Tds and Ph - Safe Drinking Water Foundation
TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids and pH is a measurement of acidity or alkalinity. The Safe Drinking Water Foundation may use TDS and pH measurements to ensure that drinking water meets quality standards.
FAQ
Q: What is TDS?
A: TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids. It refers to the total amount of dissolved substances in water, including minerals, salts, and other organic matter.
Q: Why is TDS important in drinking water?
A: TDS can affect the taste, odor, and appearance of water. High TDS levels can also indicate the presence of contaminants, such as lead or arsenic.
Q: What is the acceptable TDS level for drinking water?
A: The acceptable TDS level for drinking water is generally below 500 mg/L (milligrams per liter), as recommended by the Safe Drinking Water Foundation.
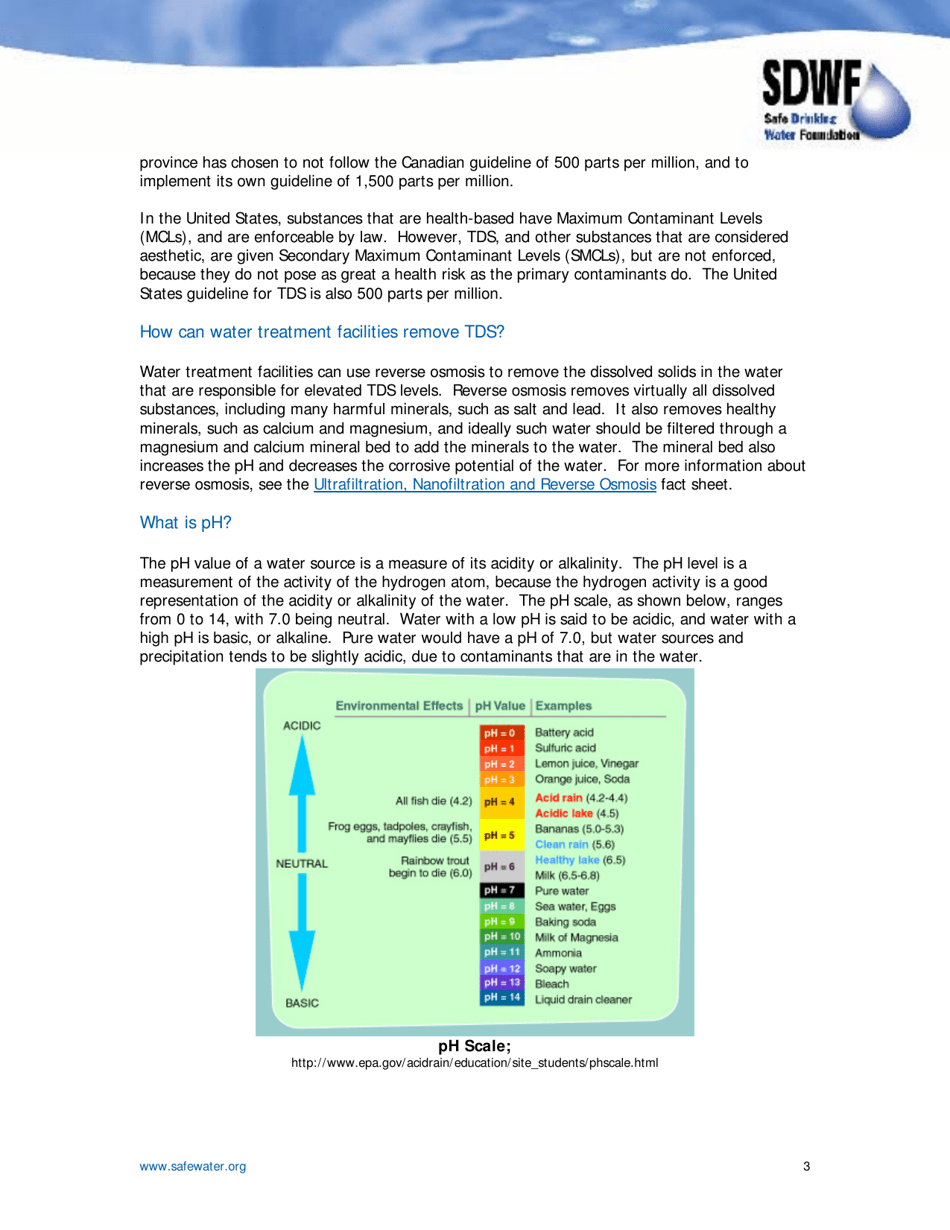
Q: What is pH?
A: pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of water. It indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in the water.
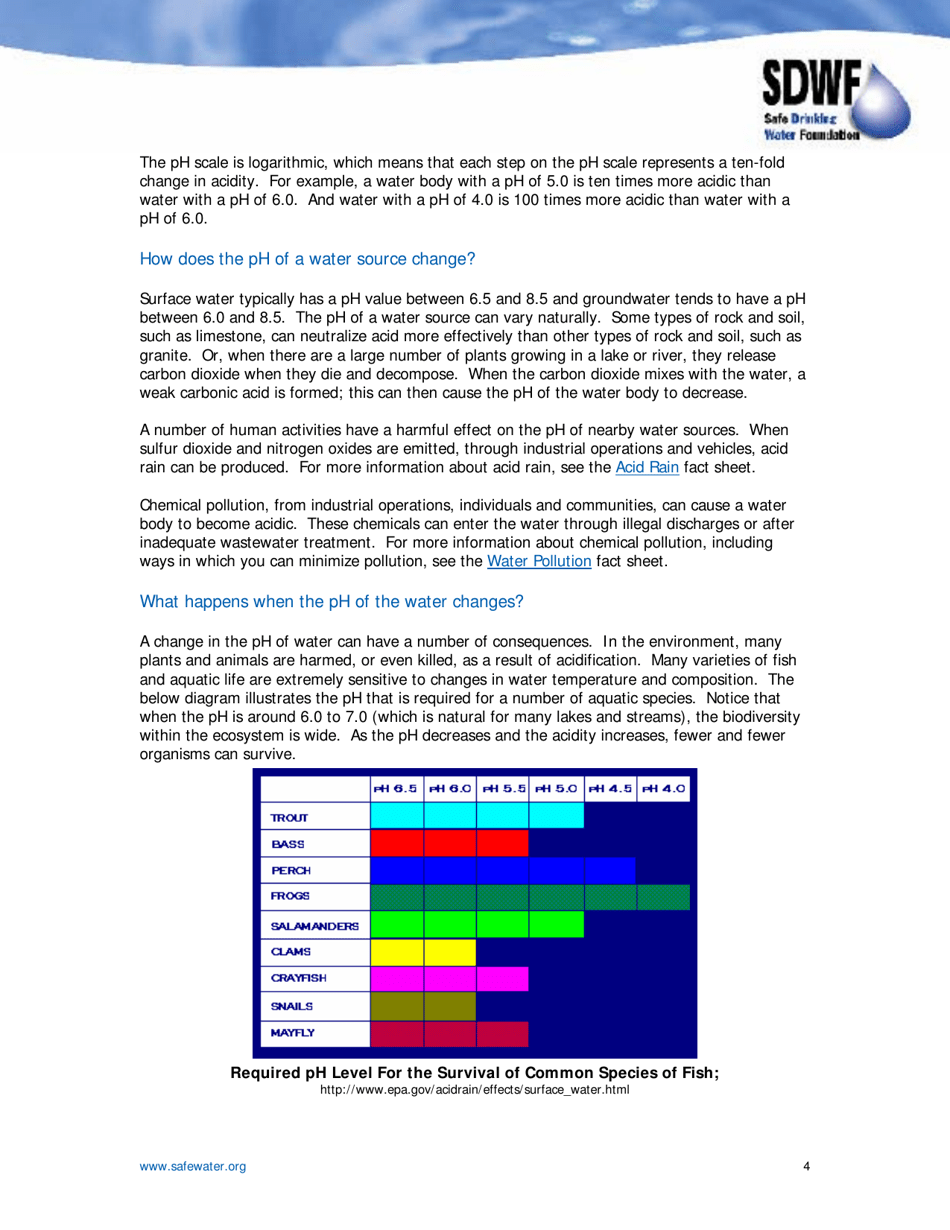
Q: Why is pH important in drinking water?
A: pH can affect the taste, corrosiveness, and effectiveness of disinfection processes in water. It also plays a role in the solubility of minerals and chemicals.
Q: What is the ideal pH range for drinking water?
A: The ideal pH range for drinking water is between 6.5 and 8.5, as recommended by the Safe Drinking Water Foundation.