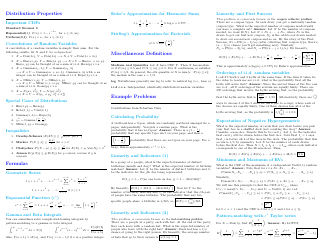
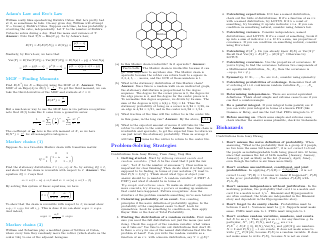
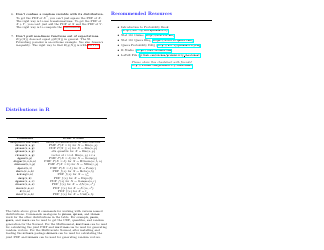
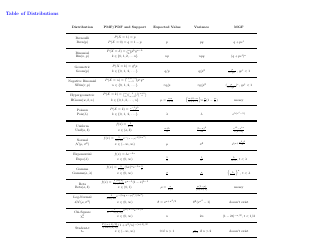
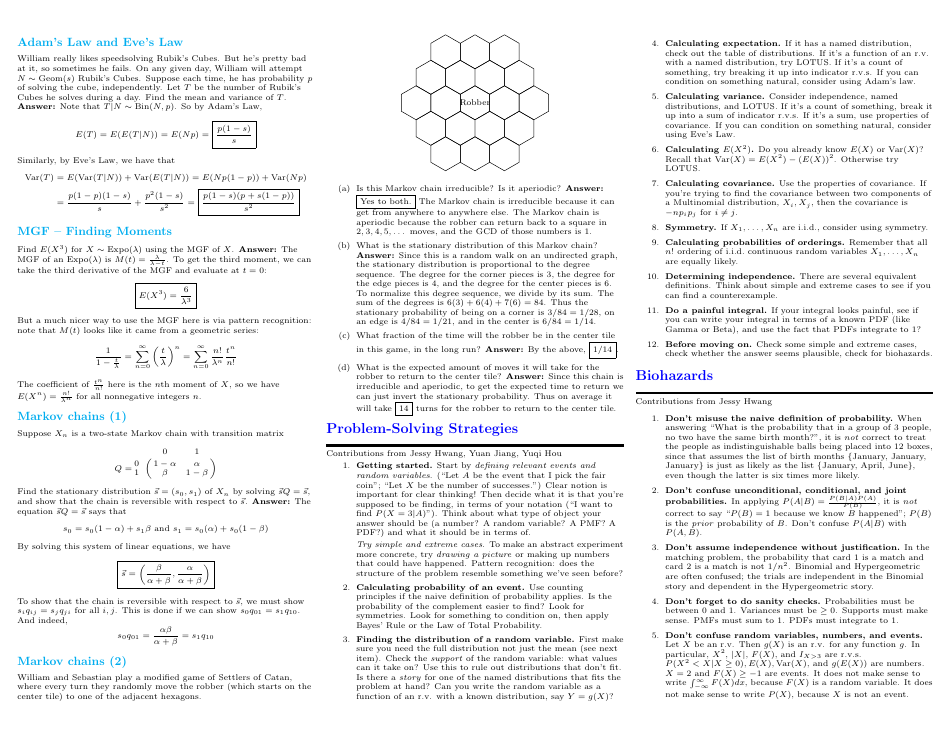
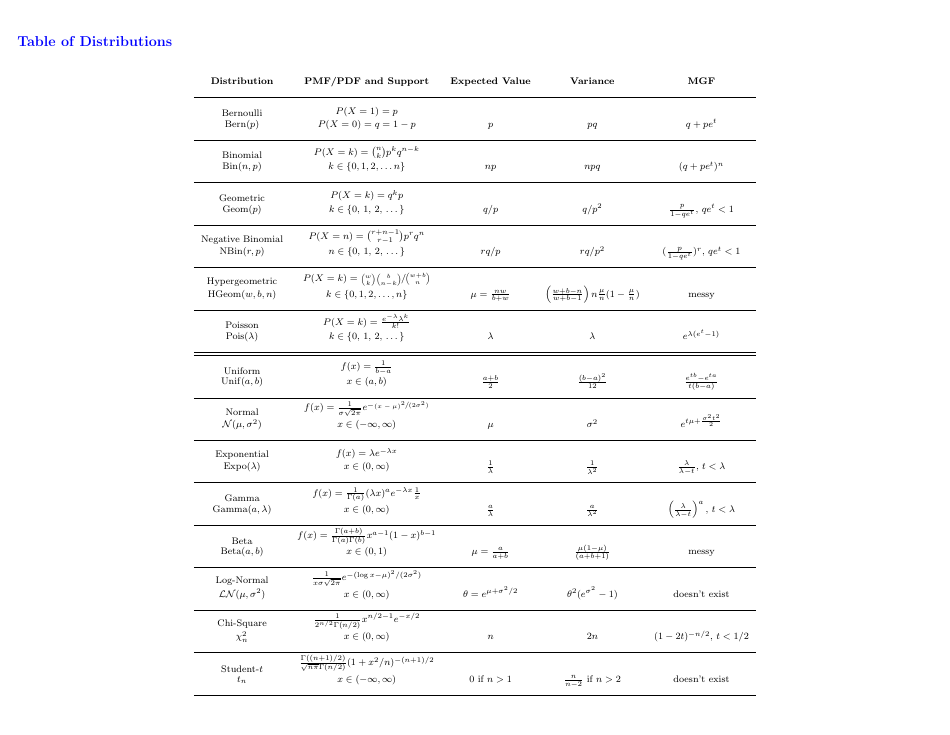
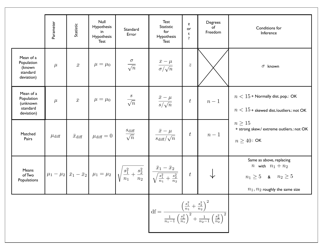
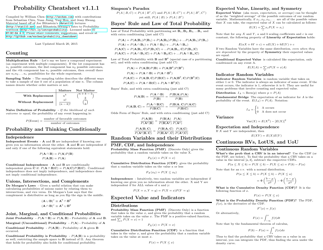
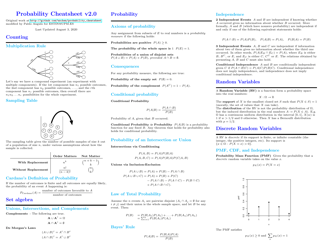
Probability Cheatsheet - Varicolored
The "Probability Cheatsheet - Varicolored" is a document that provides a quick reference guide for understanding and solving probability problems. It helps to easily access key concepts, formulas, and methods related to probability.
FAQ
Q: What is probability?
A: Probability is the likelihood of an event or outcome occurring.
Q: How is probability measured?
A: Probability is measured on a scale of 0 to 1, where 0 indicates no chance of an event occurring, and 1 indicates certainty.
Q: What is the difference between theoretical probability and experimental probability?
A: Theoretical probability is calculated based on mathematical principles, while experimental probability is determined through repeated trials or observations.
Q: What is the probability of an event that is certain to happen?
A: The probability of an event that is certain to happen is 1.
Q: What is the probability of an event that is impossible to happen?
A: The probability of an event that is impossible to happen is 0.
Q: What is the formula for calculating probability?
A: The probability of an event is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes.
Q: What is a sample space?
A: A sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment or event.
Q: What is the difference between independent and dependent events?
A: Independent events are events whose outcomes do not affect each other, while dependent events are events whose outcomes do affect each other.
Q: What is the multiplication rule in probability?
A: The multiplication rule states that the probability of two independent events happening together is the product of their individual probabilities.
Q: What is the addition rule in probability?
A: The addition rule states that the probability of either of two mutually exclusive events happening is the sum of their individual probabilities.