Macromolecule Reading Worksheet
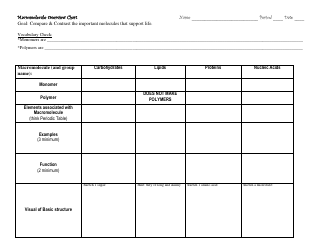
A Macromolecule Reading Worksheet is typically used to help students learn and understand the concepts and properties of macromolecules, which are large molecules essential for life processes. The worksheet may contain information and questions related to carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, and can be used for studying and revision.
FAQ
Q: What are macromolecules?
A: Macromolecules are large and complex molecules made up of smaller units called monomers.
Q: What are the four major types of macromolecules?
A: The four major types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids.
Q: What is the function of carbohydrates?
A: Carbohydrates are a source of energy and provide structural support.
Q: What is the function of proteins?
A: Proteins have a variety of functions, including enzymes catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and transporting molecules.
Q: What is the function of nucleic acids?
A: Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.
Q: What is the function of lipids?
A: Lipids serve as a source of energy, insulation, and are important for cell structure and signaling.
Q: What are monomers?
A: Monomers are the smaller subunits that make up macromolecules.
Q: What is the process of joining monomers called?
A: The process of joining monomers together to form a macromolecule is called polymerization.
Q: What is an example of a carbohydrate?
A: An example of a carbohydrate is glucose, which is a simple sugar.
Q: What is an example of a protein?
A: An example of a protein is hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood.
Q: What is an example of a nucleic acid?
A: An example of a nucleic acid is DNA, which contains genetic information.
Q: What is an example of a lipid?
A: An example of a lipid is cholesterol, which is important for cell membrane structure.