Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet - Seventeen Points
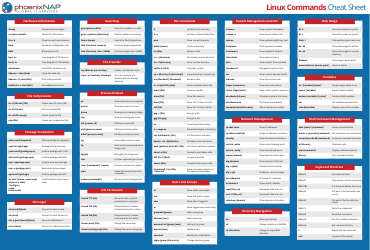
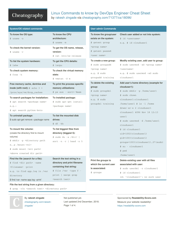
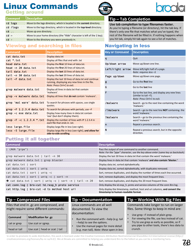
The Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet - Seventeen Points is a reference document that provides a quick summary of commonly used commands in the Linux operating system. It is helpful for both beginners and experienced users to quickly access and remember important commands.
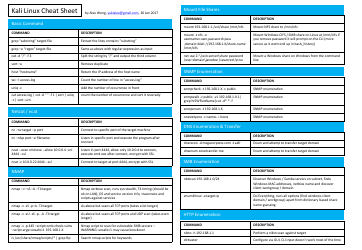
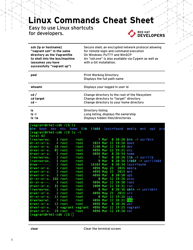
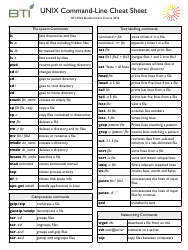
FAQ
Q: What is Linux?
A: Linux is an open-source operating system that is based on the Unix operating system.
Q: What is the command line?
A: The command line is a text-based interface where users can interact with the operating system by typing commands.
Q: What is a shell?
A: A shell is a program that provides the command line interface in Linux. The most common shell in Linux is called Bash (Bourne Again Shell).
Q: How do I navigate through directories?
A: You can use the 'cd' command to change directories. For example, 'cd /home' will take you to the 'home' directory.
Q: How do I list files and directories?
A: You can use the 'ls' command to list the files and directories in the current directory. Adding options like '-l' will provide more details.
Q: How do I create a new directory?
A: You can use the 'mkdir' command followed by the name of the directory you want to create. For example, 'mkdir mydirectory' will create a directory called 'mydirectory'.
Q: How do I create a new file?
A: You can use the 'touch' command followed by the name of the file you want to create. For example, 'touch myfile.txt' will create a file called 'myfile.txt'.
Q: How do I copy files or directories?
A: You can use the 'cp' command followed by the name of the file or directory you want to copy, and then the destination. For example, 'cp myfile.txt /home/user/' will copy 'myfile.txt' to the '/home/user/' directory.
Q: How do I move files or directories?
A: You can use the 'mv' command followed by the name of the file or directory you want to move, and then the destination. For example, 'mv myfile.txt /home/user/' will move 'myfile.txt' to the '/home/user/' directory.
Q: How do I delete files or directories?
A: You can use the 'rm' command followed by the name of the file or directory you want to delete. For example, 'rm myfile.txt' will delete the file 'myfile.txt'. Use the '-r' option to delete directories and their contents.
Q: How do I search for a file or directory?
A: You can use the 'find' command followed by the starting directory and the name or pattern of the file you are looking for. For example, 'find /home -name myfile.txt' will search for 'myfile.txt' in the '/home' directory.
Q: How do I view the contents of a file?
A: You can use the 'cat' command followed by the name of the file you want to view. For example, 'cat myfile.txt' will display the contents of 'myfile.txt'.
Q: How do I edit a file?
A: You can use a text editor like 'vi' or 'nano' to edit a file. For example, 'vi myfile.txt' will open 'myfile.txt' in the vi editor.
Q: How do I display system information?
A: You can use commands like 'uname' to display system information. For example, 'uname -a' will display all system information.
Q: How do I check my IP address?
A: You can use the 'ifconfig' command to check your IP address. For example, 'ifconfig' will display network interface information including the IP address.
Q: How do I check disk space?
A: You can use the 'df' command to check disk space. For example, 'df -h' will display disk space usage in a human-readable format.
Q: How do I check system resources?
A: You can use commands like 'top', 'htop', or 'free' to check system resources such as CPU and memory usage.