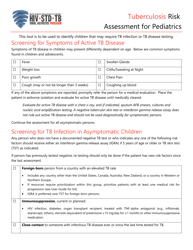
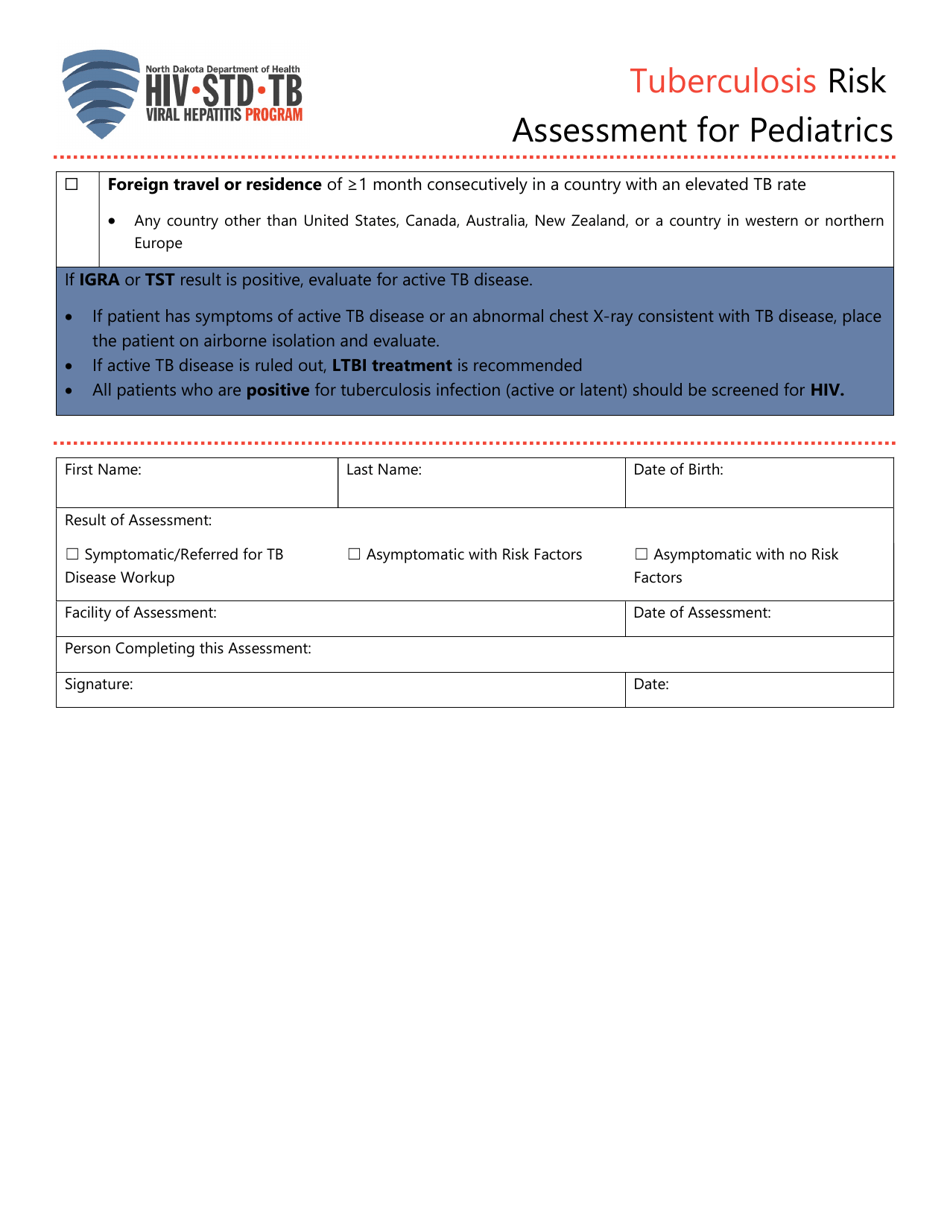
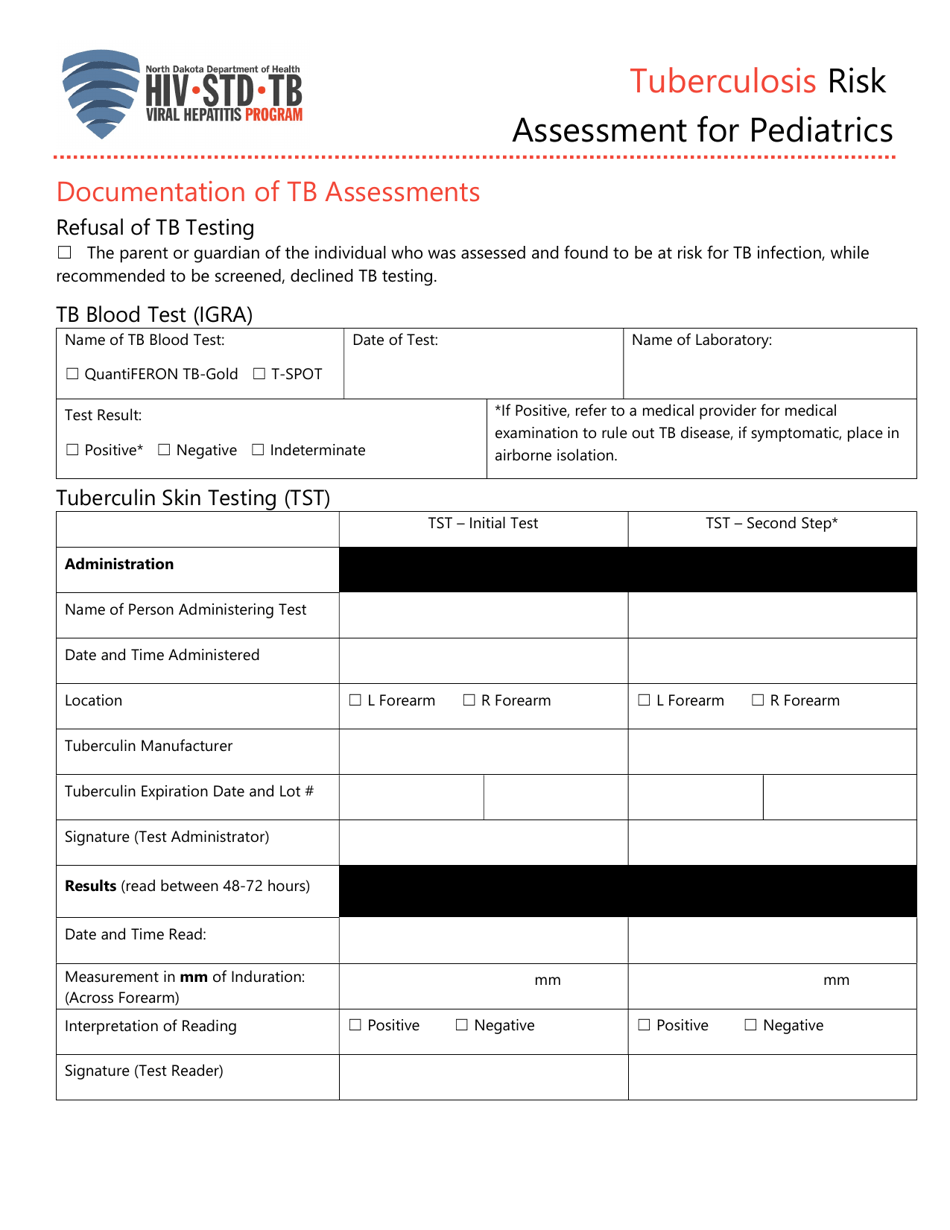
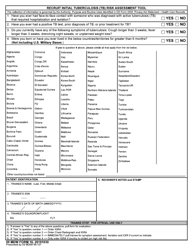
Tuberculosis Risk Assessment for Pediatrics - North Dakota
Tuberculosis Risk Assessment for Pediatrics is a legal document that was released by the North Dakota Department of Health and Human Services - a government authority operating within North Dakota.
FAQ
Q: What is tuberculosis?
A: Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body.
Q: How is tuberculosis spread?
A: TB is spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, releasing bacteria into the air.
Q: What are the symptoms of tuberculosis?
A: Common symptoms of TB include coughing for more than 3 weeks, chest pain, weakness, weight loss, fever, and night sweats.
Q: Who is at higher risk for tuberculosis?
A: People with weak immune systems, such as infants, elderly individuals, and those with certain medical conditions, are at higher risk for developing TB.
Q: How is tuberculosis diagnosed?
A: TB is diagnosed through a combination of tests, including a physical exam, medical history, chest X-ray, and a test to detect the presence of TB bacteria.
Q: Can tuberculosis be treated?
A: Yes, TB can be treated with a combination of antibiotics for a specific duration, usually 6 to 9 months.
Q: How can tuberculosis be prevented?
A: Preventing tuberculosis involves identifying and treating infected individuals, promoting good hygiene practices, and ensuring vaccination with the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine in high-risk populations.
Q: Is tuberculosis common in North Dakota?
A: TB rates in North Dakota are generally low, but cases can still occur, especially in individuals with risk factors.
Form Details:
- The latest edition currently provided by the North Dakota Department of Health and Human Services;
- Ready to use and print;
- Easy to customize;
- Compatible with most PDF-viewing applications;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a printable version of the form by clicking the link below or browse more documents and templates provided by the North Dakota Department of Health and Human Services.