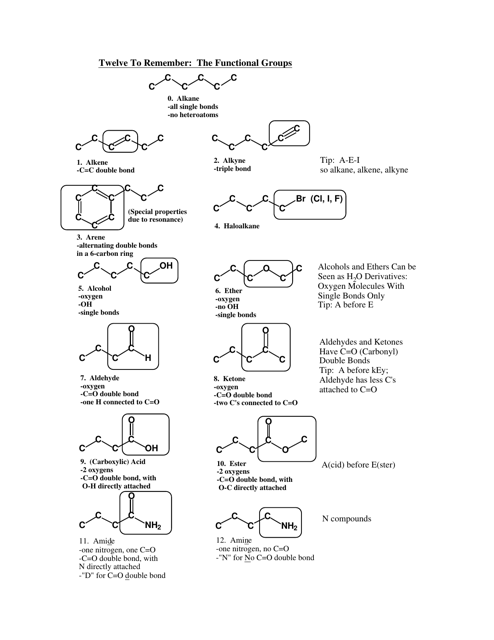
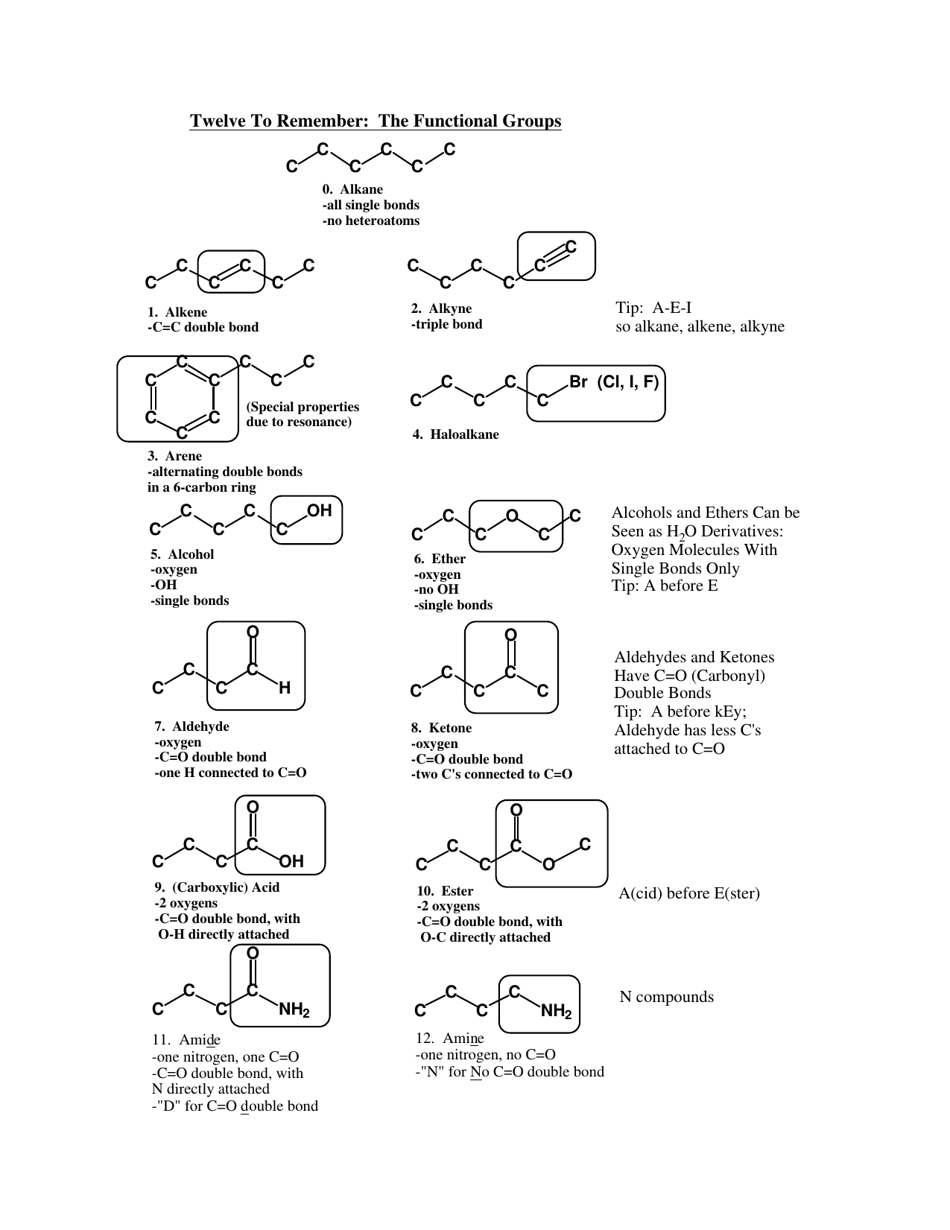
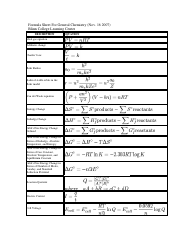
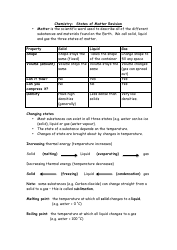
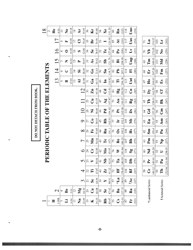
Chemistry Cheat Sheet: the Functional Groups
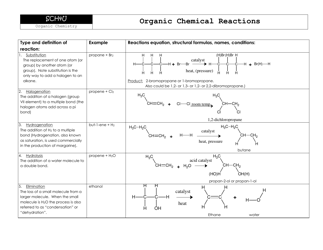
A Chemistry Cheat Sheet: Functional Groups is a document that provides a quick reference guide for the different functional groups found in organic chemistry. It helps students and professionals identify and understand the properties and characteristics of various organic compounds.
FAQ
Q: What are functional groups?
A: Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that are responsible for the chemical reactions and properties of organic compounds.
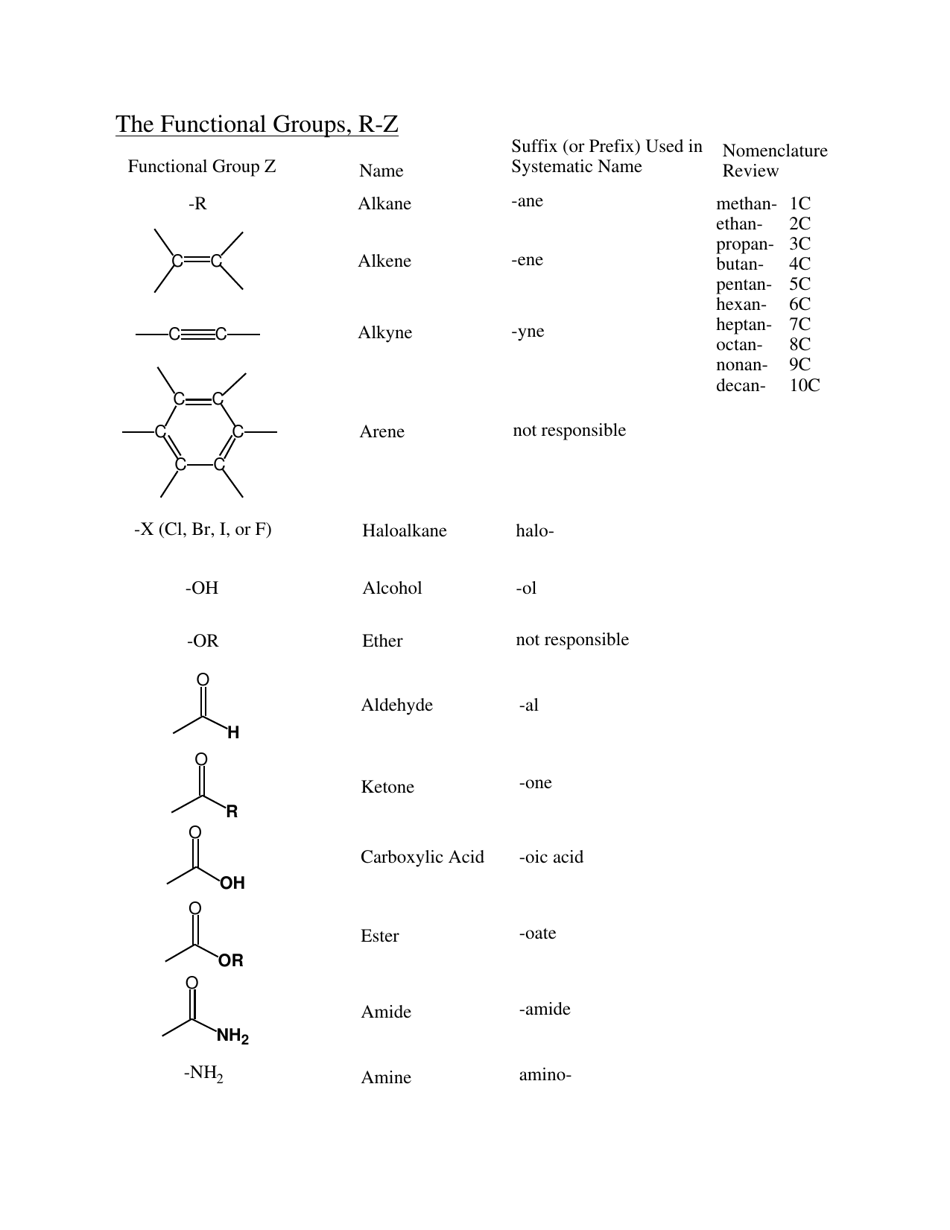
Q: What is the functional group in alcohols?
A: The functional group in alcohols is the hydroxyl group (-OH).
Q: What are some examples of alcohols?
A: Examples of alcohols include ethanol, methanol, and isopropyl alcohol.
Q: What is the functional group in aldehydes?
A: The functional group in aldehydes is the carbonyl group (C=O), with a hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon atom.
Q: What are some examples of aldehydes?
A: Examples of aldehydes include formaldehyde and acetaldehyde.
Q: What is the functional group in ketones?
A: The functional group in ketones is also the carbonyl group (C=O), but with two carbon atoms bonded to the carbonyl carbon.
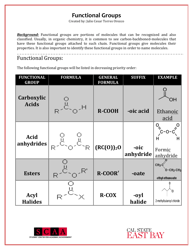
Q: What is the functional group in carboxylic acids?
A: The functional group in carboxylic acids is the carboxyl group (COOH), which consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group.
Q: What are some examples of carboxylic acids?
A: Examples of carboxylic acids include acetic acid, formic acid, and benzoic acid.
Q: What is the functional group in esters?
A: The functional group in esters is the ester group (RCOOR'), which consists of a carbonyl group bonded to an oxygen atom and an alkyl group.
Q: What are some examples of esters?
A: Examples of esters include methyl acetate, ethyl butanoate, and isopropyl propionate.
Q: What is the functional group in amines?
A: The functional group in amines is the amino group (-NH2), which consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl or aryl groups.
Q: What are some examples of amines?
A: Examples of amines include ethylamine, aniline, and dimethylamine.
Q: What is the functional group in amides?
A: The functional group in amides is the amide group (RCONH2), which consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom and an alkyl or aryl group.
Q: What are some examples of amides?
A: Examples of amides include acetamide, N,N-dimethylacetamide, and benzanamide.