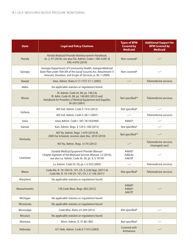
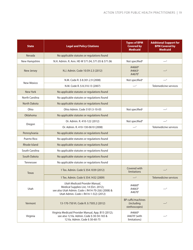
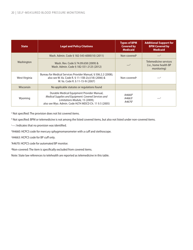
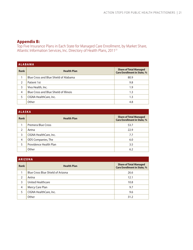
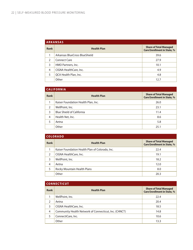
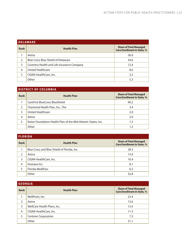
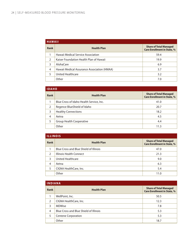
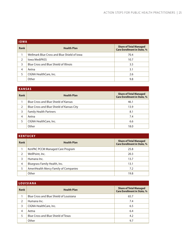
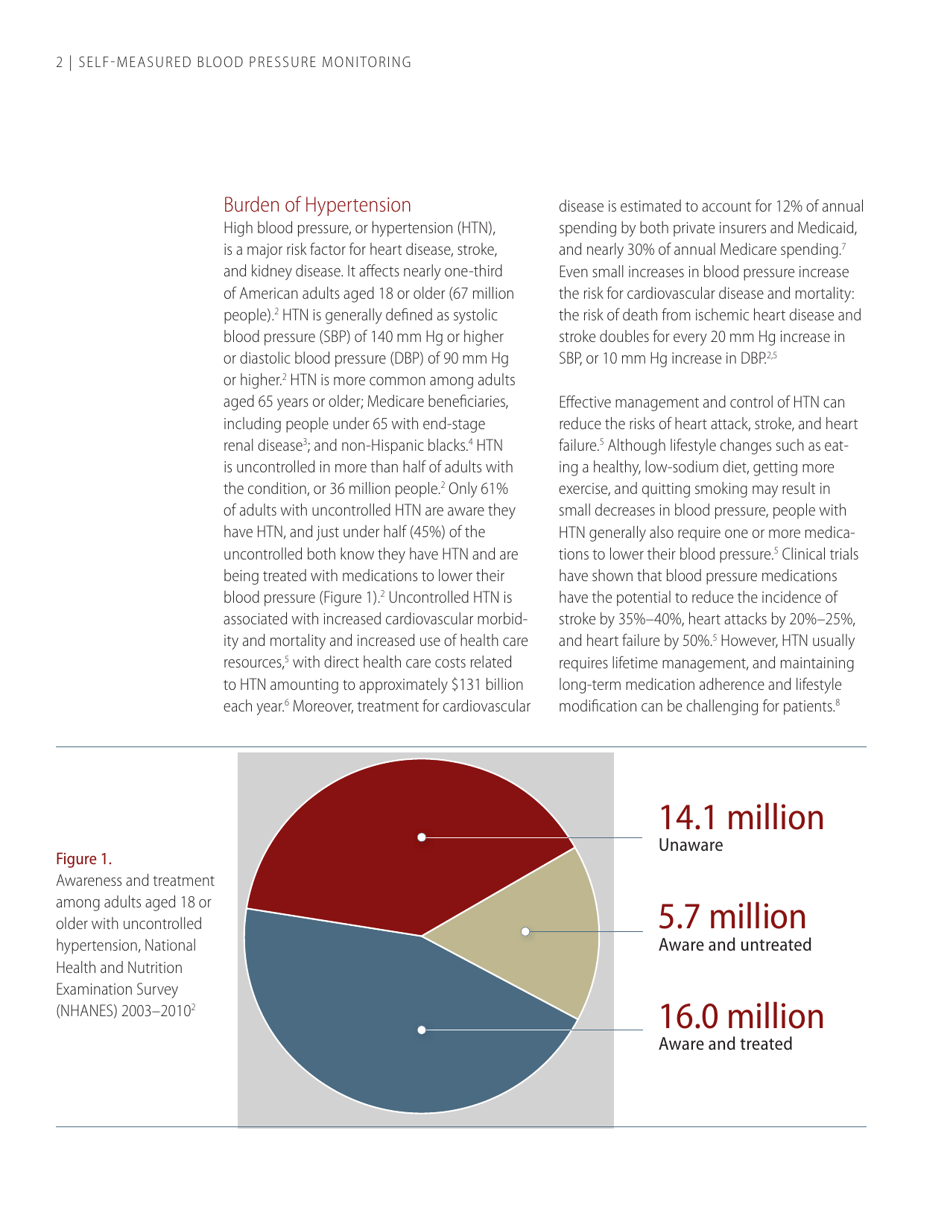
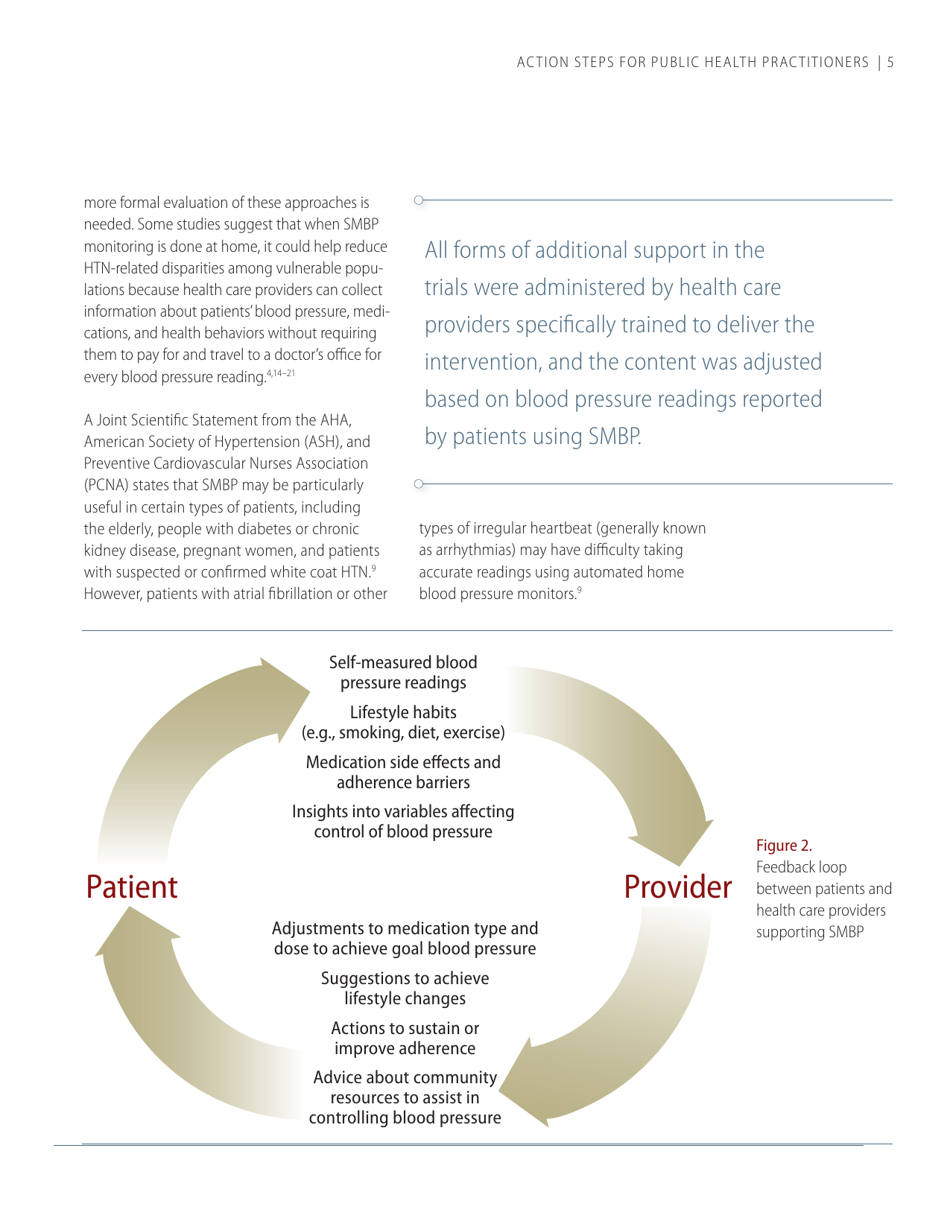
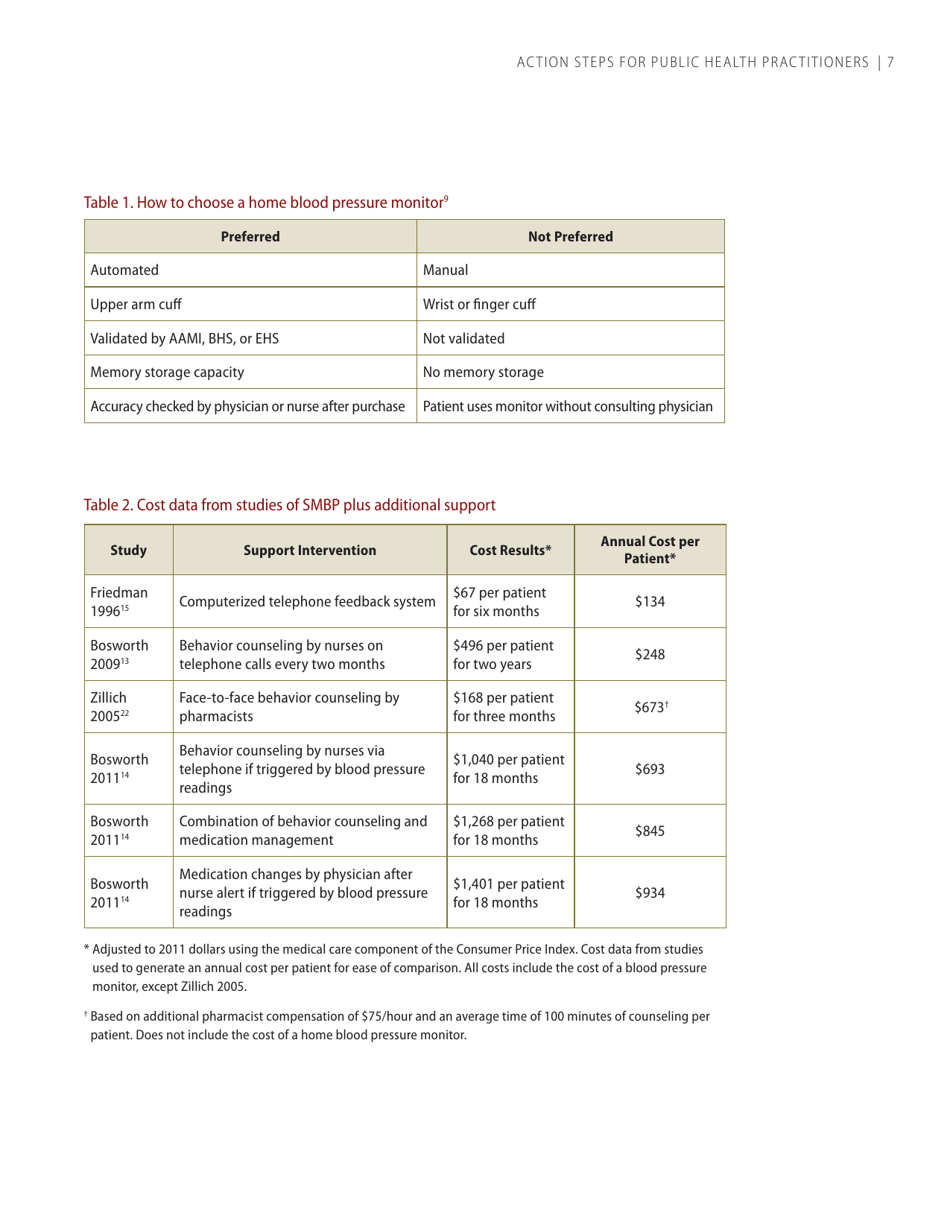
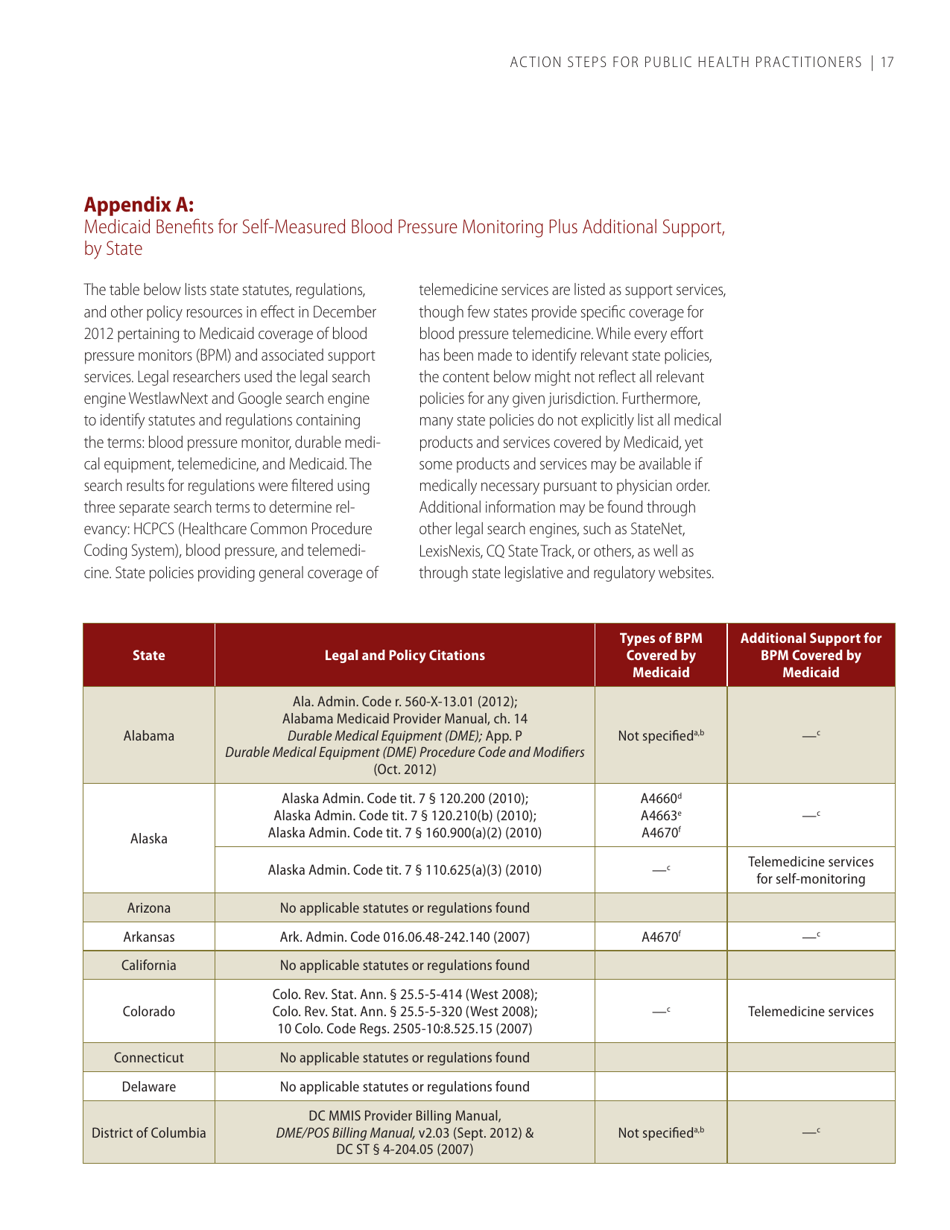
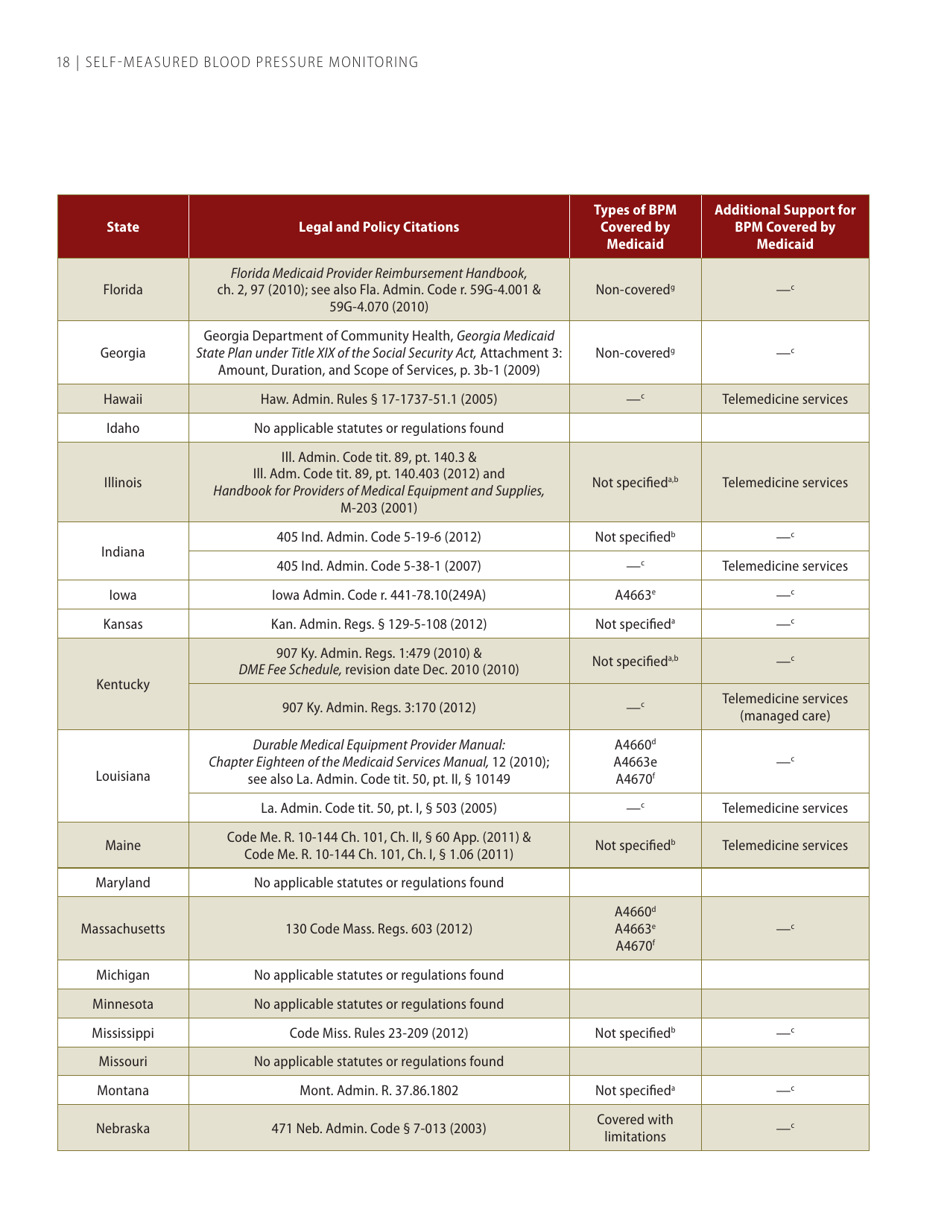
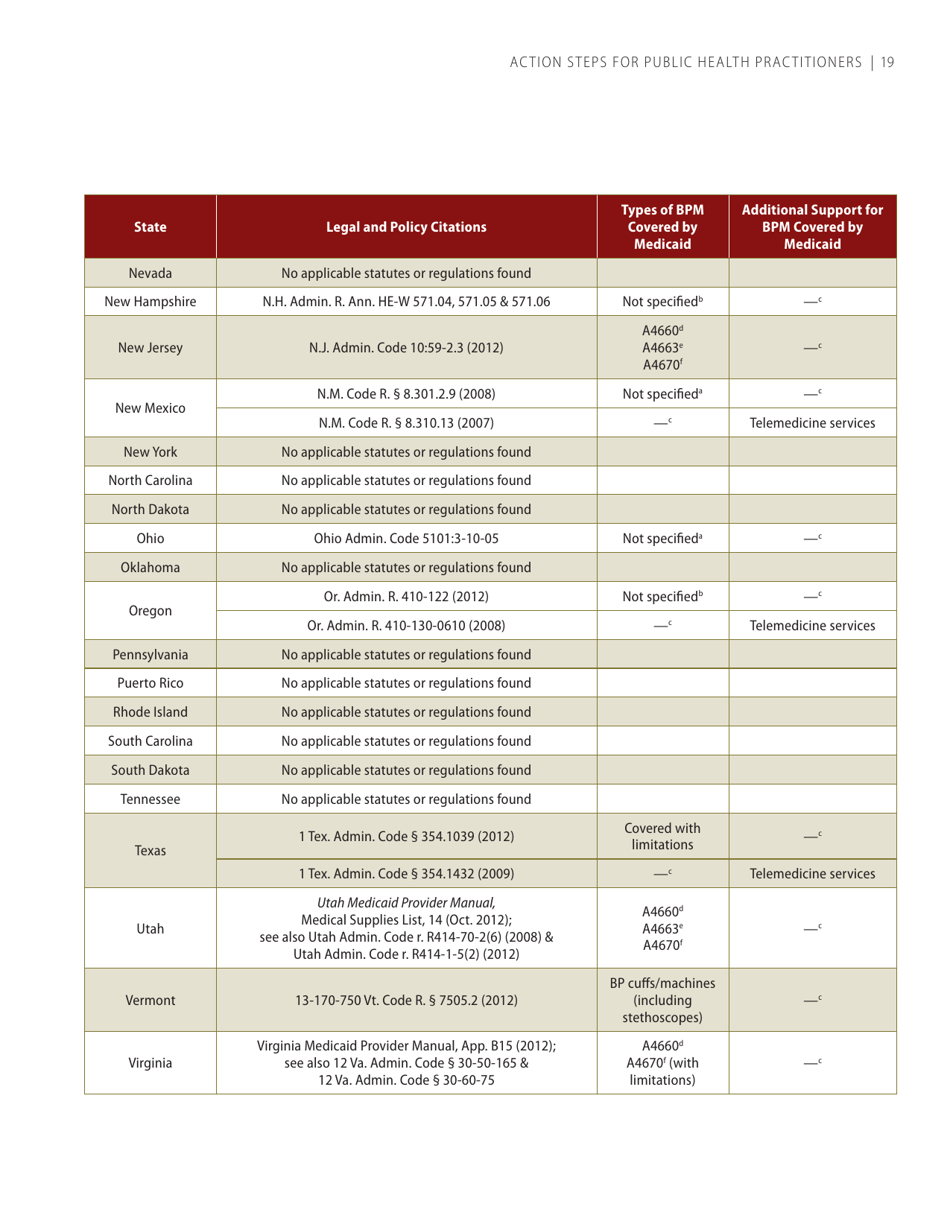
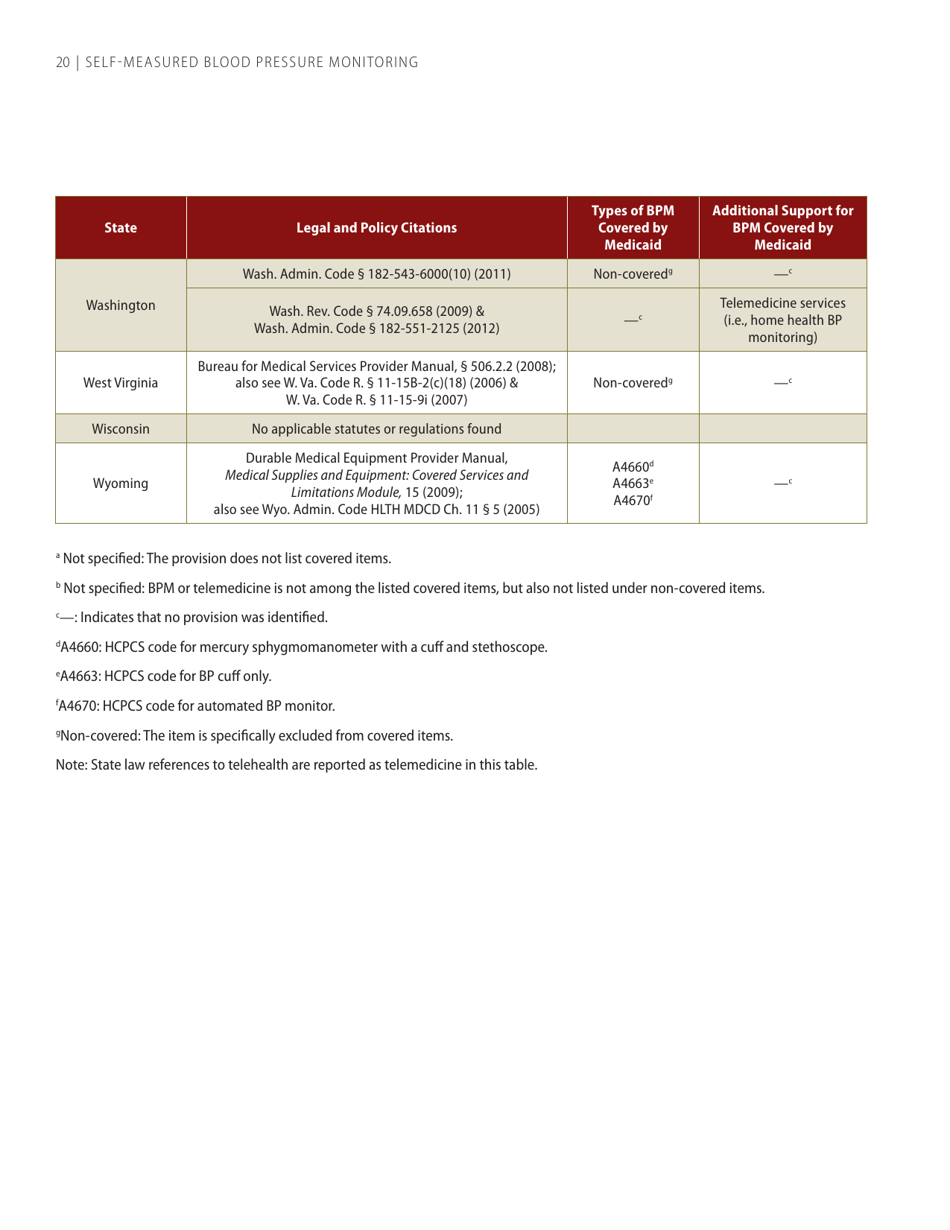
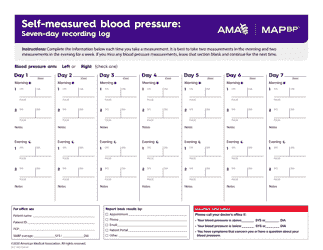
Self-measured Blood Pressure Monitoring: Action Steps for Public Health Practitioners
Self-measured Blood Pressure Monitoring: Action Steps for Public Health Practitioners is a 40-page legal document that was released by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on February 1, 2013 and used nation-wide.
FAQ
Q: What is self-measured blood pressure monitoring?
A: Self-measured blood pressure monitoring is the process of individuals measuring and tracking their own blood pressure readings at home.
Q: Why is self-measured blood pressure monitoring important?
A: Self-measured blood pressure monitoring is important because it allows individuals to track their blood pressure on a regular basis, which can help detect and manage high blood pressure.
Q: How can public health practitioners promote self-measured blood pressure monitoring?
A: Public health practitioners can promote self-measured blood pressure monitoring by providing education and information about the benefits of monitoring blood pressure at home.
Q: What are the action steps for public health practitioners in promoting self-measured blood pressure monitoring?
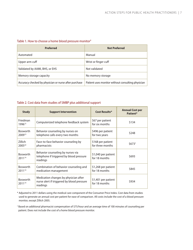
A: Public health practitioners can take action by collaborating with healthcare providers, communities, and individuals to raise awareness, provide resources and support for self-measured blood pressure monitoring.
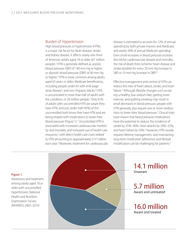
Q: What are the benefits of self-measured blood pressure monitoring?
A: The benefits of self-measured blood pressure monitoring include early detection of high blood pressure, improved blood pressure control, and better management of hypertension.
Q: Can self-measured blood pressure monitoring replace regular visits to the doctor?
A: No, self-measured blood pressure monitoring should not replace regular visits to the doctor. It should be used as a complement to regular medical care.
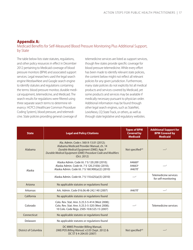
Q: Are there any specific guidelines or recommendations for self-measured blood pressure monitoring?
A: Yes, there are guidelines and recommendations for self-measured blood pressure monitoring, including proper technique, device validation, and interpretation of results. These guidelines should be followed for accurate and reliable readings.
Q: Can self-measured blood pressure monitoring be used by anyone?
A: Self-measured blood pressure monitoring can be used by anyone, but it is especially beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure or those at risk for developing it.
Q: Are there any risks or potential drawbacks of self-measured blood pressure monitoring?
A: Some potential drawbacks of self-measured blood pressure monitoring include user error, device inaccuracies, and the need for regular calibration and maintenance of the devices.
Form Details:
- The latest edition currently provided by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;
- Ready to use and print;
- Easy to customize;
- Compatible with most PDF-viewing applications;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a printable version of the form by clicking the link below or browse more legal forms and templates provided by the issuing department.