Community Eligibility: Making High-Poverty Schools Hunger Free - Frac
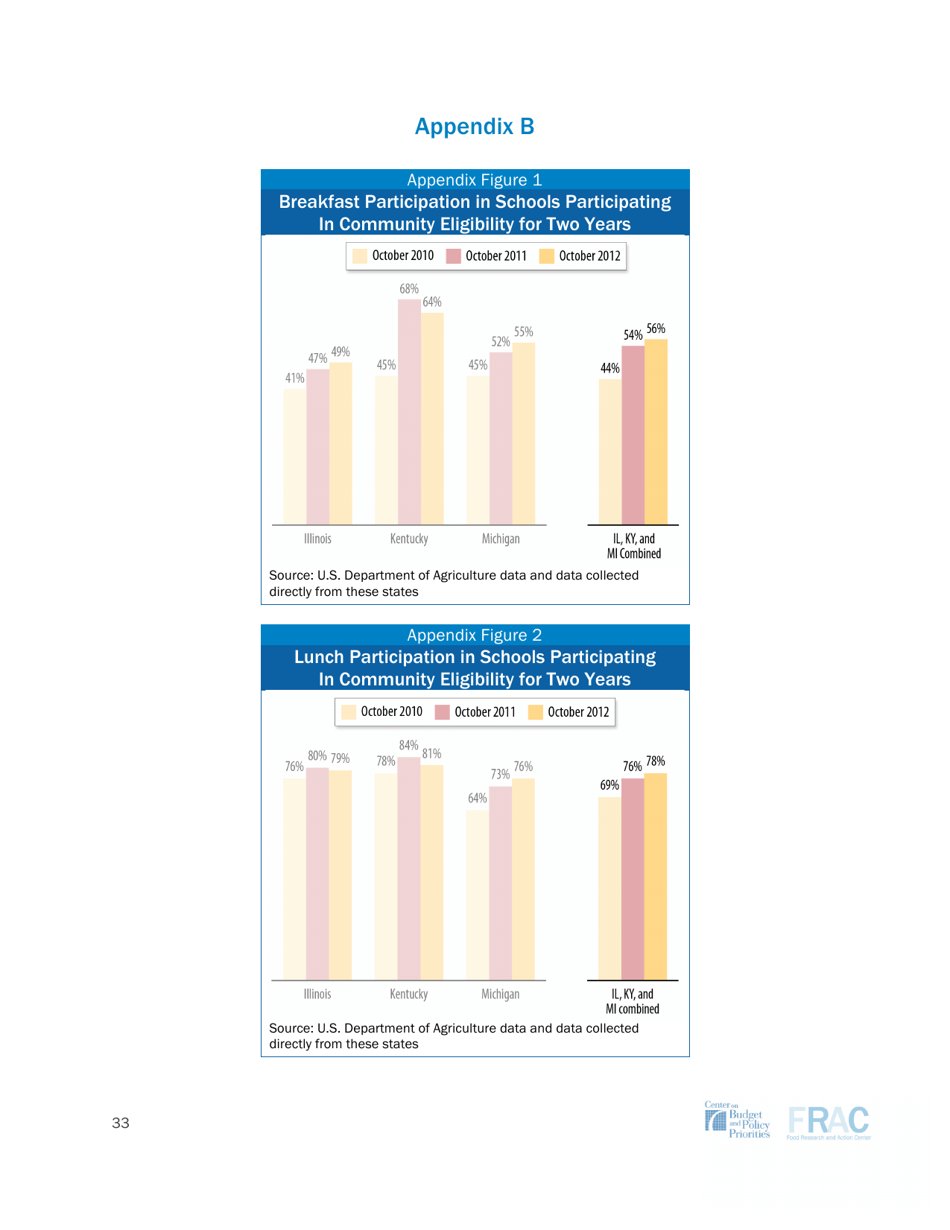
The Community Eligibility Provision (CEP) is a program introduced by the USDA. It allows high-poverty schools to provide free breakfast and lunch to all students, regardless of their families' income. It aims to reduce food insecurity and ensure that all students have access to nutritious meals at school.
The Community Eligibility program is filed by schools and school districts. The Food Research & Action Center (FRAC) provides resources and information to support schools in implementing the program.
FAQ
Q: What is community eligibility?
A: Community eligibility is a program that allows high-poverty schools to provide free breakfast and lunch to all students without requiring individual applications.
Q: Who is eligible for community eligibility?
A: Schools with a high percentage of low-income students are eligible for community eligibility.
Q: How does community eligibility work?
A: Community eligibility works by using information from other programs, such as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) and Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF), to determine the number of low-income students in a school.
Q: Why is community eligibility important?
A: Community eligibility is important because it helps ensure that all students have access to healthy meals, regardless of their family's income.
Q: What are the benefits of community eligibility?
A: The benefits of community eligibility include reducing paperwork for families and school administrators, increasing participation in school meal programs, and reducing the stigma associated with free meals.
Q: Are there any drawbacks to community eligibility?
A: Some potential drawbacks of community eligibility include the need for schools to have a high percentage of low-income students to qualify, and the potential for reduced funding for schools that rely on meal reimbursements.