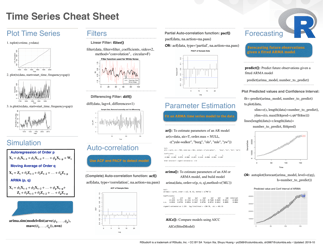
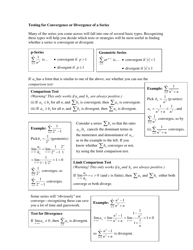
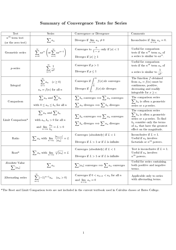
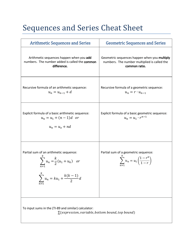
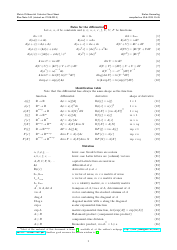
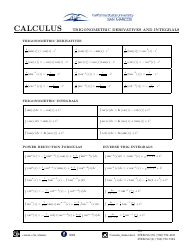
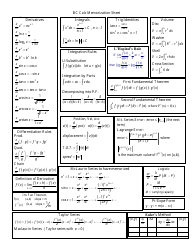
Calculus II Cheat Sheet - Series
The Calculus II Cheat Sheet - Series is a reference guide that helps students studying Calculus II to understand and apply concepts related to series. It provides concise summaries, formulas, and examples to assist students in their studies and problem solving.
FAQ
Q: What are series in Calculus II?
A: Series in Calculus II refer to the summation of an infinite sequence of terms.
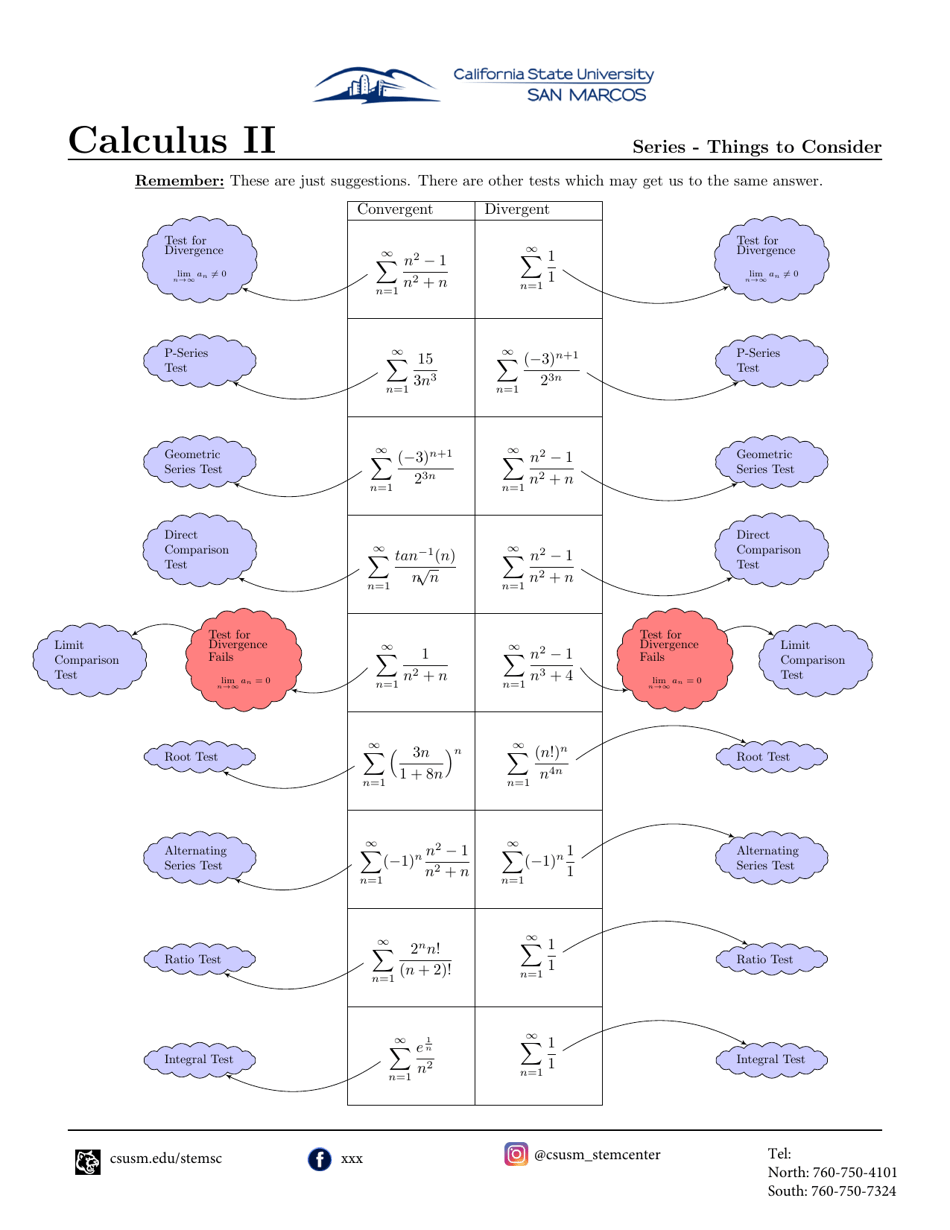
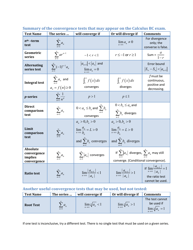
Q: What is the nth term test for divergence?
A: The nth term test for divergence states that if the nth term of a series does not approach zero, then the series diverges.
Q: What is the integral test?
A: The integral test states that if a series has a corresponding improper integral that converges, then the series also converges.
Q: What is the comparison test?
A: The comparison test states that if a series can be compared to another series whose convergence is known, then the original series has the same convergence.
Q: What is the limit comparison test?
A: The limit comparison test states that if the limit of the ratio between the terms of a series and the terms of a known convergent series is a positive constant, then the original series has the same convergence.
Q: What is the ratio test?
A: The ratio test states that if the limit of the absolute value of the ratio between consecutive terms of a series is less than one, then the series converges.
Q: What is the root test?
A: The root test states that if the nth root of the absolute value of the terms of a series converges to a value less than one, then the series converges.
Q: What is the alternating series test?
A: The alternating series test states that if a series alternates in sign and the absolute value of its terms decreases monotonically to zero, then the series converges.
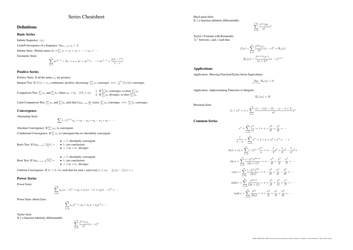
Q: What is the remainder estimation theorem?
A: The remainder estimation theorem provides a way to estimate the error in truncating a series to a finite number of terms.
Q: What is the Taylor series?
A: The Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of its derivatives at a single point.