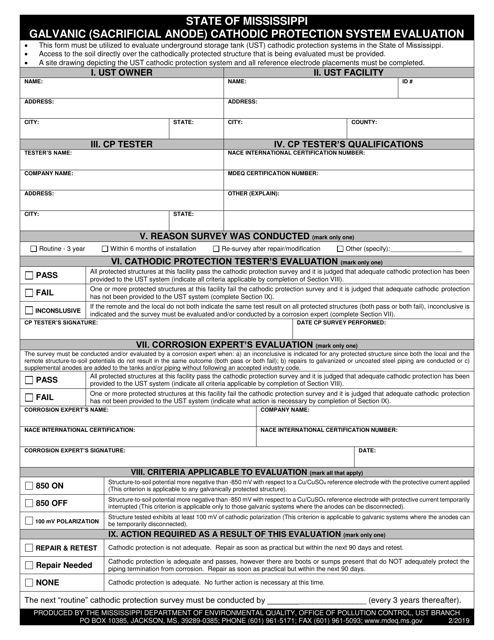
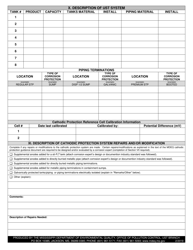
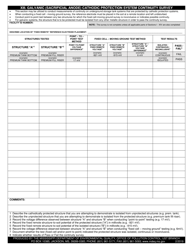
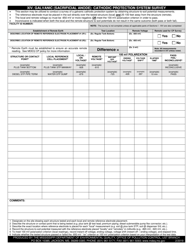
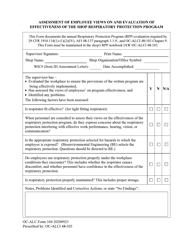
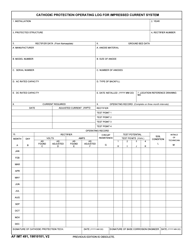
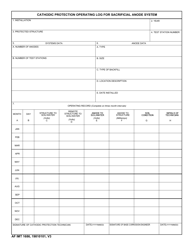
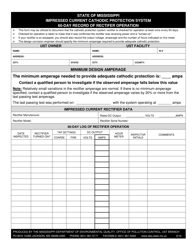
Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System Evaluation - Mississippi
Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System Evaluation is a legal document that was released by the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality - a government authority operating within Mississippi.
FAQ
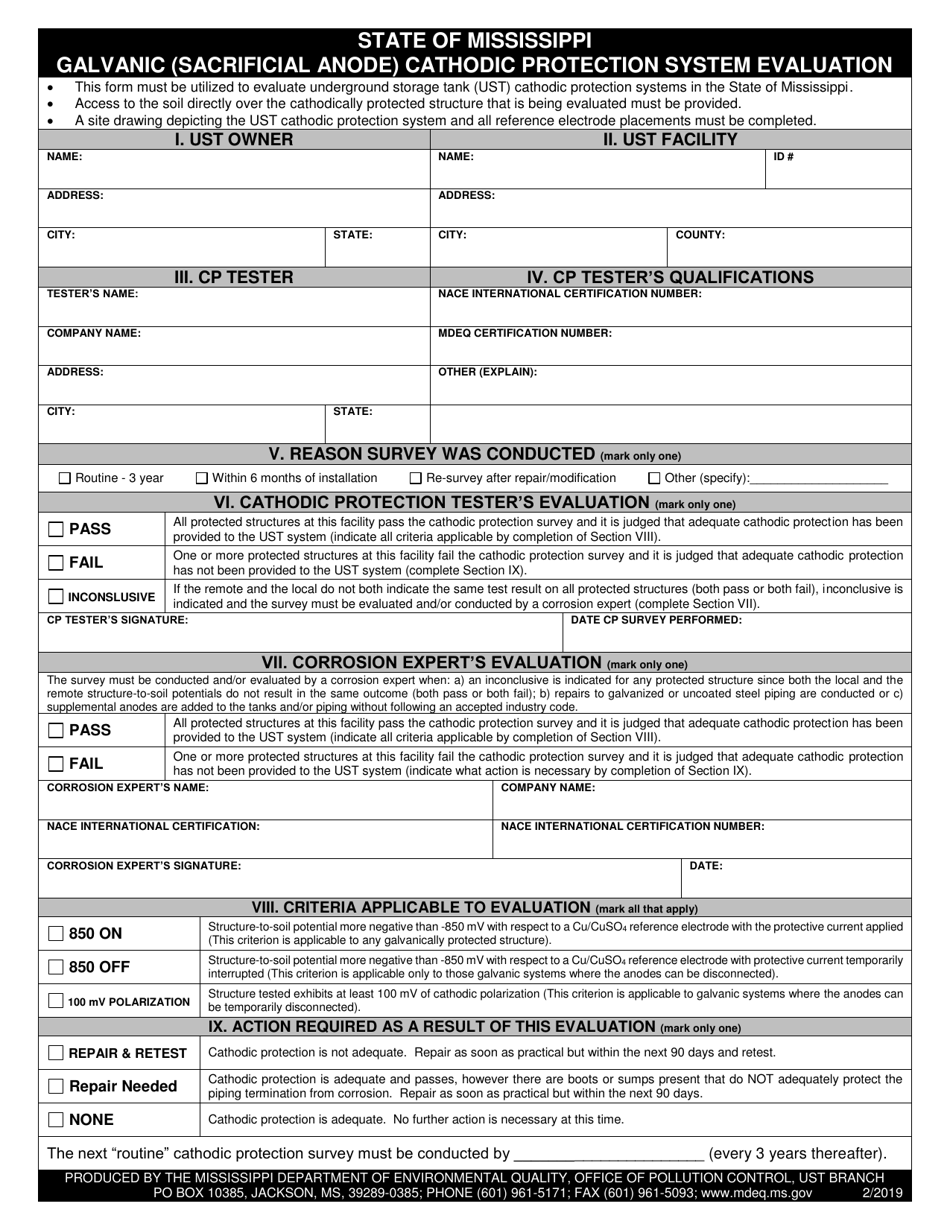
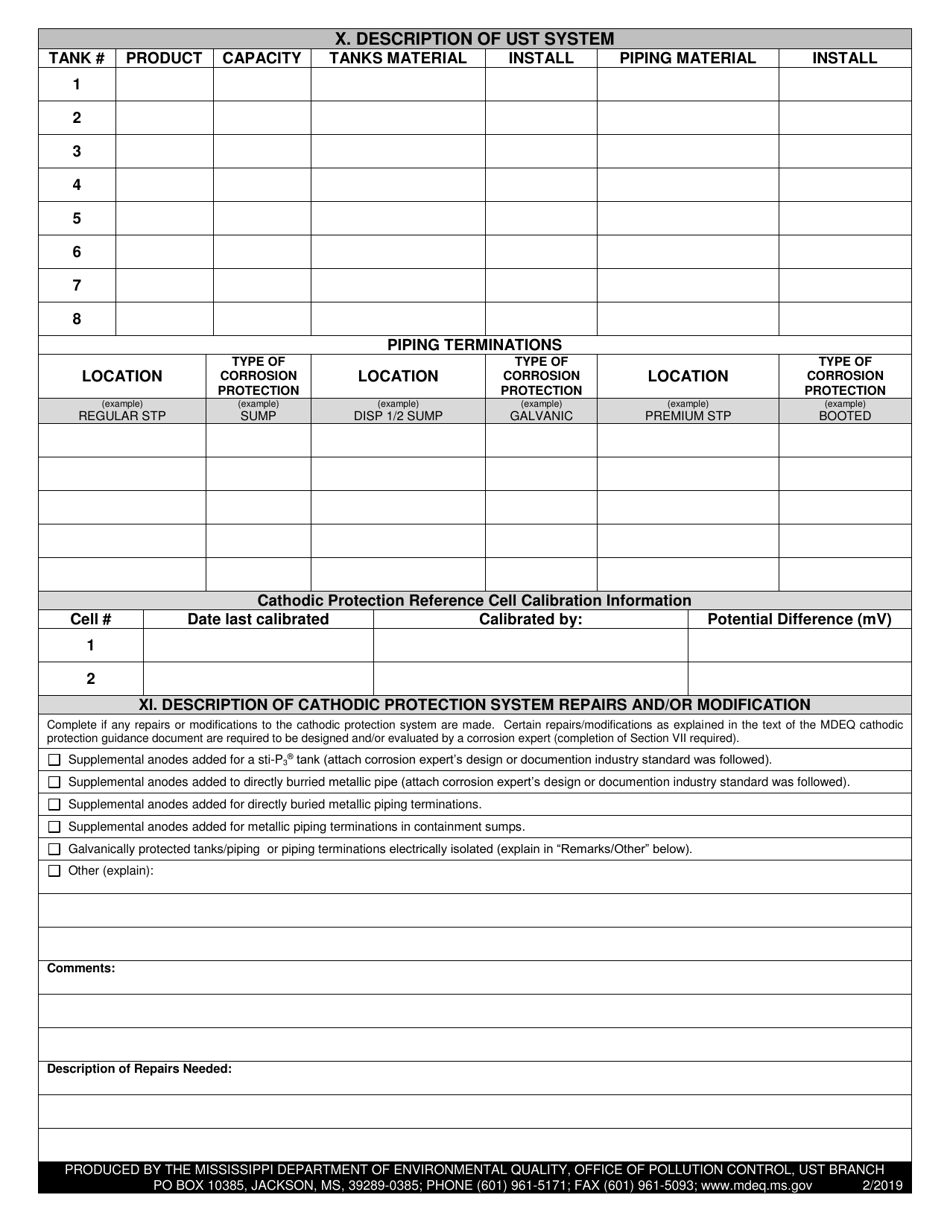
Q: What is a Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System?
A: A Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System is a method used to protect metal structures from corrosion by using a more reactive metal as an anode to corrode instead of the protected metal.
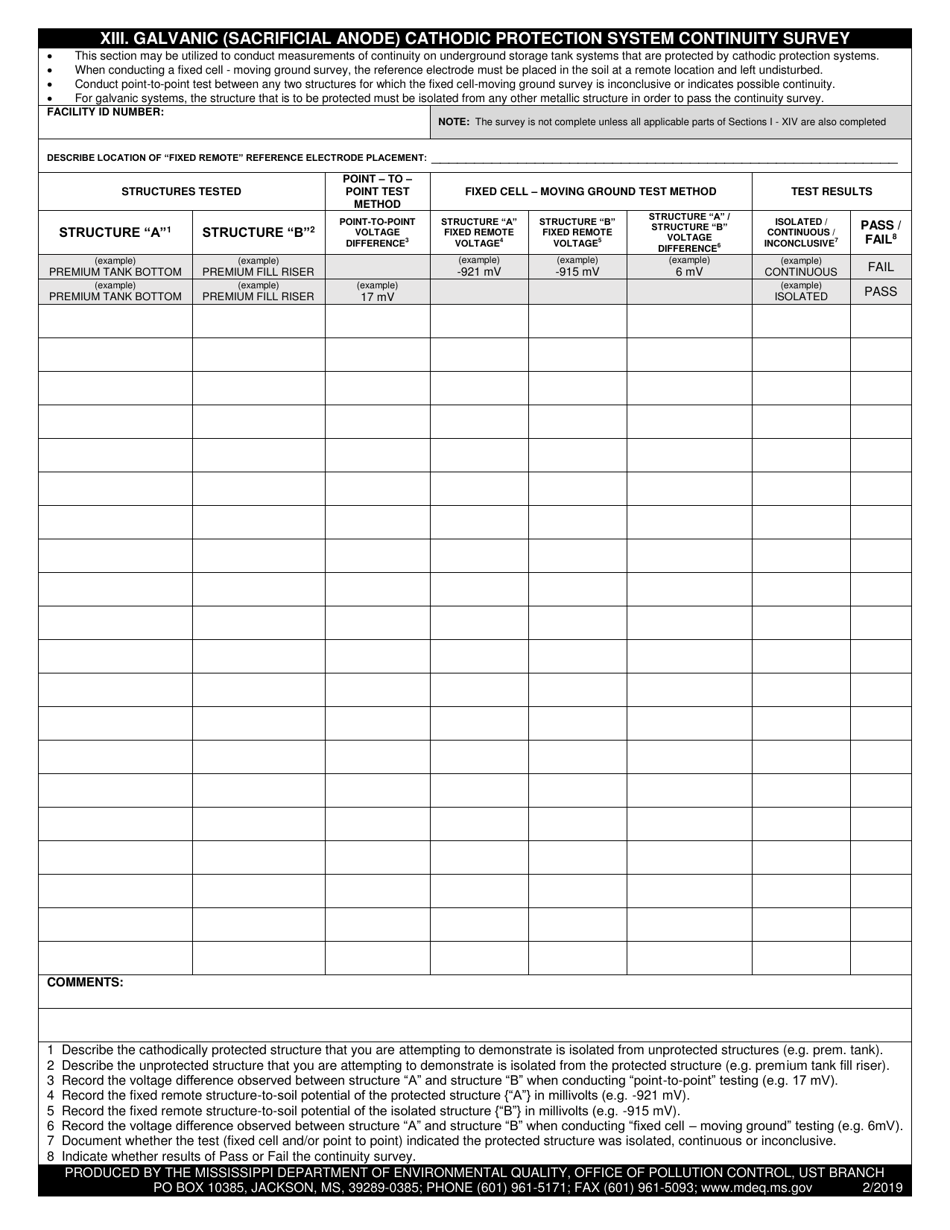
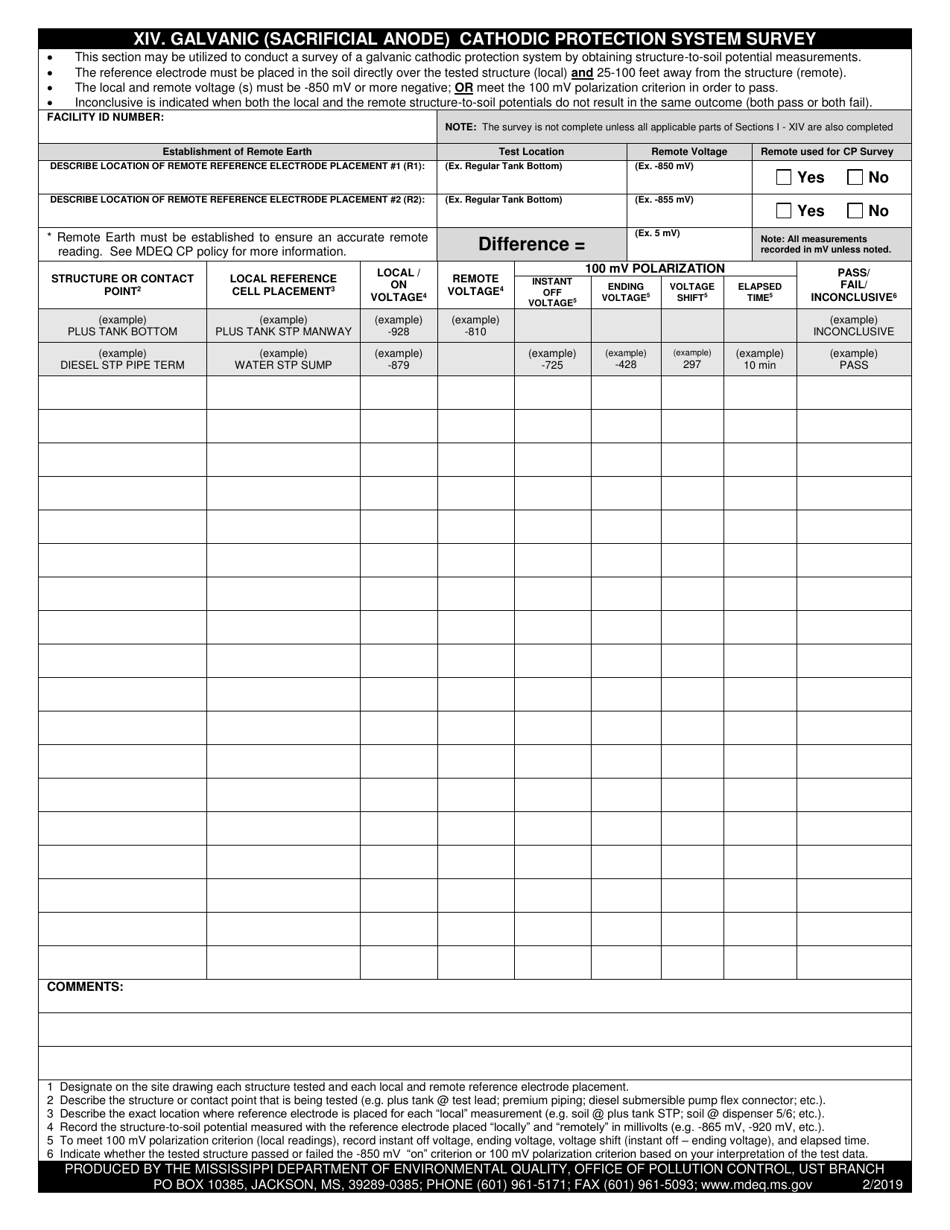
Q: How does a Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System work?
A: The more reactive metal, referred to as the sacrificial anode, is connected to the metal structure to be protected. When the galvanic couple is in contact with an electrolyte (usually soil or water), the anode corrodes sacrificially, thus protecting the structure.
Q: What is the purpose of a Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System?
A: The purpose of a Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System is to prevent or minimize corrosion on metal structures, such as pipelines, underground tanks, or offshore platforms, by sacrificing a more reactive metal.
Q: Why is a Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System evaluated in Mississippi?
A: The evaluation of a Galvanic (Sacrificial Anode) Cathodic Protection System in Mississippi is likely conducted to assess its effectiveness in protecting metal structures from corrosion in the specific environmental conditions of the state.
Form Details:
- Released on February 1, 2019;
- The latest edition currently provided by the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality;
- Ready to use and print;
- Easy to customize;
- Compatible with most PDF-viewing applications;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a fillable version of the form by clicking the link below or browse more documents and templates provided by the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality.