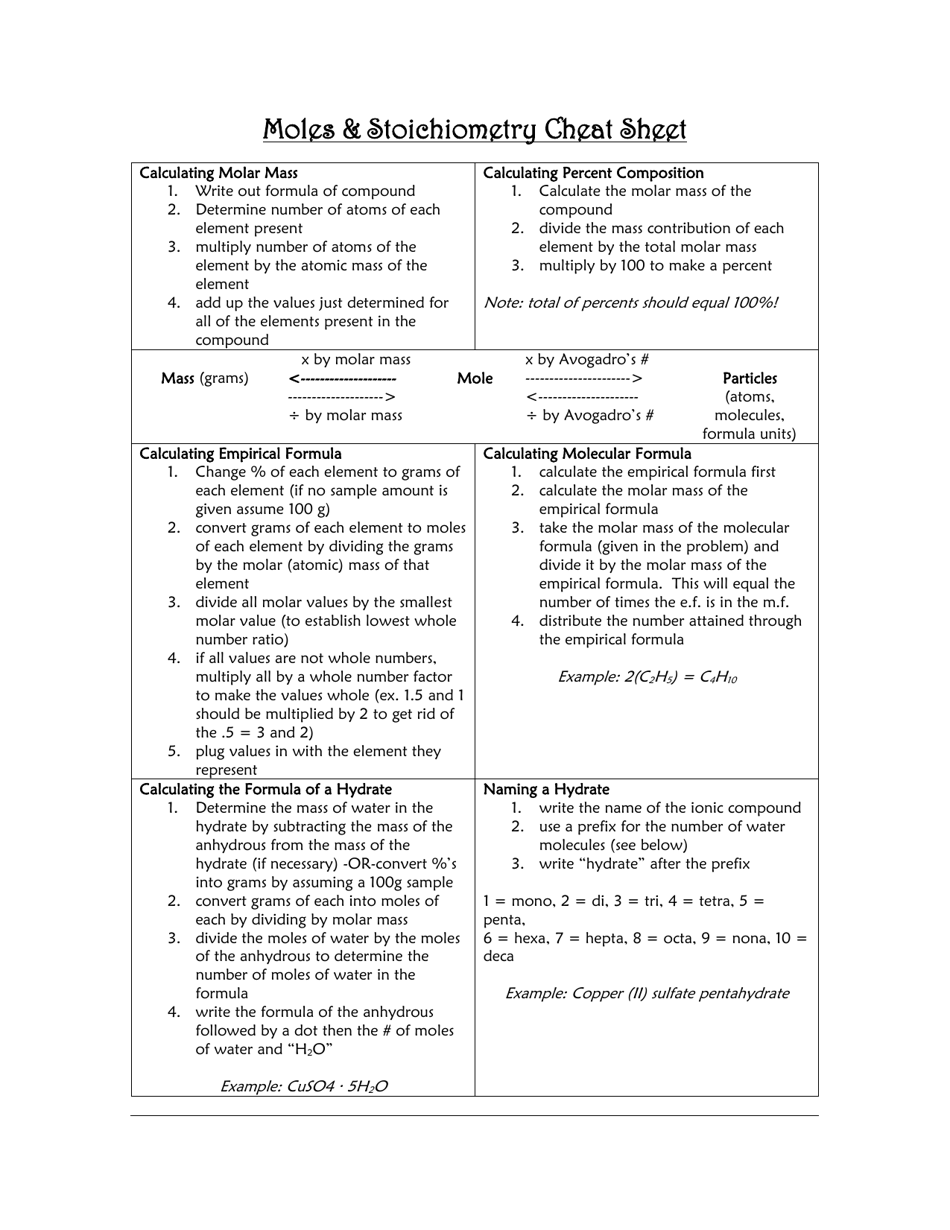
A Moles & Stoichiometry Cheat Sheet is a document that provides a quick reference guide for understanding and solving problems related to moles and stoichiometry in chemistry. It contains formulas, equations, and explanations to help students or individuals grasp these concepts more easily.
FAQ
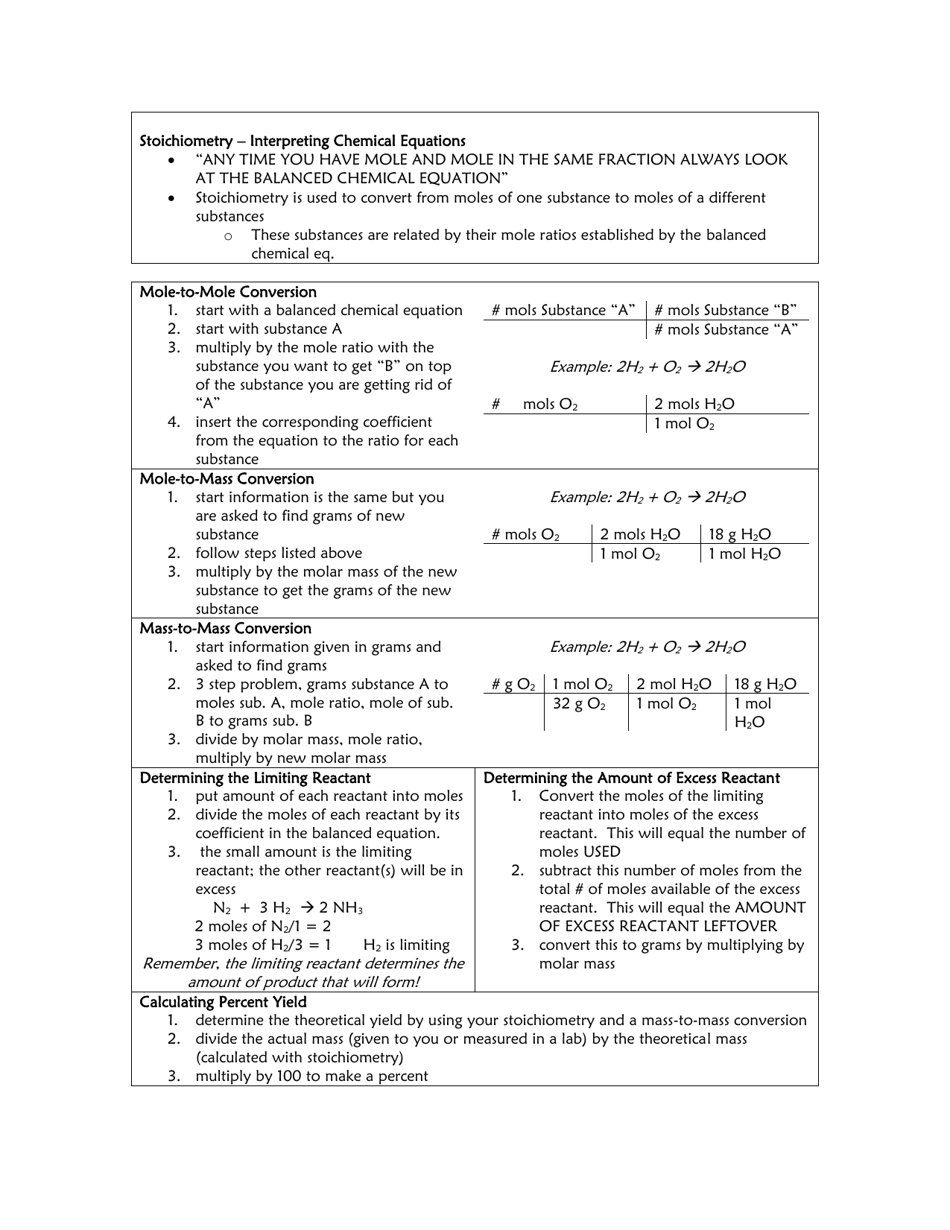
Q: What is stoichiometry?
A: Stoichiometry is the calculation of the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
Q: What is a mole?
A: A mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to represent the amount of a substance.
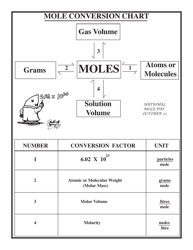
Q: What is Avogadro's number?
A: Avogadro's number is 6.022 x 10^23, and it represents the number of atoms or molecules in one mole of a substance.
Q: How do you calculate the number of moles?
A: You can calculate the number of moles by dividing the mass of a substance by its molar mass.
Q: What is a molar mass?
A: Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, and it is expressed in grams per mole.
Q: What is a chemical equation?
A: A chemical equation represents the balanced formula of a chemical reaction, with reactants on the left side and products on the right side.
Q: What is a stoichiometric coefficient?
A: A stoichiometric coefficient is the number written in front of a chemical formula in a balanced equation, and it represents the ratio of moles for each substance involved in the reaction.
Q: What is percent yield?
A: Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction, calculated by dividing the actual yield by the theoretical yield and multiplying by 100.
Q: What is a limiting reactant?
A: A limiting reactant is the reactant that gets completely consumed in a chemical reaction, thus limiting the amount of product that can be formed.
Q: What is excess reactant?
A: An excess reactant is the reactant that is not completely consumed in a chemical reaction and is left over after the reaction is complete.