Standard Operating Procedures for Hot Holding - Alaska
Standard Operating Procedures for Hot Holding is a legal document that was released by the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation - a government authority operating within Alaska.
FAQ
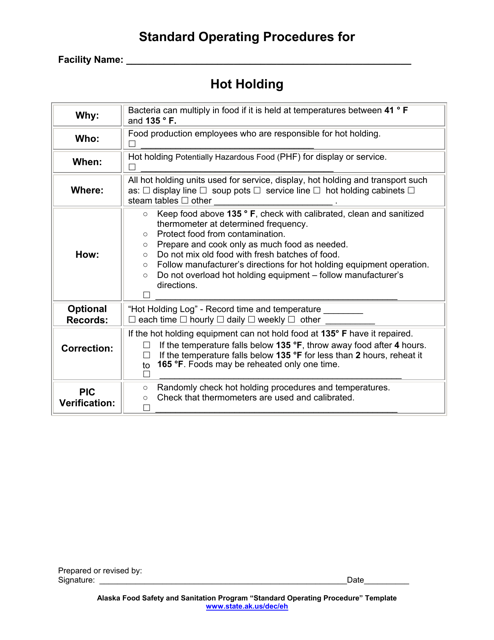
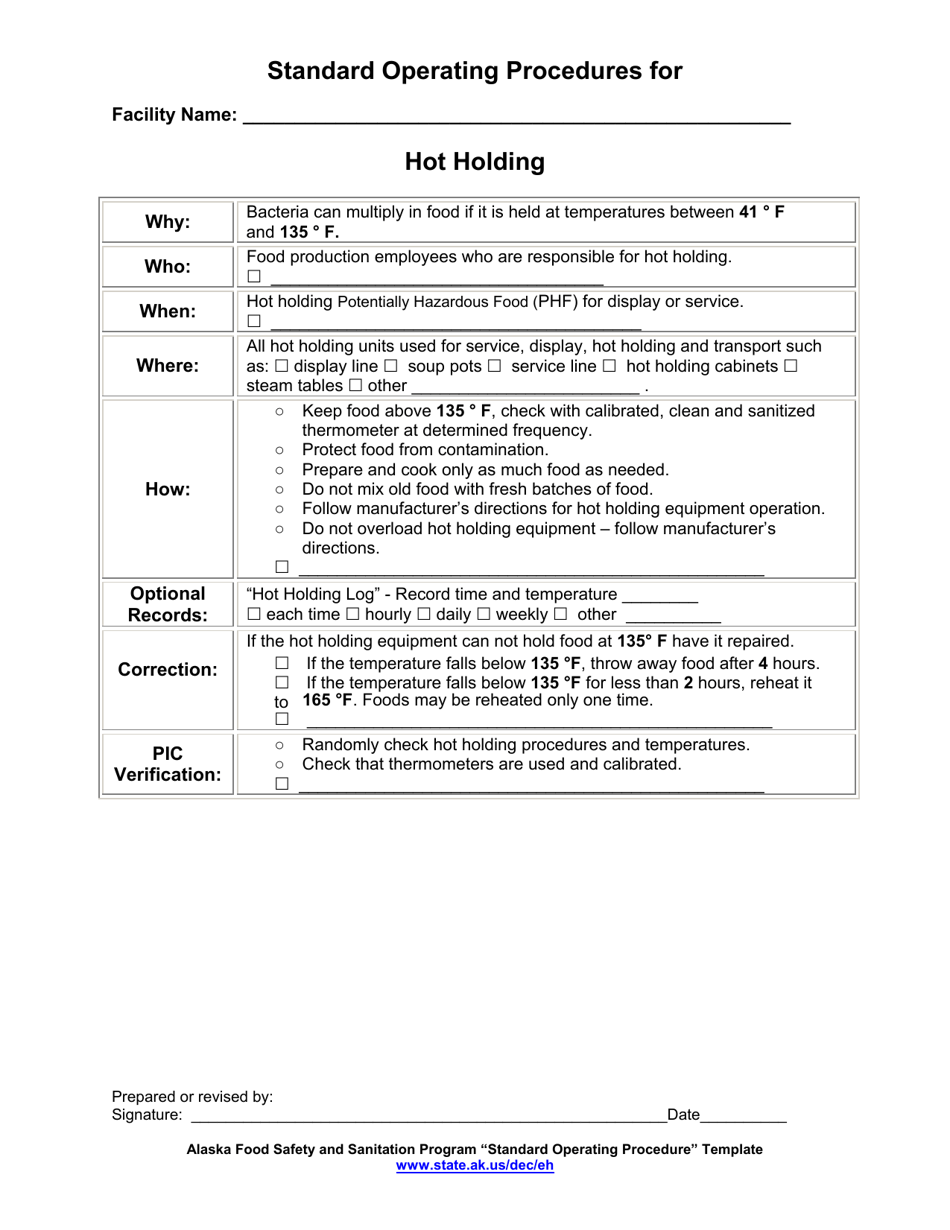
Q: What are hot holding procedures?
A: Hot holding procedures are guidelines for safely storing and maintaining cooked food at a temperature that prevents bacterial growth.
Q: Why is hot holding important?
A: Hot holding is important to prevent the growth of bacteria in cooked food, which can cause foodborne illnesses.
Q: What is the recommended temperature for hot holding?
A: The recommended temperature for hot holding is 135°F (57°C) or above.
Q: How long can food be safely hot held?
A: Food can be safely hot held for a maximum of four hours.
Q: What should be done with leftover hot held food?
A: Leftover hot held food should be discarded after four hours to ensure food safety.
Q: What should be done if the hot holding temperature falls below 135°F?
A: If the hot holding temperature falls below 135°F, the food should be reheated to 165°F (74°C) and then returned to the hot holding unit.
Q: Can food be reheated and hot held multiple times?
A: No, food should not be reheated and hot held multiple times. It should be discarded after the initial hot holding period.
Q: Can hot held food be mixed with fresh food?
A: Hot held food should not be mixed with fresh food, as it can contaminate the fresh food with bacteria.
Q: Are there any exceptions to the hot holding time limit?
A: Yes, there are some exceptions for certain types of food, such as whole roasts, that can be hot held for longer periods if certain conditions are met.
Q: Who is responsible for following hot holding procedures?
A: It is the responsibility of food handlers and operators of food establishments to follow hot holding procedures to ensure food safety.
Form Details:
- The latest edition currently provided by the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation;
- Ready to use and print;
- Easy to customize;
- Compatible with most PDF-viewing applications;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a printable version of the form by clicking the link below or browse more documents and templates provided by the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation.