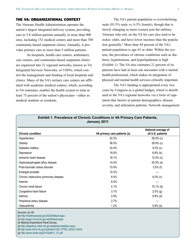
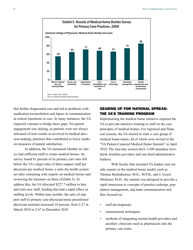
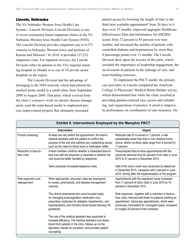
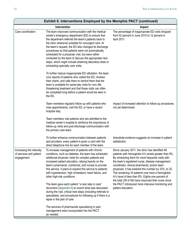
The Veterans Health Administration: Implementing Patient-Centered Medical Homes in the Nation's Largest Integrated Delivery System - the Commonwealth Fund Case Study
The Commonwealth Fund case study is about implementing patient-centered medical homes in the Veterans Health Administration, which is the largest integrated delivery system in the country. It examines the efforts and outcomes of this implementation.
The Commonwealth Fund files The Veterans Health Administration: Implementing Patient-Centered Medical Homes in the Nation's Largest Integrated Delivery System case study.
FAQ
Q: What is the Veterans Health Administration?
A: The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is a part of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and is responsible for providing healthcare services to eligible military veterans.
Q: What is a patient-centered medical home?
A: A patient-centered medical home is a model of primary care that provides comprehensive, coordinated, and patient-centered care with a focus on prevention and disease management.
Q: Why did the Veterans Health Administration implement patient-centered medical homes?
A: The VHA implemented patient-centered medical homes to improve the quality and coordination of care for veterans, enhance access to healthcare services, and increase patient satisfaction.
Q: What are the benefits of patient-centered medical homes?
A: Patient-centered medical homes have been shown to improve patient outcomes, enhance patient experience, reduce healthcare costs, and increase healthcare efficiency.
Q: How did the Veterans Health Administration implement patient-centered medical homes?
A: The VHA implemented patient-centered medical homes by redesigning its primary care clinics, adopting health information technology, and implementing care coordination strategies.
Q: Was the implementation of patient-centered medical homes successful in the Veterans Health Administration?
A: Yes, the implementation of patient-centered medical homes in the VHA has been successful, resulting in improved quality of care, enhanced access to care, and increased patient satisfaction.