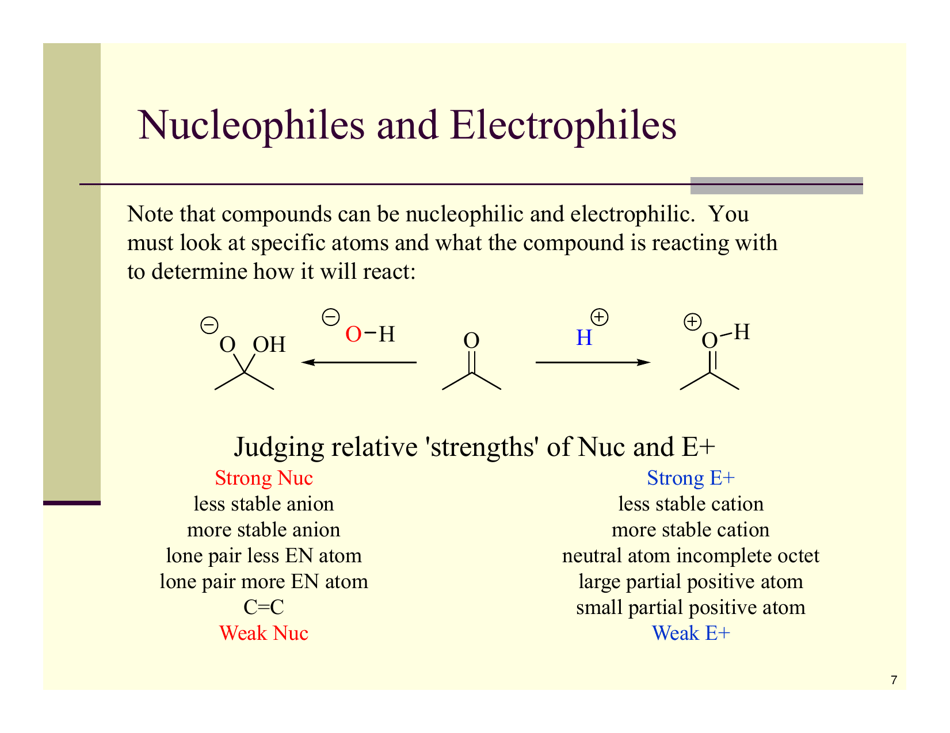
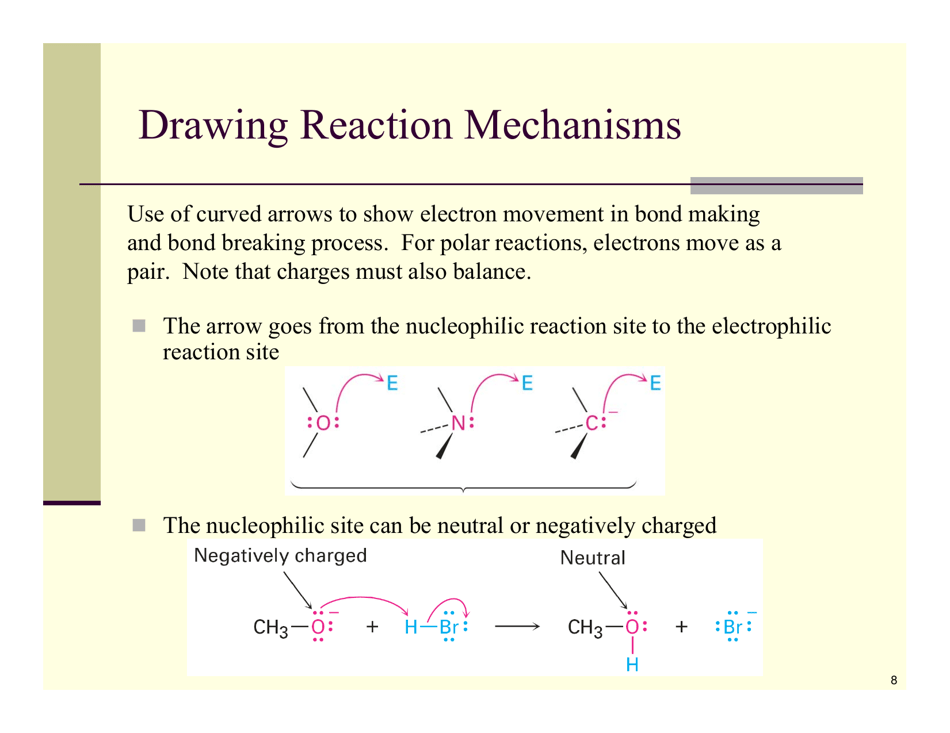
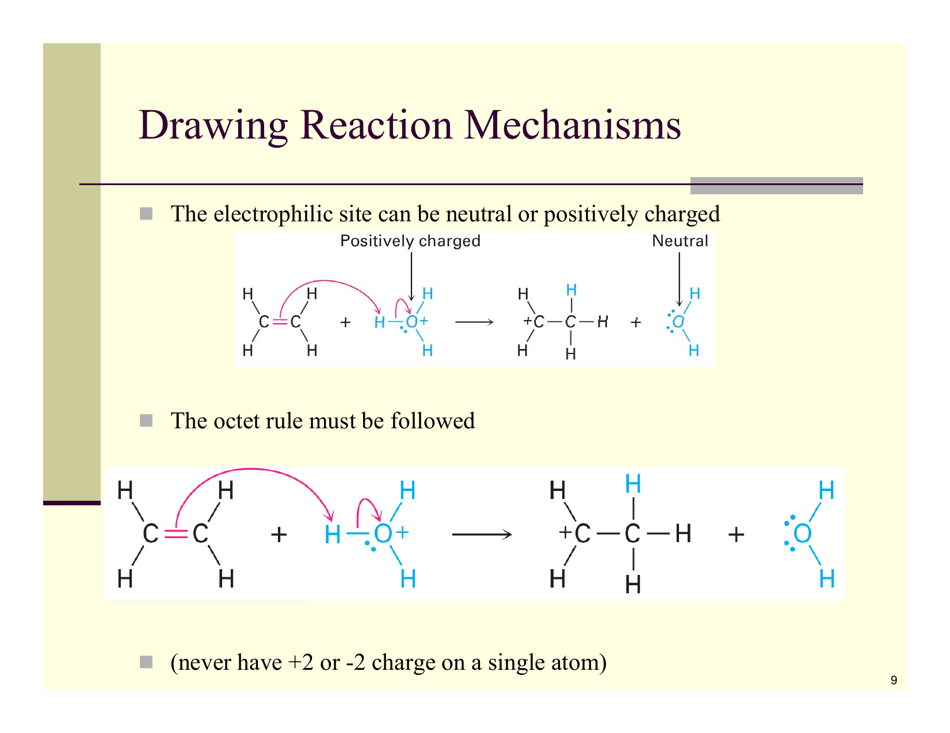
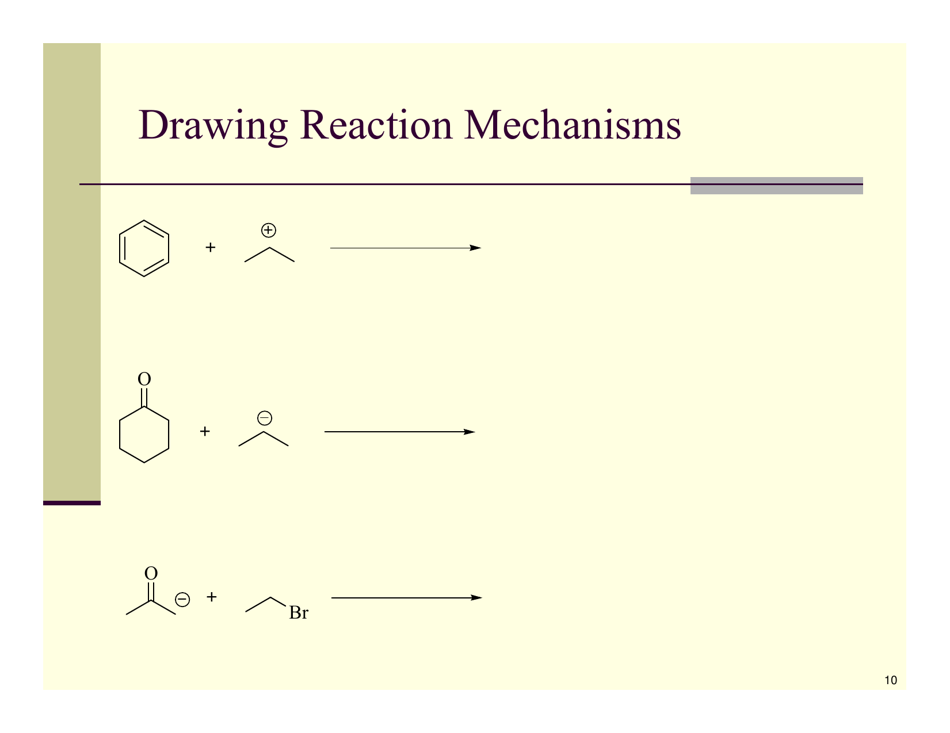
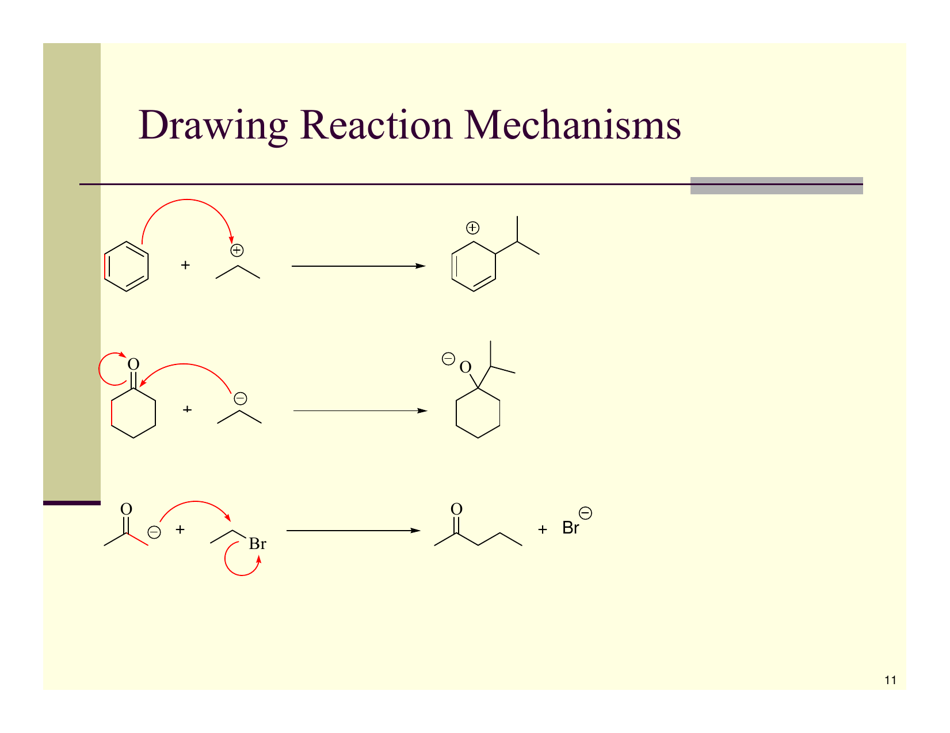
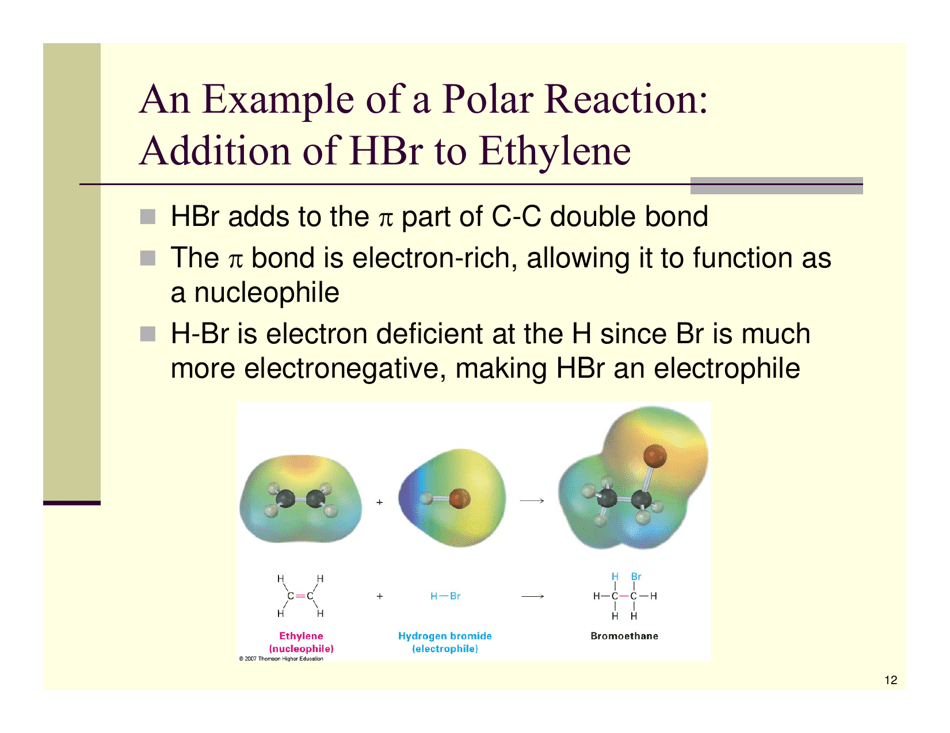
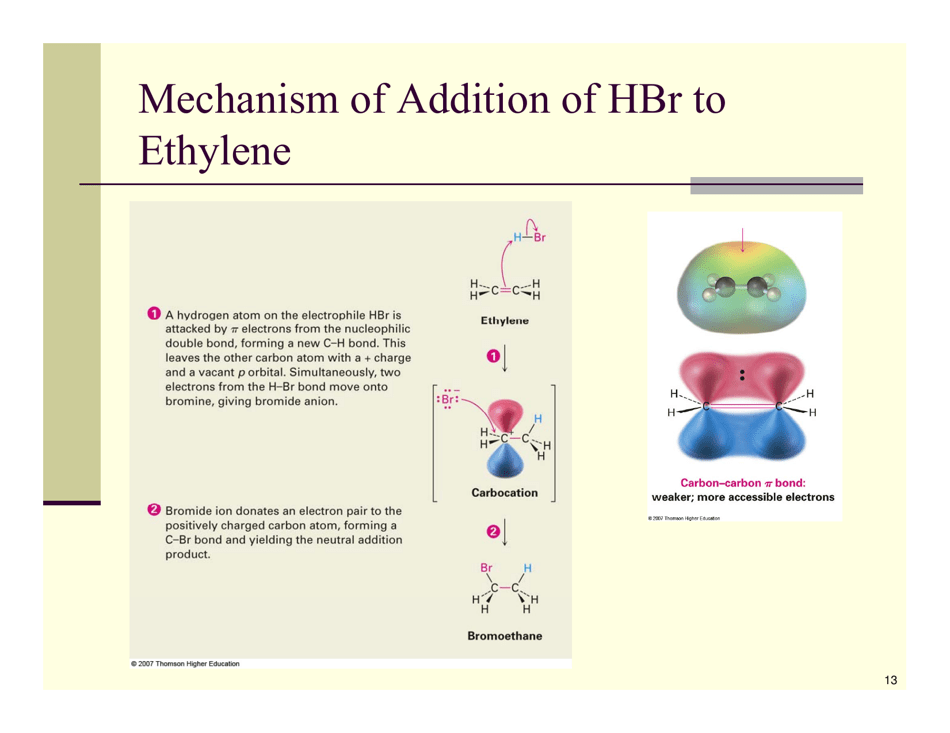
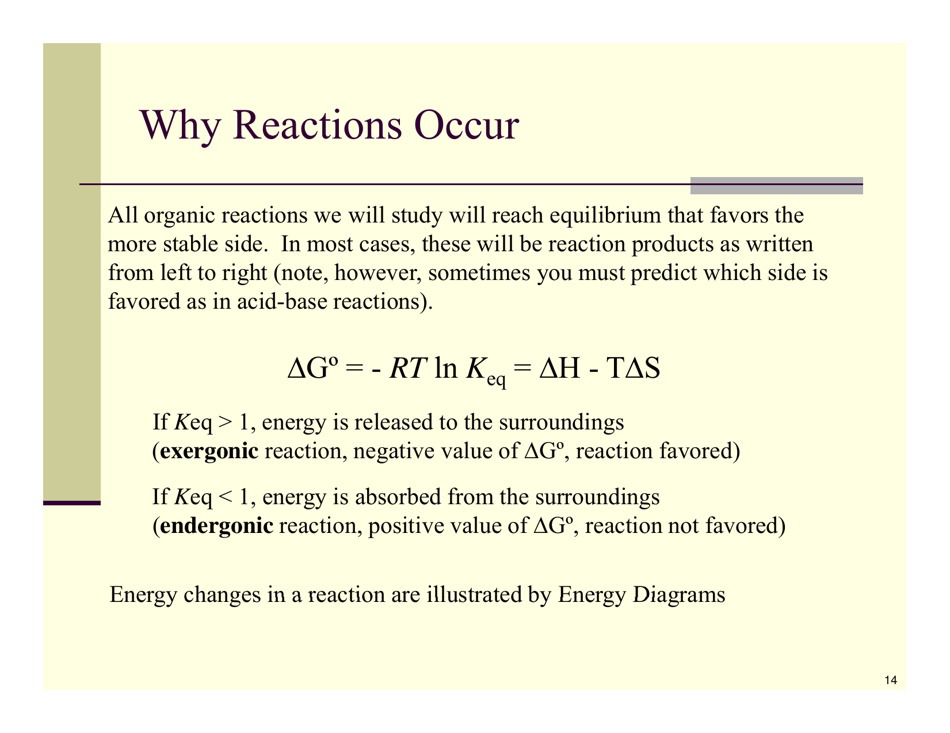
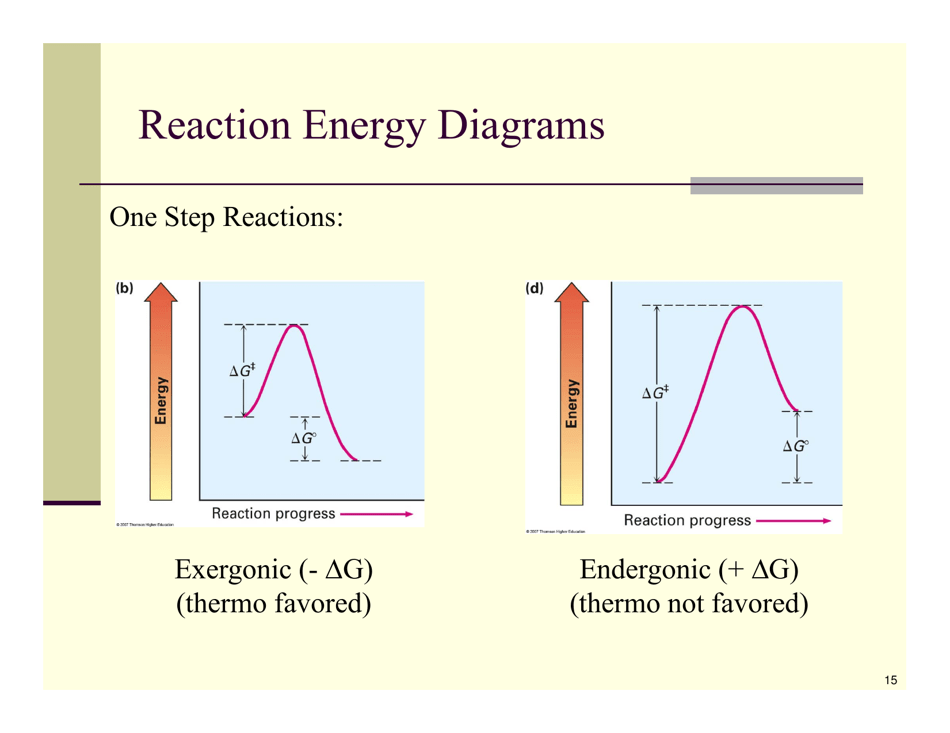
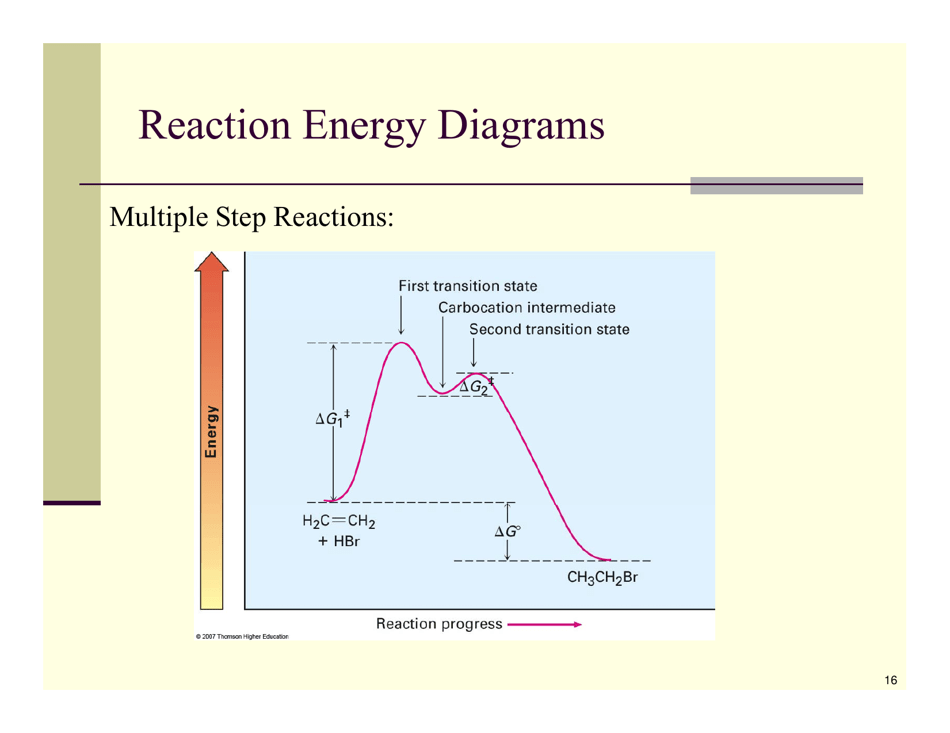
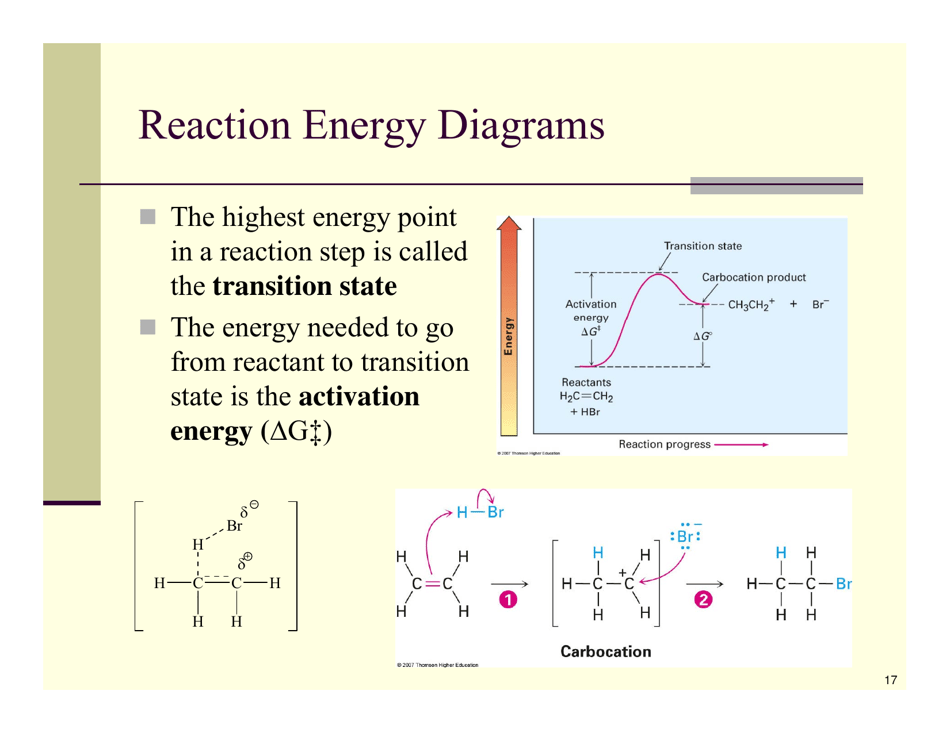
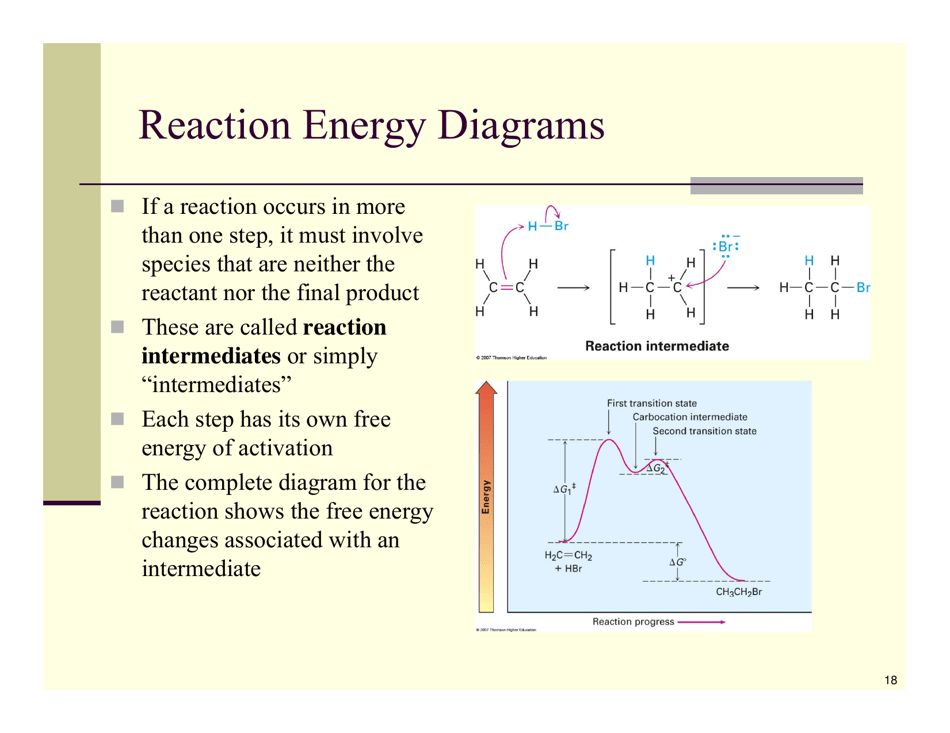
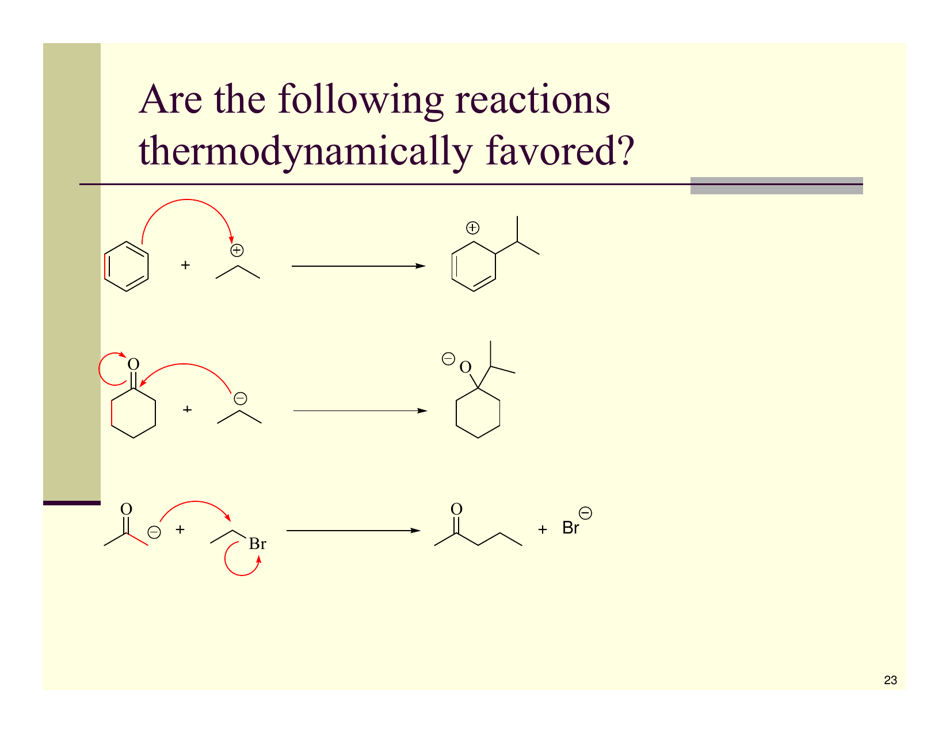
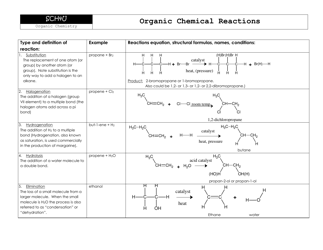
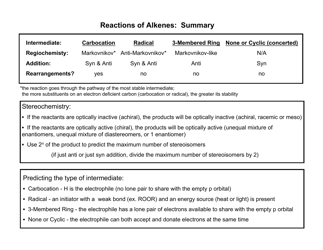
Organic Reactions Cheat Sheet
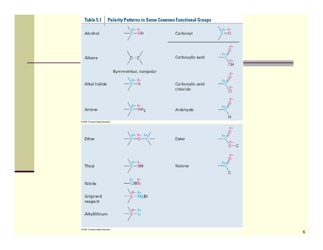
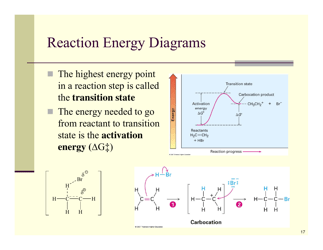
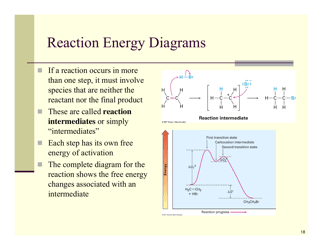
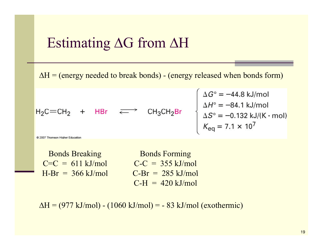
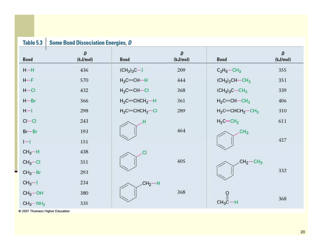
The Organic Reactions Cheat Sheet is a reference document that provides a summary of various organic reactions and their mechanisms. It is designed to help students and professionals in the field of organic chemistry quickly review and understand the key concepts and reactions involved in organic synthesis.
FAQ
Q: What are organic reactions?
A: Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds.
Q: Why are organic reactions important?
A: Organic reactions are important for the synthesis of new compounds and the development of new drugs.
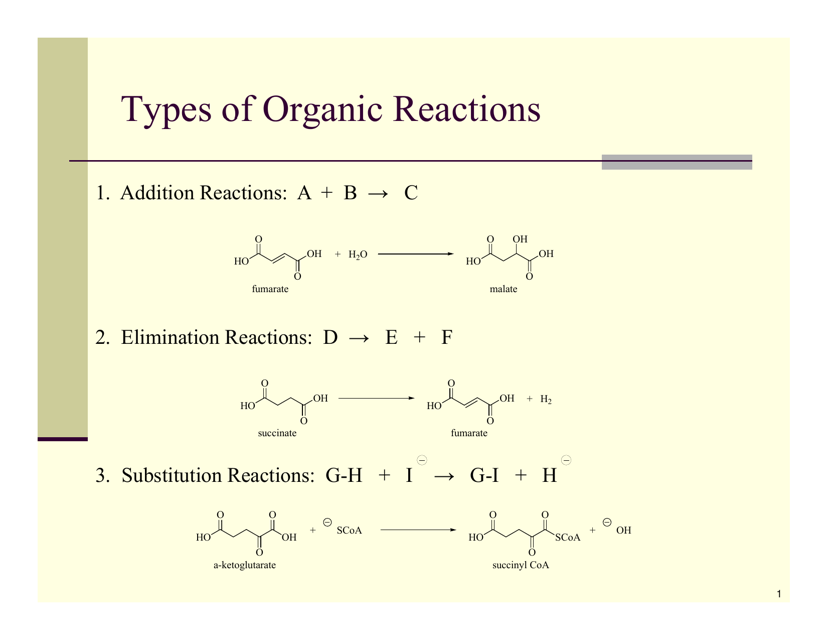
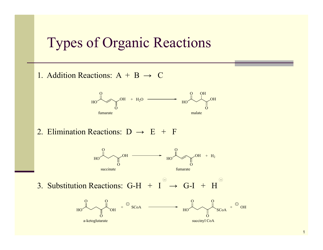
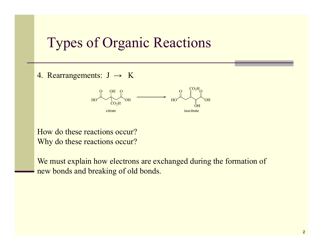
Q: What are some types of organic reactions?
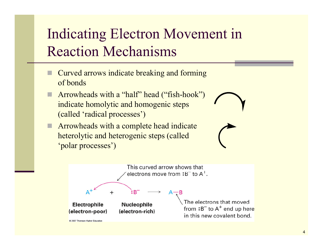
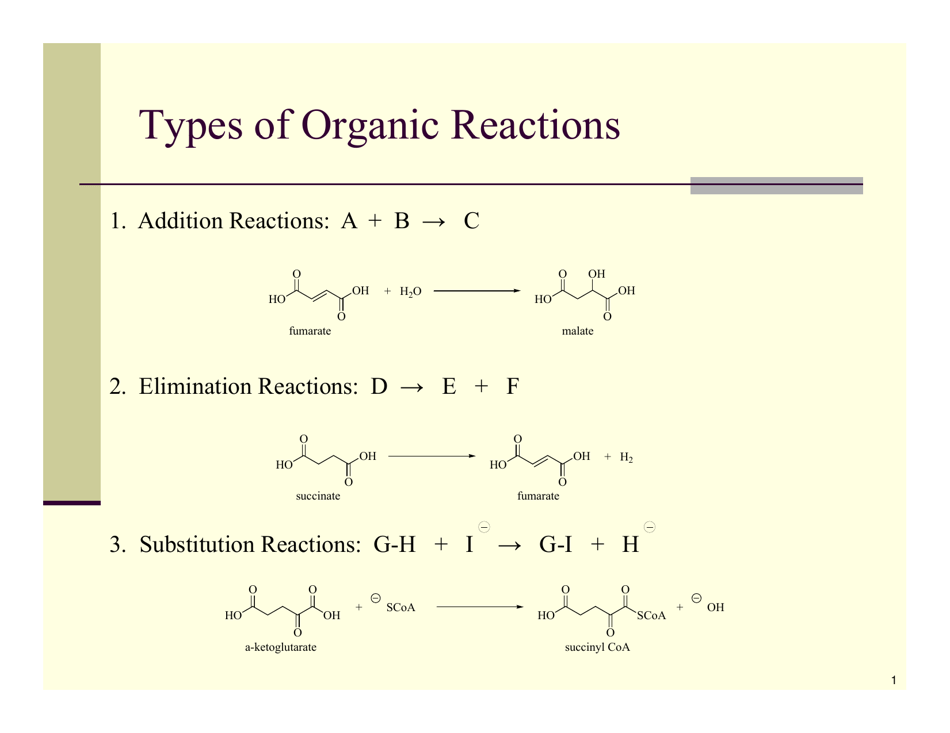
A: Some types of organic reactions include substitution, addition, elimination, and oxidation-reduction reactions.
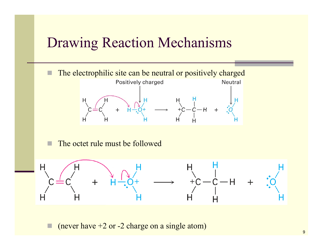
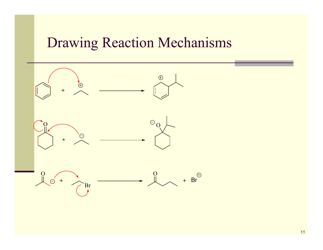
Q: What is a substitution reaction?
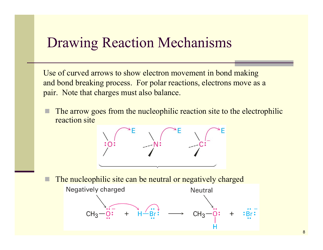
A: A substitution reaction is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms.
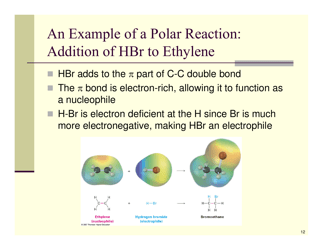
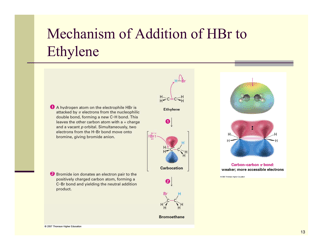
Q: What is an addition reaction?
A: An addition reaction is a reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a single product.
Q: What is an elimination reaction?
A: An elimination reaction is a reaction where a molecule loses a small molecule, such as water or a halide, resulting in the formation of a new compound.
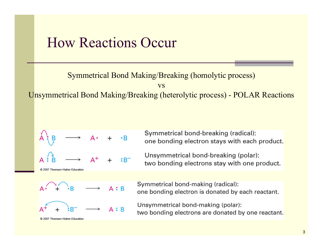
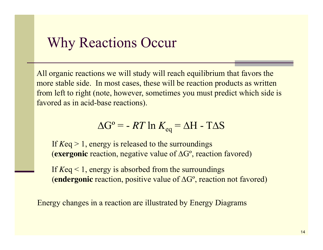
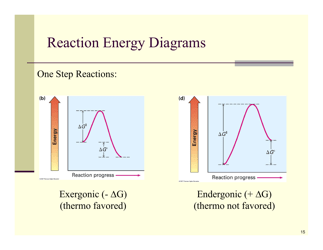
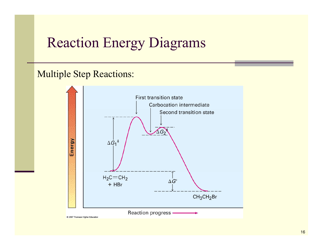
Q: What is an oxidation-reduction reaction?
A: An oxidation-reduction reaction, also known as a redox reaction, is a reaction where electrons are transferred between molecules.
Q: What are some examples of organic reactions?
A: Examples of organic reactions include esterification, Friedel-Crafts acylation, and nucleophilic substitution.
Q: What is esterification?
A: Esterification is a reaction between an alcohol and an acid, resulting in the formation of an ester.
Q: What is Friedel-Crafts acylation?
A: Friedel-Crafts acylation is a reaction where an acyl group is added to an aromatic compound, typically with the use of a Lewis acid catalyst.
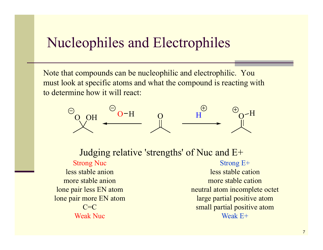
Q: What is nucleophilic substitution?
A: Nucleophilic substitution is a reaction where a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule.
Q: Can you provide an example of an organic reaction?
A: One example is the reaction between ethanol and acetic acid to form ethyl acetate through esterification.