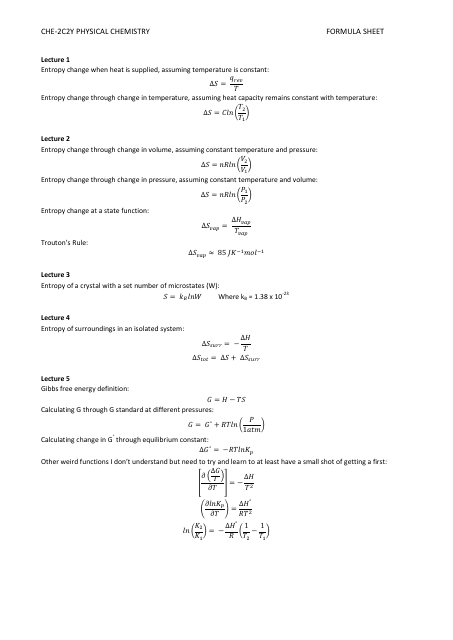
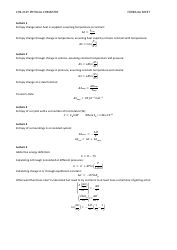
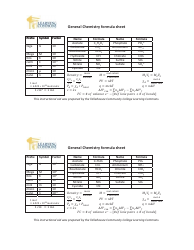
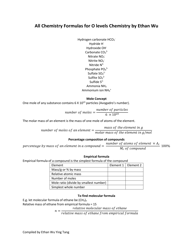
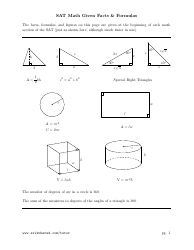
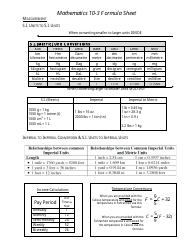
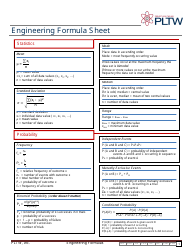
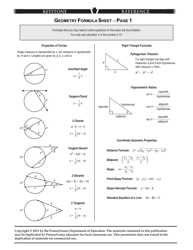
Physical Chemistry Formula Sheet
A Physical Chemistry Formula Sheet is a condensed compilation of the most important formulas, equations, and constants used in the field of Physical Chemistry. It serves as a quick reference guide for students and professionals, allowing them to easily access and utilize the necessary formulas while solving problems or conducting experiments.
The physical chemistry formula sheet is typically provided by the educational institution or provided by the instructor of the course. There is no specific entity that files it.
FAQ
Q: What is physical chemistry?
A: Physical chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the physical properties and behavior of matter, as well as the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions.
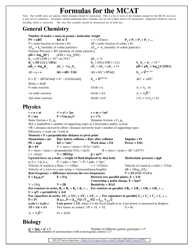
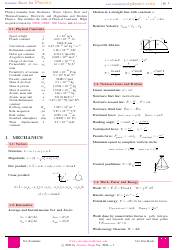
Q: What are some common formulas used in physical chemistry?
A: Some common formulas used in physical chemistry include the ideal gas law, the Beer-Lambert law, the Nernst equation, and the Arrhenius equation.
Q: What is the ideal gas law?
A: The ideal gas law is a mathematical relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the temperature.
Q: What is the Beer-Lambert law?
A: The Beer-Lambert law relates the concentration of a solute in a solution to the absorbance of light by the solution. It is expressed as A = ɛcl, where A is the absorbance, ɛ is the molar absorptivity, c is the concentration, and l is the path length.
Q: What is the Nernst equation?
A: The Nernst equation is an equation that relates the concentration of an ion in a solution to its standard electrode potential. It is expressed as E = E° - (RT/nF)ln(Q), where E is the electrode potential, E° is the standard electrode potential, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature, n is the number of moles of electrons transferred in the reaction, F is Faraday's constant, and Q is the reaction quotient.
Q: What is the Arrhenius equation?
A: The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant of a chemical reaction to the temperature and the activation energy. It is expressed as k = Ae^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature.