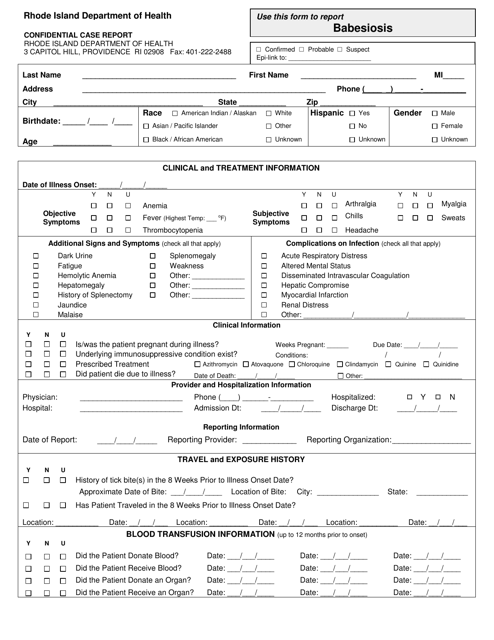
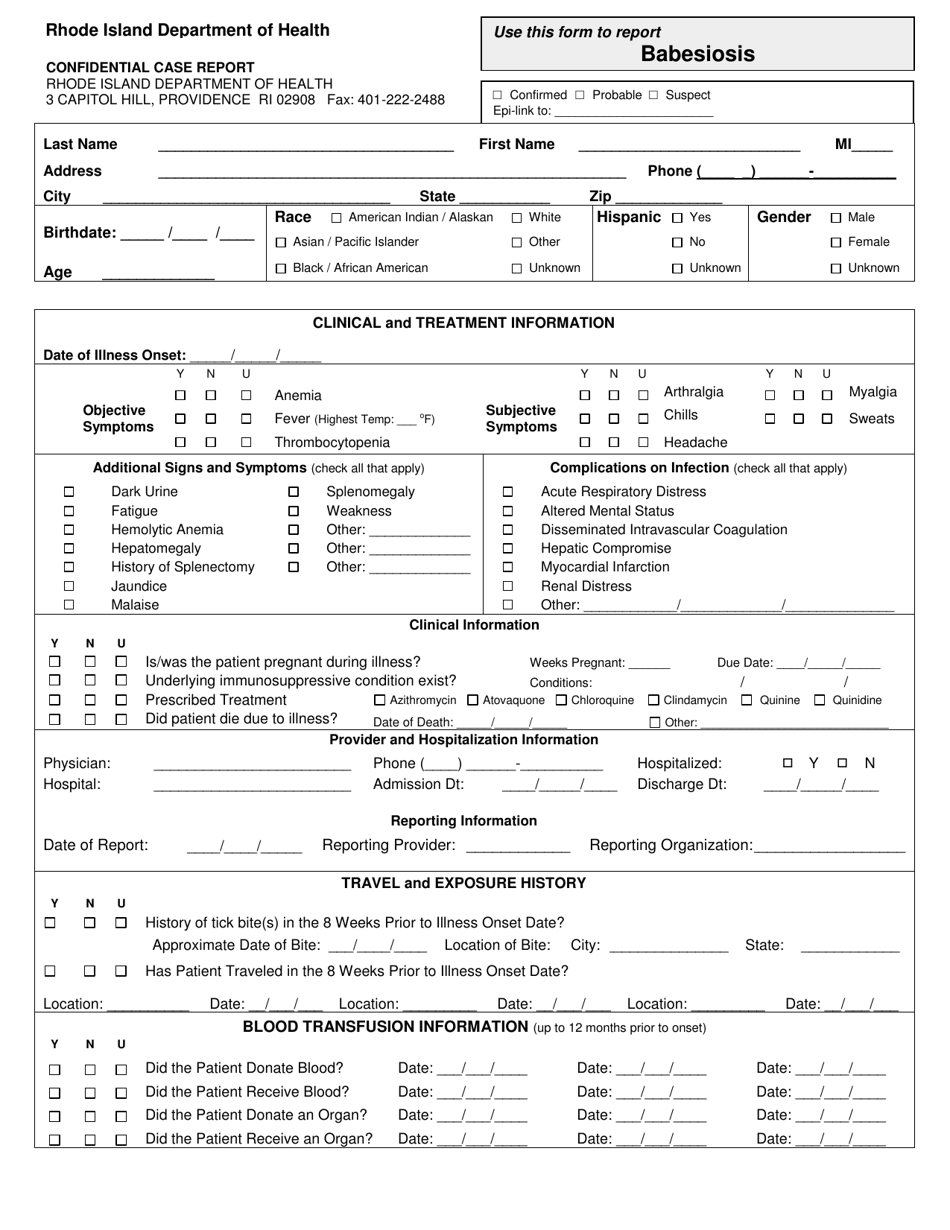
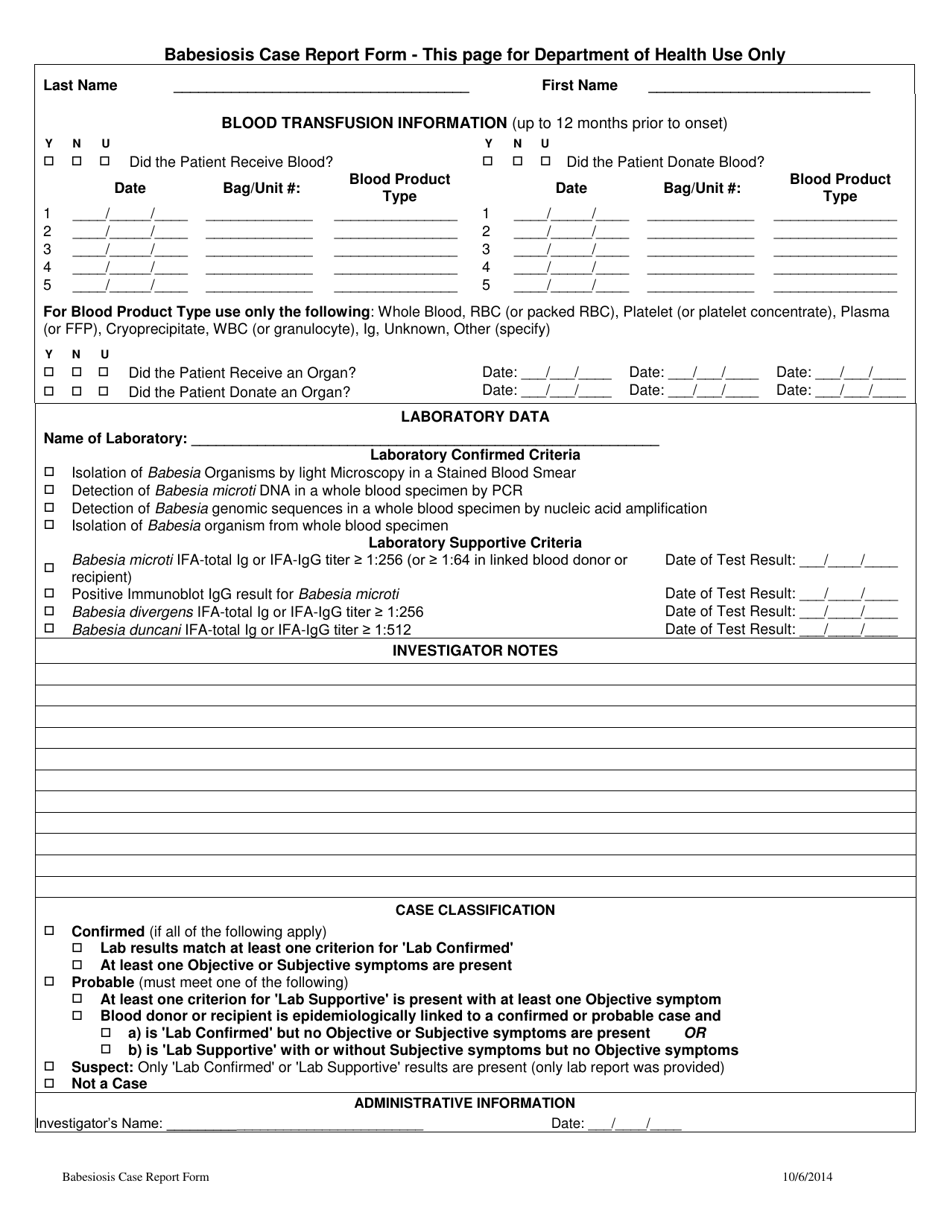
Confidential Case Report - Babesiosis - Rhode Island
Confidential Case Report - Babesiosis is a legal document that was released by the Rhode Island Department of Health - a government authority operating within Rhode Island.
FAQ
Q: What is babesiosis?
A: Babesiosis is a tick-borne disease caused by microscopic parasites that infect red blood cells.
Q: How is babesiosis transmitted?
A: Babesiosis is most commonly transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks.
Q: What are the symptoms of babesiosis?
A: Symptoms of babesiosis can include fever, fatigue, muscle aches, and anemia.
Q: Is babesiosis common in Rhode Island?
A: Babesiosis is relatively rare in Rhode Island, but cases have been reported.
Q: How is babesiosis diagnosed?
A: Babesiosis is diagnosed through laboratory tests that detect the presence of the parasite in blood samples.
Q: What is the treatment for babesiosis?
A: Babesiosis is usually treated with a combination of antibiotics.
Q: Can babesiosis be prevented?
A: Prevention of babesiosis involves avoiding tick bites and using insect repellent when in tick-infested areas.
Q: Is babesiosis contagious?
A: Babesiosis cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Q: Are there any long-term complications of babesiosis?
A: In some cases, babesiosis can cause serious complications, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Form Details:
- Released on October 6, 2014;
- The latest edition currently provided by the Rhode Island Department of Health;
- Ready to use and print;
- Easy to customize;
- Compatible with most PDF-viewing applications;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a printable version of the form by clicking the link below or browse more documents and templates provided by the Rhode Island Department of Health.