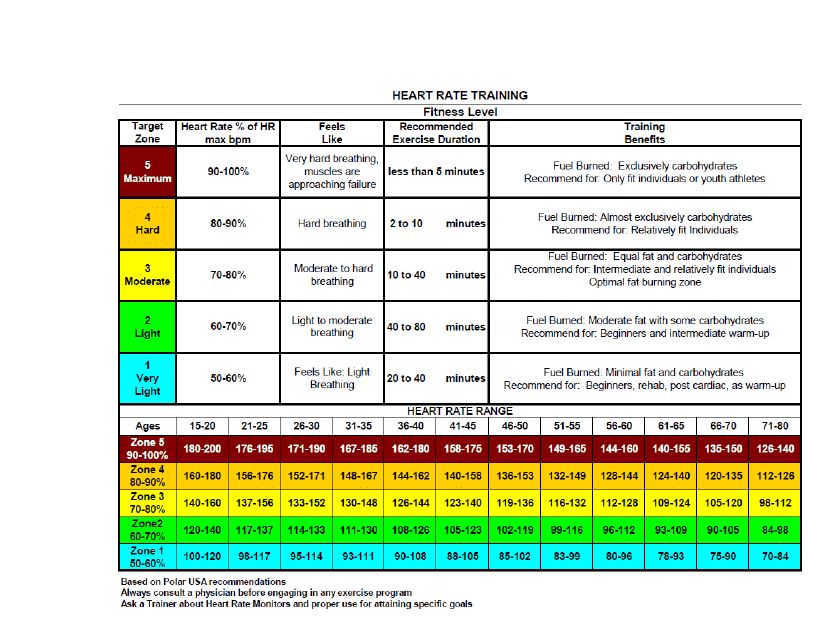
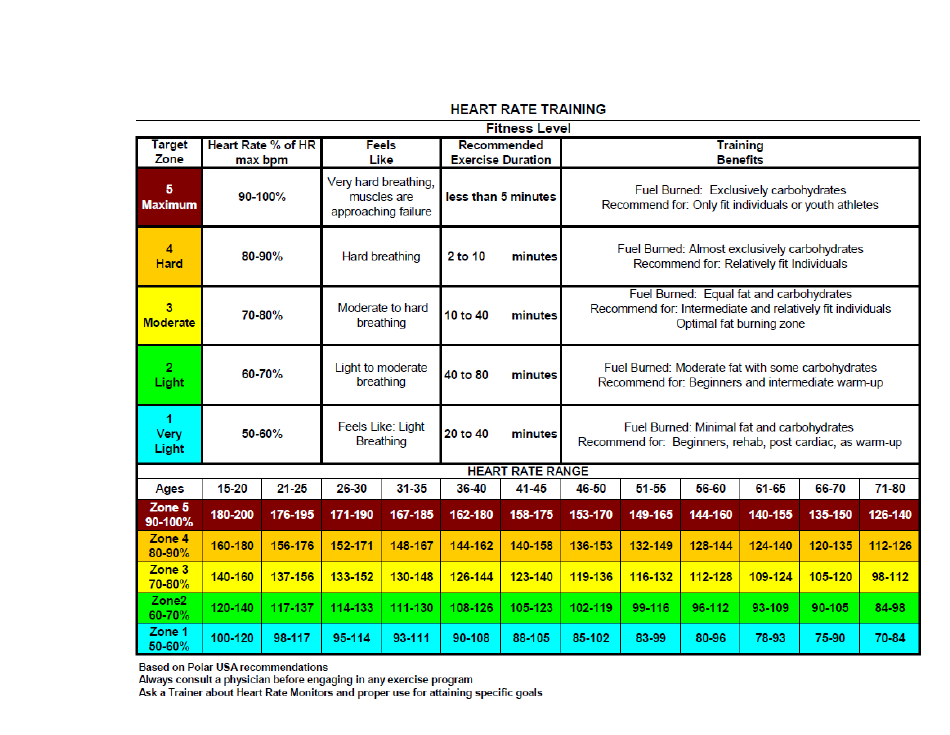
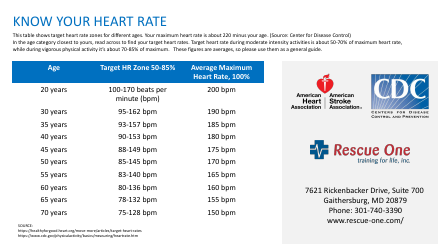
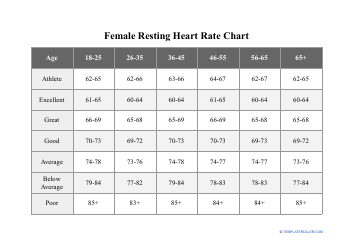
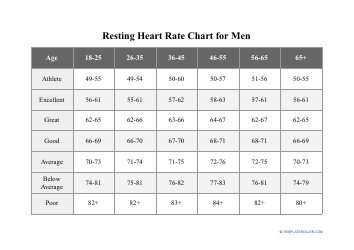
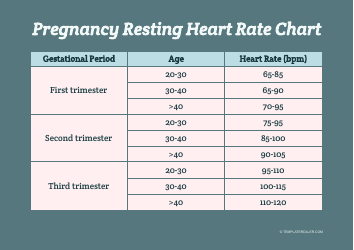
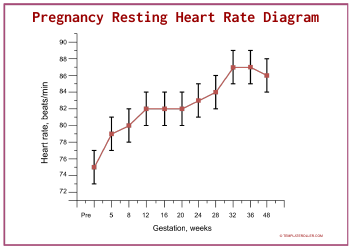
Heart Rate Training Table
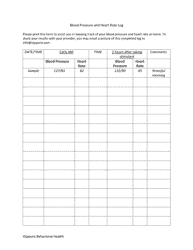
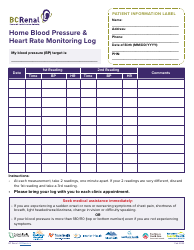
The Heart Rate Training Table is a tool used to determine target heart rate zones for effective cardiovascular exercise. It helps individuals track and monitor their heart rate to optimize their workout intensity and achieve specific fitness goals.
FAQ
Q: What is heart rate training?
A: Heart rate training is a method of exercising based on monitoring and controlling your heart rate.
Q: Why is heart rate training important?
A: Heart rate training helps you optimize your workouts by ensuring you are exercising at the right intensity for your goals.
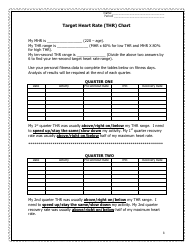
Q: How do you calculate your maximum heart rate?
A: The most commonly used formula to estimate maximum heart rate is 220 minus your age.
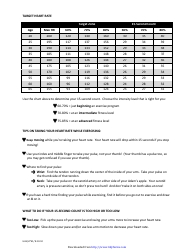
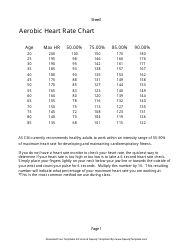
Q: What is a heart rate training table?
A: A heart rate training table is a tool used to guide you in selecting the appropriate heart rate zone for different workout intensities.
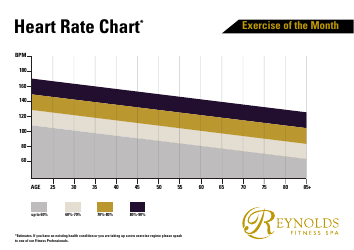
Q: What are the different heart rate zones?
A: Heart rate zones are typically divided into five zones: easy, moderate, warm-up, threshold, and maximum.
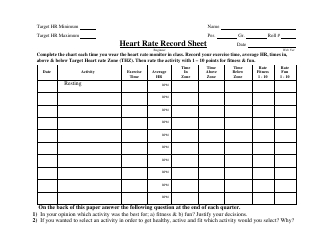
Q: How do you use a heart rate training table?
A: To use a heart rate training table, you need to know your maximum heart rate and then find the corresponding heart rate zones based on your training goals.
Q: What are the benefits of heart rate training?
A: Heart rate training can help improve cardiovascular fitness, increase endurance, burn fat, and prevent overtraining.
Q: Can anyone use heart rate training?
A: Heart rate training can be used by individuals of all fitness levels, but it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program.
Q: How often should I do heart rate training?
A: The frequency of heart rate training depends on your fitness level and goals. It is generally recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Q: Are there any risks associated with heart rate training?
A: While heart rate training is generally safe, it is important to listen to your body and not exceed your fitness level. If you experience any chest pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath, stop exercising and seek medical attention.