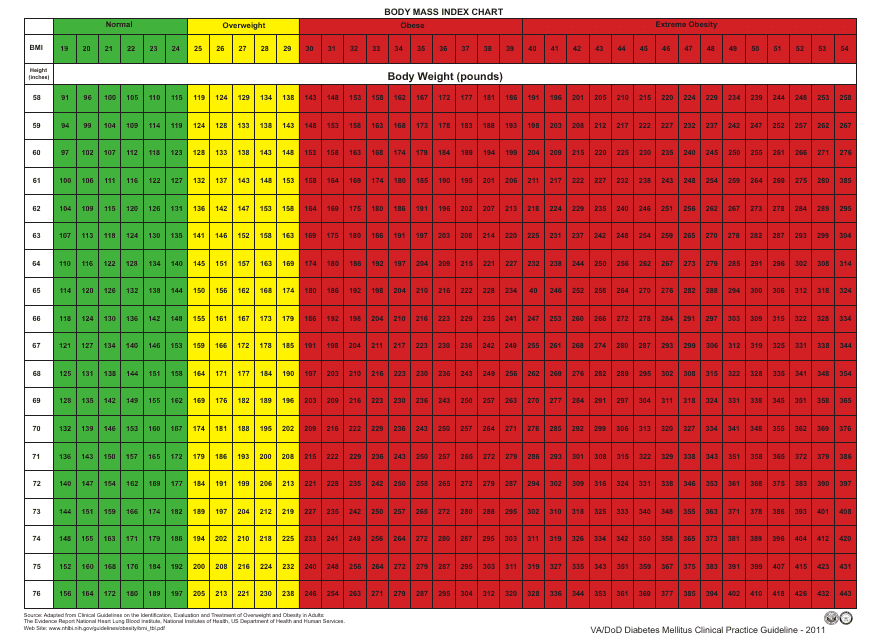
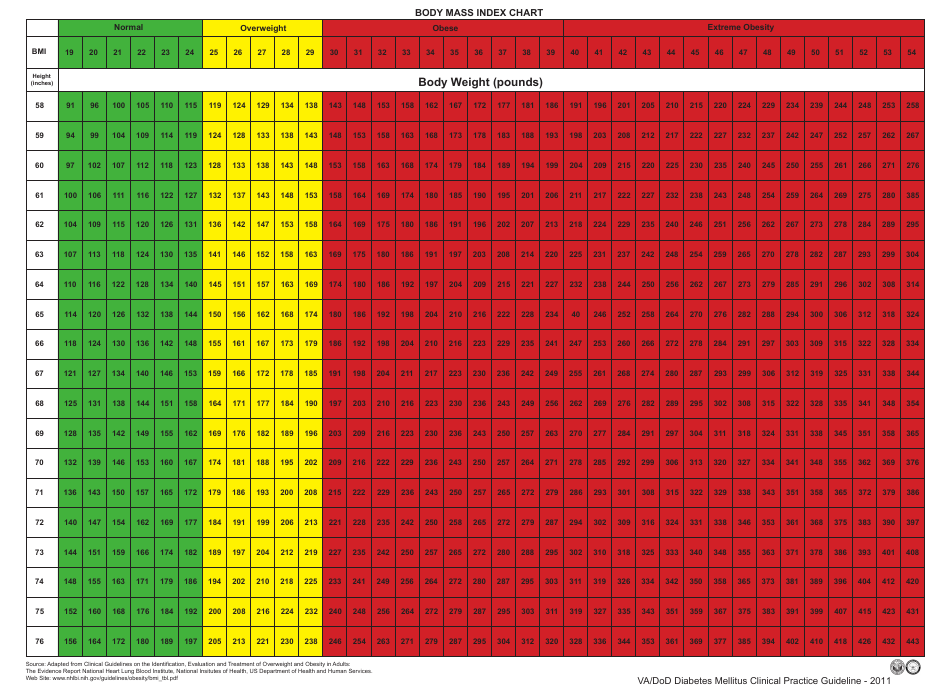
Body Mass Index Chart - Diabetes Mellitus Clinical Practice Guideline
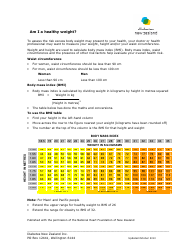
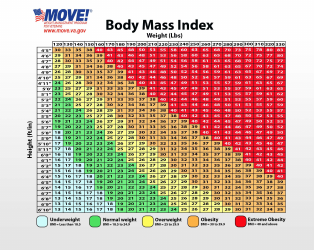
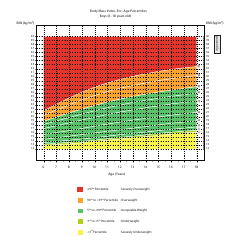
The Body Mass Index (BMI) Chart - Diabetes Mellitus Clinical Practice Guideline is used to assess the weight status of individuals and their risk for developing diabetes. It provides a range of BMI values and corresponding categories (underweight, healthy weight, overweight, and obesity) to guide healthcare professionals in identifying individuals at risk for diabetes. The guideline aims to support healthcare providers in making recommendations for prevention, diagnosis, and management of diabetes based on a person's BMI.
The organization or individuals responsible for filing the Body Mass Index Chart in the Diabetes Mellitus Clinical Practice Guideline are not specified in the document.
FAQ
Q: What is the Body Mass Index (BMI)?
A: The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on a person's height and weight.
Q: How is BMI calculated?
A: BMI is calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters.
Q: What are the different BMI categories?
A: The BMI categories are: underweight (BMI less than 18.5), normal weight (BMI 18.5-24.9), overweight (BMI 25-29.9), and obese (BMI 30 or higher).
Q: What is the significance of BMI in diabetes mellitus?
A: BMI is used as an indicator of weight status and can help identify individuals at risk for diabetes mellitus.
Q: How does BMI affect diabetes mellitus?
A: Higher BMI is associated with increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus.
Q: How can BMI be used in managing diabetes mellitus?
A: Maintaining a healthy BMI through weight management can help in the prevention and management of diabetes mellitus.
Q: What are the recommended BMI targets for individuals with diabetes mellitus?
A: For individuals with diabetes mellitus, a BMI target of less than 25 is recommended to reduce the risk of complications.
Q: Are there any limitations to using BMI?
A: BMI does not directly measure body fat percentage and may not be accurate for athletes or individuals with high muscle mass.