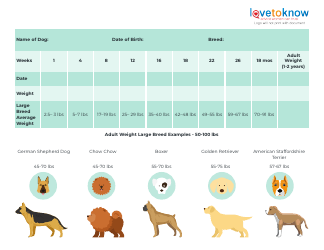
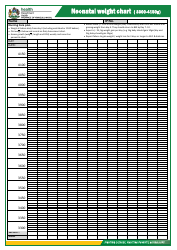
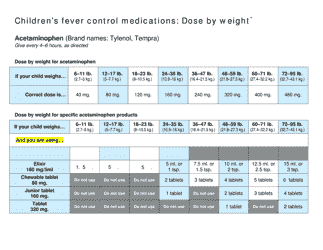
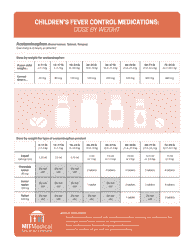
Birth Weight Chart
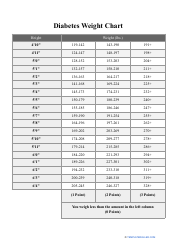
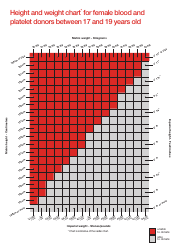
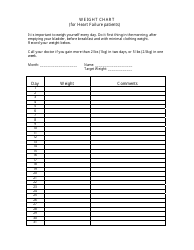
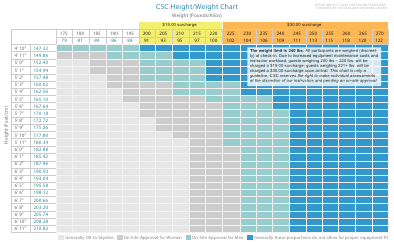
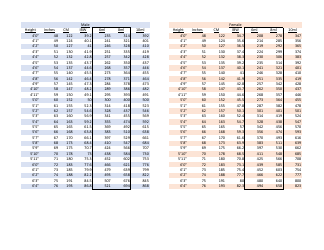
A birth weight chart is used to track and compare the weight of a newborn baby to a standard range of weights for babies of the same age and gender. It helps healthcare providers monitor the growth and development of a baby and identify any potential health issues.
The birth weight chart is typically maintained by healthcare professionals, such as doctors or nurses, who record the weight of newborn babies.
FAQ
Q: What is a birth weight chart?
A: A birth weight chart is a tool used to track the average weight of babies at different gestational ages.
Q: Why is a birth weight chart important?
A: A birth weight chart is important because it allows healthcare providers to monitor a baby's growth and development.
Q: How is a birth weight chart used?
A: A birth weight chart is used by comparing a baby's weight to the average weight for their gestational age. This helps identify any potential issues or abnormal growth patterns.
Q: What are the different percentiles on a birth weight chart?
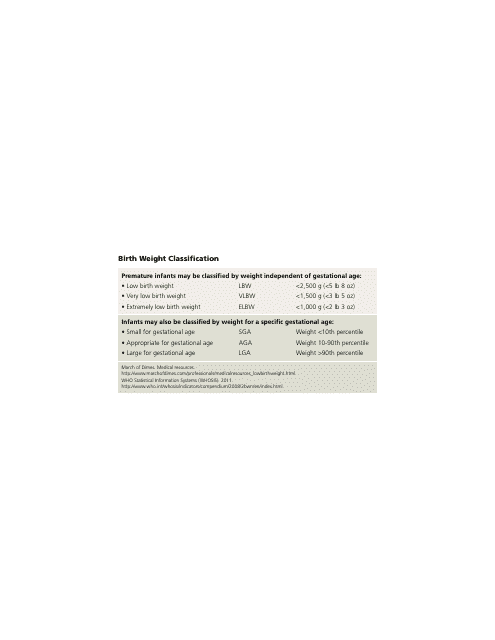
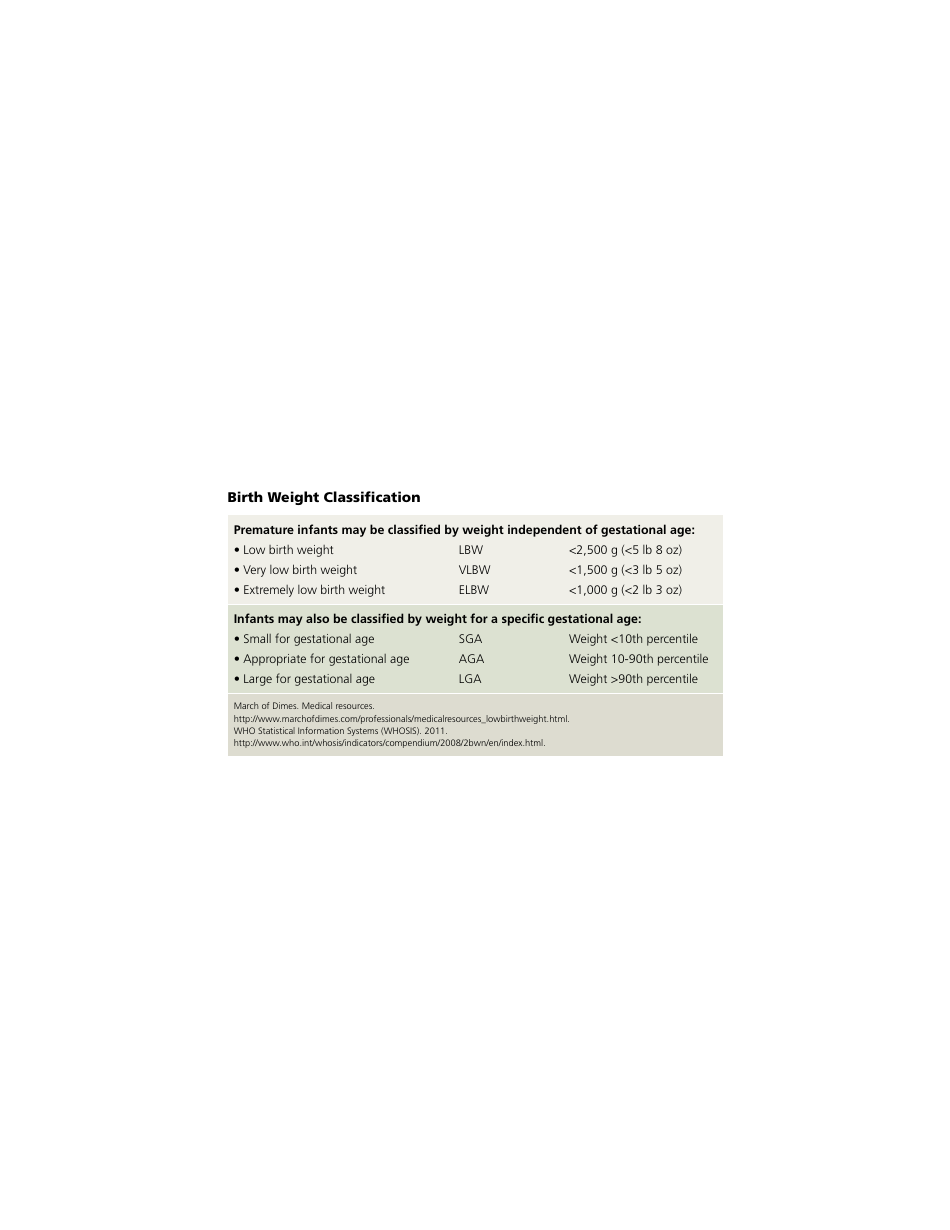
A: A birth weight chart typically includes percentiles ranging from the 10th to the 90th. This shows where a baby's weight falls compared to other babies of the same gestational age.
Q: What is considered a normal birth weight?
A: A normal birth weight for a full-term baby is typically between 5.5 and 8.8 pounds.
Q: What factors can affect a baby's birth weight?
A: Factors that can affect a baby's birth weight include genetics, maternal health, prenatal care, and gestational age.
Q: What does it mean if a baby has a low birth weight?
A: A low birth weight is typically defined as weighing less than 5.5 pounds at birth. It can be a sign of prematurity, growth restriction, or other health issues.
Q: What does it mean if a baby has a high birth weight?
A: A high birth weight is typically defined as weighing more than 8.8 pounds at birth. It can be a sign of gestational diabetes or other maternal health conditions.
Q: Can birth weight predict a baby's future growth?
A: While birth weight can provide some insight into a baby's growth, it is not a definitive predictor of future growth. Other factors, such as nutrition and genetics, also play a role.