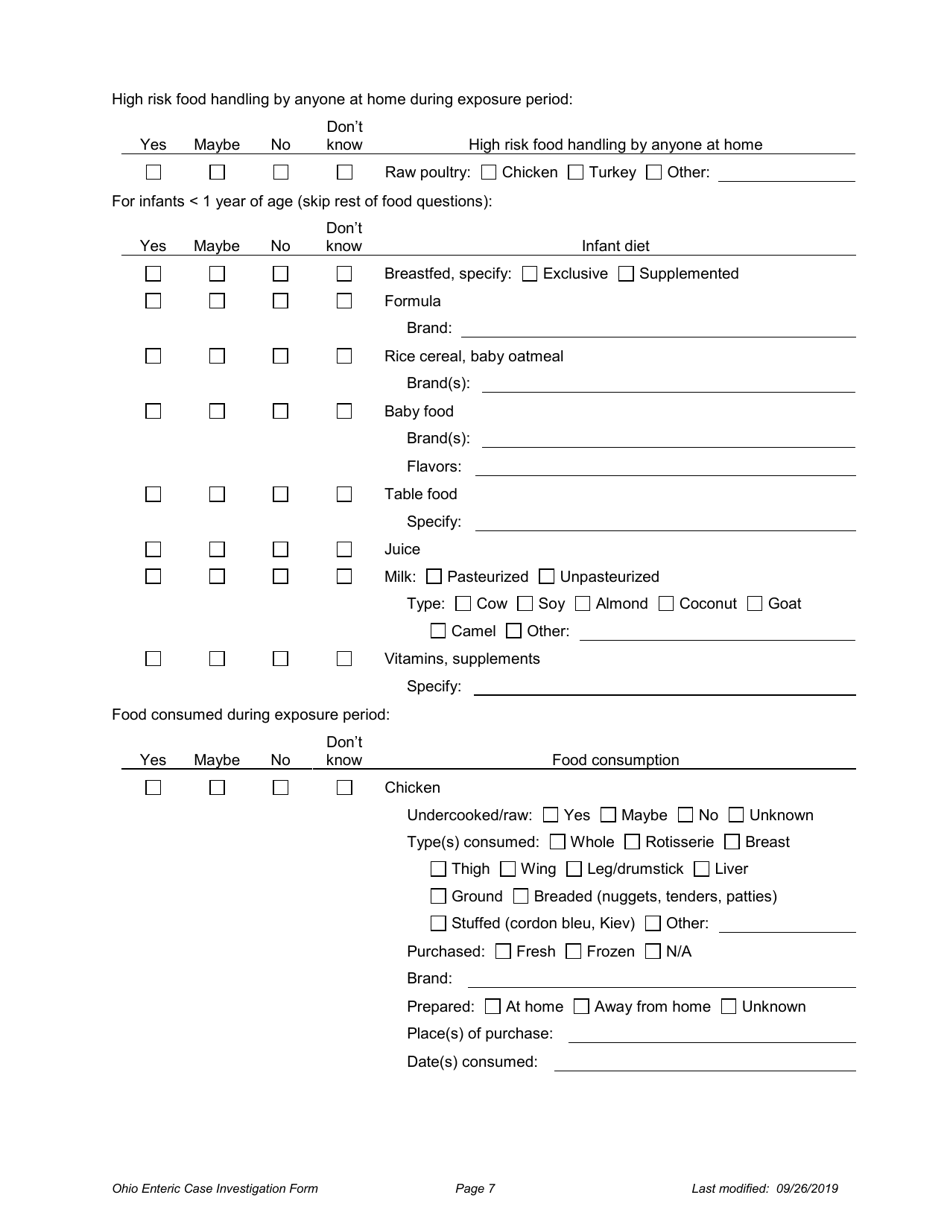
Ohio Case Investigation Form - Campylobacteriosis - Ohio
Ohio Case Investigation Form - Campylobacteriosis is a legal document that was released by the Ohio Department of Health - a government authority operating within Ohio.
FAQ
Q: What is Campylobacteriosis?
A: Campylobacteriosis is a bacterial infection caused by the Campylobacter bacteria.
Q: How is Campylobacteriosis transmitted?
A: Campylobacteriosis is usually transmitted through the consumption of contaminated food, especially raw or undercooked poultry.
Q: What are the symptoms of Campylobacteriosis?
A: Symptoms of Campylobacteriosis include diarrhea (often bloody), abdominal pain, fever, and nausea.
Q: How long does it take for symptoms to appear after exposure?
A: Symptoms of Campylobacteriosis usually appear 2-5 days after exposure, but it can take up to 10 days.
Q: Is Campylobacteriosis contagious?
A: Yes, Campylobacteriosis can be contagious. It can spread from person to person through fecal-oral transmission.
Q: How is Campylobacteriosis diagnosed?
A: Campylobacteriosis is diagnosed through a stool sample test.
Q: How is Campylobacteriosis treated?
A: Most cases of Campylobacteriosis resolve on their own without treatment. In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Q: How can Campylobacteriosis be prevented?
A: Campylobacteriosis can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, thoroughly cooking food (especially poultry), and avoiding cross-contamination of raw and cooked foods.
Form Details:
- Released on September 26, 2019;
- The latest edition currently provided by the Ohio Department of Health;
- Ready to use and print;
- Easy to customize;
- Compatible with most PDF-viewing applications;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a printable version of the form by clicking the link below or browse more documents and templates provided by the Ohio Department of Health.