This version of the form is not currently in use and is provided for reference only. Download this version of
Form T2091(IND)
for the current year.
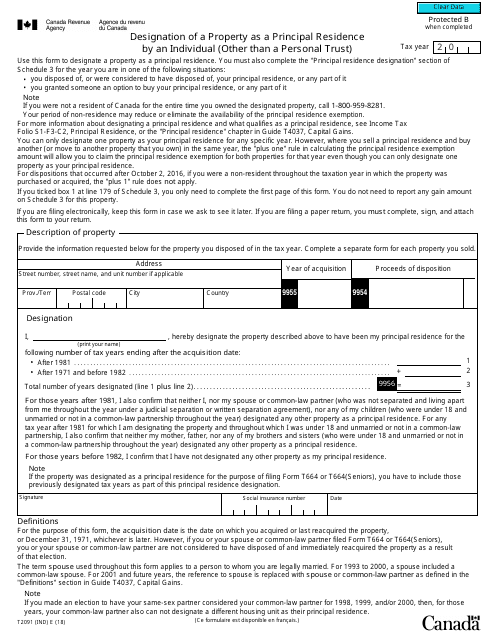
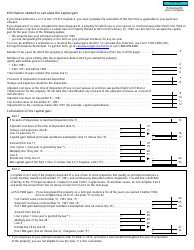
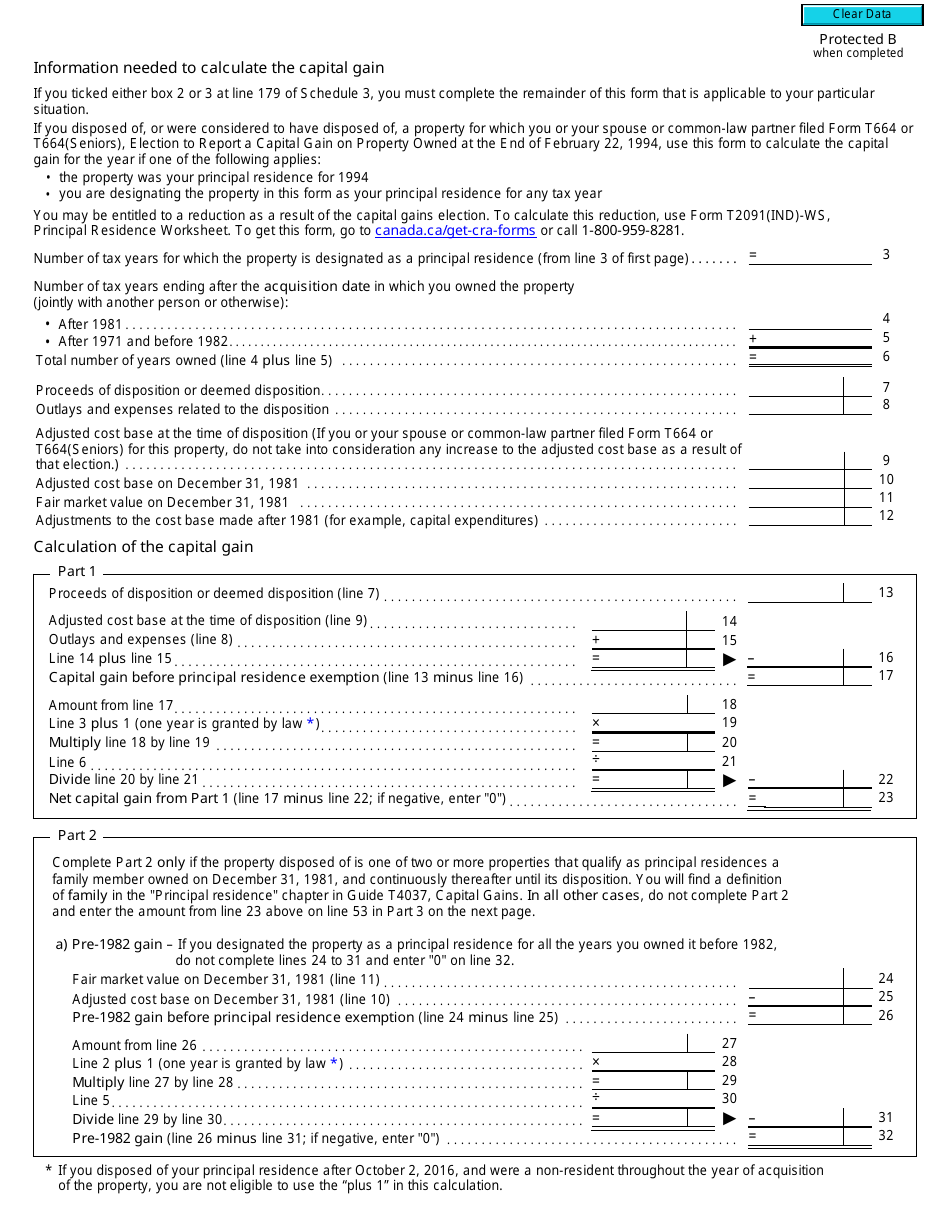
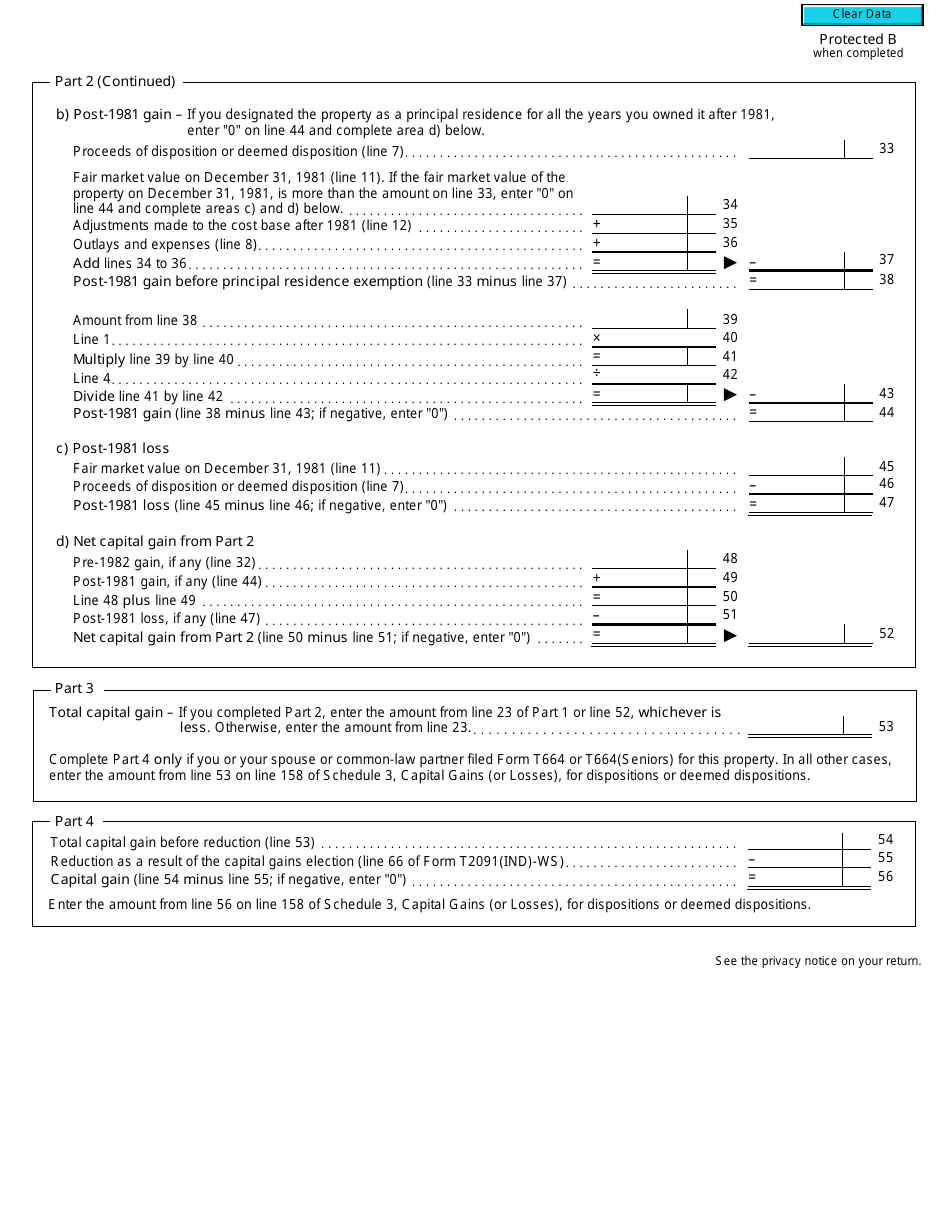
Form T2091(IND) Designation of a Property as a Principal Residence by an Individual (Other Than a Personal Trust) - Canada
Form T2091(IND) is a Canadian Revenue Agency form also known as the "Form T2091(ind) "designation Of A Property As A Principal Residence By An Individual (other Than A Personal Trust)" - Canada" . The latest edition of the form was released in January 1, 2018 and is available for digital filing.
Download a PDF version of the Form T2091(IND) down below or find it on Canadian Revenue Agency Forms website.
FAQ
Q: What is Form T2091(IND)?
A: Form T2091(IND) is a form used in Canada to designate a property as a principal residence by an individual (other than a personal trust).
Q: Who can use Form T2091(IND)?
A: Individuals (other than personal trusts) in Canada can use Form T2091(IND) to designate a property as their principal residence.
Q: What is the purpose of Form T2091(IND)?
A: The purpose of Form T2091(IND) is to notify the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) whether a property is being designated as a principal residence, which may have tax implications.
Q: Why would someone designate a property as a principal residence?
A: Designating a property as a principal residence may have tax benefits, such as the principal residence exemption which can reduce or eliminate capital gains tax when the property is sold.
Q: When does Form T2091(IND) need to be filed?
A: Form T2091(IND) generally needs to be filed when a property is sold or when there is a change in the use of the property (e.g. from a principal residence to a rental property).
Q: Are there any penalties for not filing Form T2091(IND)?
A: Failure to file Form T2091(IND) when required may result in penalties and interest charges imposed by the CRA.
Q: Can an individual designate more than one property as a principal residence?
A: No, an individual can only designate one property as their principal residence for each year.
Q: What information is required on Form T2091(IND)?
A: Form T2091(IND) requires information such as the taxpayer's personal information, details of the property, and the dates of acquisition and disposition.